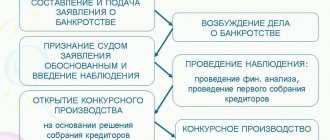
Suspension of civil proceedings
The court rejected this petition and considered the dispute on its merits.
Meanwhile, practice has shown that often the initiation of criminal proceedings by participants in arbitration disputes pursues the sole purpose of suspending proceedings in a case considered by the arbitration court.
Clause 1 of Part 1 of Article 81 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation connects the obligation of the arbitration court to suspend the proceedings not with the presence of another case or issue being considered in constitutional, civil, criminal or administrative proceedings, but with the impossibility of considering the dispute before a decision is made on another issue . Therefore, subsequently the practice of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation changed. Thus, the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 5, 2000 N 4428/00 * (128) sets out a different approach: The current code takes into account the previous experience of suspending proceedings in a case considered by an arbitration court, based on the initiation of a criminal case that is at the stage preliminary investigation.
Currently, by virtue of clause 1, part 1, art. 143 of the APC, suspension is possible only if the criminal case is already under court proceedings *(129). Judicial practice also proceeds from this understanding of this norm.
Found grounds for suspending bankruptcy. If a court of general jurisdiction accepts the materials of a criminal case, bankruptcy is suspended until the criminal case is resolved by a court of general jurisdiction. Perhaps there is another way to suspend bankruptcy if a criminal case is initiated. Without going into the complexity of the organization of defense in criminal cases, we note that the choice of strategy and construction of defense tactics depend on the results of the discussion of these issues between the suspect accused of committing such a crime and his lawyer (a separate discussion requires the choice of behavior at the stage of verification actions on the part of law enforcement agencies in relation to a legal entity or citizen, including an individual entrepreneur). The debtor, for the purpose of deliberate bankruptcy, could establish in contracts obviously unfavorable conditions for their execution in terms of quality, volume, timing, location, etc. Instead of paying from his account, the debtor could take out an unfavorable loan and pay for the contract from his loan accounts, which did not replenish in a timely manner, which entailed fines from the bank and termination of the loan agreement with the requirement of its early repayment.
Which was impossible, since the goods “were frozen in circulation by structures affiliated with the debtor. If the claim proceedings are not suspended, then the creditor’s claim presented in the bankruptcy case at the observation stage must be left without consideration (clause 29 of Resolution No. 35). Now, if the court has any doubts, you can refer to the reasoning part of the Ruling of the RF Armed Forces dated May 21, 2018 No. 305-ES17-21937. Familiarization with the material of the check on the refusal to initiate a criminal case? It is difficult to declare a large socially significant, city-forming enterprise insolvent.
Such a procedure would be quite capital-intensive and could cause quite a serious blow to the region. Current creditors, the deadline for fulfilling their claims has come after the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings, are not recognized as persons participating in the case - this is established by clause 2 of Art. 5 of the Law “On Bankruptcy “Insolvency”. In connection with issues arising in judicial practice and in order to ensure uniform approaches to their resolution, the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, on the basis of Article 13 of the Federal Constitutional Law “On Arbitration Courts in the Russian Federation,” decides to give the following clarifications to arbitration courts (hereinafter referred to as the courts). 7.
In accordance with paragraph four of paragraph 1 of Article 63 of the Bankruptcy Law, from the date the court issues a ruling on the introduction of surveillance, arrests on the debtor’s property and other restrictions regarding the disposal of the debtor’s property imposed during enforcement proceedings for property penalties are lifted, with the exception of the cases mentioned in this normal. One of the extremely effective ways to collect debts from debtors is to initiate criminal cases against managers, participants (shareholders) and chapter. accountants of bankrupt companies under Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Illegal actions in bankruptcy”, Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Intentional bankruptcy”, Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Fictitious bankruptcy”, Article 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Tax evasion and (or ) fees from an individual,” Article 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Evasion of taxes and (or) fees from an organization.” When the appropriate bankruptcy procedures have already been applied to the company (monitoring, financial recovery, etc.) and there are no visible ways for financial recovery, many managers and particularly stubborn owners sometimes do not give up and try to somehow correct the situation by any means. Let's list the most common options.
As is known, in order to ensure the legality and validity of initiating a criminal case, the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation) establishes conditions, only in the presence of which proceedings in the case can be initiated: 1) the existence of a reason to initiate a criminal case (part 1 and 1.2 Article 140 Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation); 2) existence of grounds for initiating a criminal case (part 2 of article 140 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation); 3) the absence of circumstances entailing refusal to initiate a criminal case (Part 1 of Article 24 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation). The determination of the signs of fictitious bankruptcy is carried out by the arbitration manager in the event that, at the request of the debtor, bankruptcy proceedings were initiated. The creditor's claim, confirmed by a court decision, is presented to the arbitration court considering the bankruptcy case in the manner prescribed for the corresponding stage of bankruptcy (see paragraph 4 of Article 48, paragraph 1 of Art.
71, paragraph 5 of Art. 81, paragraph 1, art. 100, paragraph 1, art.
142 of the Bankruptcy Law). If the creditor acting as a plaintiff has not exercised this right, the claim proceeding continues in the general manner and ends with the issuance of the appropriate judicial act (clause 6 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 23, 2009 No. 59 “On some issues of the practice of applying the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings in case of initiation of bankruptcy proceedings", resolutions of the FAS Volga-Vyatka District dated January 19, 2012 No. F01-5903/11, FAS West Siberian District dated December 22, 2011 No. F04-6157/11, FAS East Siberian District dated December 15, 2010 to case No. A58-4349/10). Termination of an administrative case in court due to reconciliation of the parties? The court examined the validity of the applicant's demands for approval of a temporary manager. By a ruling dated October 4, 2006, the applicant in the case was replaced by “Avtotsentr” LLC in the procedure of procedural succession.
Algorithm of actions of the debtor and creditors
Let's move directly to the algorithm of the debtor's actions that need to be performed in case of out-of-court bankruptcy. We recommend that you prepare documents and go through the procedure accompanied by a lawyer or attorney. This will avoid mistakes, the return of documents from the MFC or the termination of the case. Below we describe step-by-step instructions for completing out-of-court bankruptcy.
Step 1. Preparation of documents, checking the conditions for bankruptcy
At this stage, you need to make sure that you meet the conditions for out-of-court debt relief. Need to check:
- the total amount of debt, which, excluding penalties, should range from 50 to 500 thousand rubles;
- the absence of ongoing enforcement proceedings in the FSSP, the availability of information about completed proceedings;
- absence of property that is subject to sale (the list of property that can be preserved during sale is in Article 446 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
To accurately calculate the amount of debt, you can use loan agreements and court decisions. You can also request certificates from banks or microfinance organizations and a credit history. Our lawyers will provide assistance with this.
Step 2. Fill out an application for out-of-court bankruptcy
Application for extrajudicial bankruptcy
The Ministry of Economic Development has developed not only an application form for extrajudicial bankruptcy, but also determined the requirements for its registration. Thus, the applicant will be allowed to use black, blue or purple ink when drawing up a written form, and when typing a document on a PC for printing, use Times New Roman font with a height of 10-12 points.
(40 kb.)
The application contains a minimum set of information:
- Full name and passport details, SNILS, INN of the applicant.
- Information about the debtor's representative, if he will submit the application.
- Accommodation information.
- Consent to the processing of personal data.
- Petition for declaring bankruptcy under an out-of-court scheme.
- List of applications.
The list of creditors indicating the amount of debt owed to each of them is submitted as a separate document as an appendix. Also attached to it is a copy of the passport, identification document of the representative (if necessary), and other documents. An application is submitted at the place of residence or permanent residence of the bankrupt applicant.
The application must indicate:
- an exact list of creditors and the amount of liabilities (debt write-off will only be possible for the creditors specified in the application);
- declaring that the applicant meets the conditions for out-of-court bankruptcy;
- consent to request information about the debtor’s property from government agencies.
The first item on the list is especially important. If you do not indicate a creditor in the application, debts owed to him will not be written off after the bankruptcy is completed. However, you can use the simplified procedure again only after 10 years. Also, for obligations not specified in the application, there will be no moratorium on the accrual of interest or other penalties.
Step 3. Submitting documents to the MFC
You need to apply for simplified bankruptcy at the MFC at your place of residence or stay. These data are confirmed by a stamp in the passport or a registration certificate from the Ministry of Internal Affairs. Since the procedure for filing an application has not yet been approved, it is impossible to say whether it is possible to apply for bankruptcy through State Services or by mail.
Step 4. Procedure for simplified out-of-court bankruptcy at the MFC
Having submitted an application to the MFC, the debtor needs to wait for the results of verification of documents and information. The procedure will follow the following rules:
- within one day after receiving the application, the MFC will request data from the FSSP on completed and open enforcement proceedings;
- if, according to information from the FSSP, compliance with the conditions for simplified bankruptcy is confirmed, the MFC transmits the information to the EFRSB within three days;
- if, according to the FSSP data, the end of enforcement proceedings is not confirmed, the MFC returns the documents to the applicant. And you can resubmit them only after a month.
Extrajudicial bankruptcy lasts 6 months (in the original version of the law there was a period of 9 months). During this period of time, creditors can file objections or go to arbitration to initiate bankruptcy according to general rules. The basis for such actions will be the identification of property sufficient to pay off debts, or the citizen’s concealment of information about property.
Lawyer's comment.
Lenders will be able to check the availability of property through the databases of Rosreestr and the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, and in other ways. In this regard, the application immediately provides consent to the request for such data. The law contains another important provision. Creditors will be able to appeal simplified bankruptcy in court if the debtor has property that he has not registered in his name, although he was obliged to do so by law.
For example, when buying a car second-hand, you need to register it with the traffic police. If the debtor did not do this, but still owns the car under the contract, the creditor will be able to file a valid complaint.
For 6 months, while the simplified bankruptcy is in progress, the accrual of penalties is stopped, and a moratorium on the fulfillment of obligations is introduced (only for creditors specified in the application). The fulfillment of the following obligations does not cease:
- in relation to creditors not specified in the application;
- for obligations to compensate for property and moral damage;
- for salary payments and severance pay (this is relevant for individual entrepreneurs, who can also file for out-of-court bankruptcy);
- for alimony obligations.
During the consideration of the case, the citizen is prohibited from taking out new loans and borrowings, or carrying out transactions with property. If such facts are revealed, the procedure will be terminated.
Step 5. Declaration of bankruptcy and write-off of debts
If within 6 months the creditors have not filed any objections or complaints, or have not identified property for sale, a decision is made on bankruptcy of the individual. faces. The MFC will send the relevant information to the EFRSB, and in relation to individual entrepreneurs - to the tax authority to deregister the entrepreneur.
The consequences of simplified bankruptcy do not differ from the usual rules of Law 3 127-FZ:
- within 5 years, banks must be notified of the bankruptcy when receiving new loans;
- it will be prohibited to be a member of the management bodies of organizations (the duration of the ban depends on the type of legal entity);
- For 5 years you cannot file for bankruptcy again in court, and for a repeated simplified procedure the period will be 10 years.
For obligations that were not specified in the application, collection will continue according to the general rules. Creditors also have the opportunity to challenge a simplified bankruptcy after its completion. The basis for this may be fraud on the part of the debtor, fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy, or other illegal actions.
Suspension of bankruptcy proceedings
The current version of Law No. 127-FZ establishes a clear barrier that prevents the “express” initiation of a bankruptcy case based only on an existing claim. Now the right to appeal to the arbitration court with such a statement arises only from the bankruptcy creditor, the authorized body for monetary obligations, whose claims are confirmed by a judicial act or an arbitration award that has entered into legal force (clause 2 of Article 7 of Law No. 127-FZ)
appealing decisions and rulings made by the bankruptcy court; when it is impossible to consider a bankruptcy case before resolving another case considered by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, the constitutional court of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a court of general jurisdiction, or an arbitration court. To suspend the proceedings, the interested person must submit a corresponding petition to the court.
Continuation
the court usually suspends, because often due to the fact that it itself delays due to overload the timely consideration of claims, my opinion is that there are no grounds for suspension. The Bankruptcy Plus company has significant experience in drawing up settlement agreements in bankruptcy cases and is ready to help you realize the benefits this rehabilitation bankruptcy procedure. The main thing is that a professionally drawn up settlement agreement allows you to ensure the approval of the settlement agreement in court and thereby bring the company out of bankruptcy. Why is a settlement agreement needed? A professionally drawn up settlement agreement allows the OWNERS OF THE ORGANIZATION to bring the enterprise out of bankruptcy and preserve assets.
ZZZaec 22 Sep 2006 A small comment on the posted practice. 1. In some cases, the court comes to the conclusion that the suspension of proceedings in part considered.
What are the terms of bankruptcy?
- Collecting documents and filing an application with the court. This stage can take from 1 day to several months. Everything depends solely on the desire and capabilities of the debtor.
Important: By law, you are required to file for bankruptcy if you cannot pay your debts. The deadline for filing a bankruptcy petition is 30 days. Violation of this requirement is subject to administrative liability and a fine of 3 thousand rubles.
The restructuring procedure itself is introduced for 6 months. The procedure can be skipped if the debtor has no income.
- The period for selling property varies from 4-6 months. The specific timing of the bankruptcy procedure - the sale of property will depend on the specific situation of the debtor. Obviously, if there is no property, the process will go quickly. And if the debtor is found to have property whose location needs to be determined, the process may drag on for a year.
- As soon as the bank sends a demand to the debtor, a notice of delay - the statute of limitations begins to count from zero
- A call from a bank employee also “resets” the statute of limitations
- Partial repayment of a debt, a statement to the bank about the inability to pay, etc. will lead to a new limitation period.
Do you want to calculate the timing of the bankruptcy procedure taking into account your circumstances? Come visit us for a free consultation. An experienced specialist will help you plan bankruptcy from the beginning (collection of documents) to writing off debts and calculate the terms of bankruptcy taking into account your situation.
Get an answer to any question regarding personal bankruptcy
Bankruptcy and loan statute of limitations
Many people mistakenly believe that a 3-year delay on a loan deprives the bank of the right to demand money. And accordingly, this bank does not have to be declared bankrupt. No, that's not true. Let's explain why.
In legal practice, there are certain rules for calculating the statute of limitations. In relation to credits and loans, the rules will be as follows:
It is not worth the risk of trying to determine the statute of limitations on a creditor. Simply list all creditors on your application. This way you will protect yourself from possible problems in bankruptcy.
Deadlines in a bankruptcy case for creditors
If a creditor intends to participate in a bankruptcy case, he must apply to have his monetary claims included in the register of creditors.
The application must be motivated, legally competent and take into account the requirements of the bankruptcy law and the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
You can submit such an application after an announcement about the debtor’s bankruptcy is published in the Kommersant newspaper. By submitting an application within 2 months, the creditor receives the right to participate in the first meeting of creditors.
If the creditor does not meet the two-month deadline, his claim will be considered and included in the register of creditors (if justified) without the right to participate in the first meeting of creditors.
Peculiarities of consideration of complaints against decisions to suspend the preliminary investigation
Criminal liability under the first part of Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is established only for the actions listed in it.
Their list is exhaustive and is not subject to broad interpretation. Here it is: By fictitious bankruptcy, the Criminal Code understands “a knowingly false public announcement by the head or founder of the insolvency of the company (Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). The basis for initiating a criminal case is the decision of the arbitration court to refuse to declare the debtor bankrupt.
Any other decision excludes the possibility of bringing the company's management to criminal liability under this article. Here, as in other cases of criminal bankruptcy, it is necessary that the crime causes damage to creditors in the amount of at least 250,000 rubles.
Time limits for the sale of property in the event of bankruptcy of individuals
In addition to bankruptcy, there is the option of a 3-year debt restructuring, but since this procedure is not relevant for most, we omit its description and timing. More relevant consideration should be given to the sale of property. So, what is taken into account in the case, and what will determine the timing of the procedure?
- From the moment a citizen’s bankruptcy is approved, after a court hearing, information is submitted to the printed publication Kommersant. Preparation for publication takes 2 weeks.
- After publication, creditors have 2 months to submit their claims. Here you should also take into account the timing of the court’s consideration of such claims; they can delay the procedure for another 2-4 weeks.
- After the formation of the register, the organization of electronic trading begins and, in fact, its conduct in a bankruptcy case. There may be repeated stages if everything was not sold out the first time. All this can take up to 4 months.
- In the case, there may also be a need to cancel questionable transactions, if the statute of limitations allows. The time frame for challenging transactions varies from person to person – often such cases even reach the Supreme Court. All this can also delay the time frame for selling property in bankruptcy.
Deliberate bankruptcy
Procedure for bringing to administrative liability for deliberate bankruptcy Criminal liability
occurs if bankruptcy of a commercial organization or individual entrepreneur occurs not as a result of objective business conditions, but in connection with the deliberate actions of guilty persons - subjects of illegal actions.
Subjects of the crime
— managers or owners of commercial organizations and individual entrepreneurs.
- object of the act:
- economic interests of the debtor (legal entity or individual entrepreneur), that is, causing damage to the debtor that is not large (otherwise there are grounds for criminal prosecution);
The elements of an offense entailing administrative liability for such an act as deliberate bankruptcy are formulated in Art. 14.12. Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses: The control (supervision) body participates in court hearings when considering issues related to the approval of arbitration managers. - challenge judges, assistant judges, court session secretary, expert, specialist, translator;
Read other articles on the site:
- The director of the branch entered into an agreement in excess of his powers
- Article 306 knowingly false denunciation of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
- Time limits for criminal prosecution for especially serious crimes
- Acts on conducting training when threats are received by telephone
- The investigator in the process of initiating a criminal case, his skills and abilities
Dear colleagues, I wish each of us to hold high the title of lawyer, unswervingly adhering to the principles of impartiality and objectivity!
Video on bankruptcy of individuals from the Supreme Court
Get an answer to any question regarding personal bankruptcy
Last revised July 18, 2019
Reading time 3 minutes
Attractive slogans like “We will bankrupt you in just 3 months!” can be found on the Internet quite often. Another question is how realistic is this? It is the timing of procedures in bankruptcy of individuals that is one of the most pressing topics. How long can the procedure last, and how are precious hours spent? Let's find out!
Popular tags
Committing a crime Composition of a crime Article of the Criminal Code car administrative initiation civil money activity document complaint law statement health property execution supervision punishment sample application release grounds liability refusal to submit police receiving order resolution right preliminary termination involvement causing harm production prosecutor's office prosecutor process decision witness investigation deadlines judicial condition petition storage
Bankruptcy deadlines for individual entrepreneurs
The procedure for entrepreneurs remains almost the same as for ordinary citizens. The only difference is that entrepreneurs may need longer preparation - in particular, deregistering themselves from the registration of individual entrepreneurs with the Federal Tax Service. Otherwise the procedure remains the same.
If you are interested in bankruptcy, contact our specialists! We will be happy to provide detailed, informative consultations and help you understand all the nuances of the procedure!
We will solve your debt problem. Free legal consultation.
Bankruptcy is a frequently used institution. On the one hand, it allows the debtor to finally get rid of debts, even if he loses his property. On the other hand, bankruptcy of the debtor is often the last or even the only option for the creditor to collect at least part of the debt from him.
Bankruptcy Application: Important Facts
In Russia, bankruptcy is based on the principle of insolvency. Those. a debtor who has a real opportunity to repay debts to creditors cannot count on relief from payments as a result of the bankruptcy procedure.
Bankruptcy proceedings can be initiated both in relation to an organization and in relation to an individual.
Regardless of whether the debtor is an organization, an individual entrepreneur or just an individual, the case must be heard in an arbitration court. Those. exclusive jurisdiction is established for bankruptcy cases.
One of the following parties may file an application to declare a debtor bankrupt:
- Creditor.
- Directly the debtor himself.
- Authorized body.
Fictitious and deliberate bankruptcies are crimes under Russian law.
Video: How to file for bankruptcy
Who can file a claim for insolvency of a legal entity
In accordance with Art. 224 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 7 No. 127 of the Federal Law, certain persons may file an insolvency claim with the court, namely:
- the debtor himself;
- lender;
- bankruptcy lender;
- authorized bodies;
- former employees or other team members who have not received full payment in the form of salary or funds paid upon leaving work.
The debtor must apply for recognition of insolvency in the following situations:
- If it is known that covering debts will contribute to the development of an inability to make mandatory payments.
- The founder of the company, shareholders or owners made a common decision to file a bankruptcy petition in court.
- If debts are covered with existing tangible property, it will lead to more serious problems in the process of economic activity.
- There are facts and signs confirming the insolvency or shortage of property.
- Lack of wages or other benefits and payments for more than three months.
Each applicant has its own peculiarities of filing a claim for bankruptcy of a legal entity, a sample of which can be seen at the end of the article. Table 1 describes the main persons who have the right to go to court regarding the debtor's insolvency.
| Applicant | Deadline for filing a claim | Causes and conditions |
| Debtor | 30 days from the date of discovery of the impossibility of covering debts or circumstances that will definitely lead to this in the future. | Lack of sufficient funds in the account to repay existing debt obligations. |
| Creditor | There are no restrictions. | Having a debt that has not been repaid within 90 days. In addition, there was no desire or initiative to take any action to eliminate the problem that had arisen. |
| Authorized body | One month with the same conditions as for the debtor. | It was revealed that the company was unable to pay its debts at the closing stage. |
Reasons for termination of bankruptcy proceedings
- manager's reporting documentation;
- document certifying the registration of the enterprise;
- a document justifying the right to appeal to the justice authorities;
- minutes of the creditors' meeting;
- claims made by creditors in the register.
| Financial issue |
|
| Petition | |
| Settlement agreement |
|