Application to the bailiff to cancel the enforcement fee
Also, through legal proceedings, he can return the enforcement fee from the bailiffs if he has already paid it, without going into details. Unlawful actions of bailiffs There is another way to cancel the enforcement fee of bailiffs. As stated above, the obligation to pay a debt arises for a citizen only after he receives a writ of execution. This document can be handed to him personally against signature or sent by mail. If sent by registered mail, the date of receipt of the document is determined by postal notification. If the writ of execution was sent by regular letter, i.e., without notification of delivery, it is considered received 5 business days after sending. It is from this moment that the countdown begins in which the citizen must fulfill the debt obligations imposed on him.
Voluntary compliance with requirements
To get rid of headaches, the easiest way for a citizen is to follow the path of least resistance, that is, to voluntarily pay off the debt. After the court hearing at which the decision was made, the citizen receives a letter containing:
- period of voluntary execution;
- a list of consequences that will result from failure to comply with a court decision;
- bailiff details;
- obligations of the debtor and information about the punishment that will entail their failure to fulfill.
After repaying the debt, the debtor must receive the appropriate paper from the creditor, which will serve as confirmation of payment of the debt. After receiving the document, the citizen will need to appear with it at the authorized body of the bailiff department.
How can I reduce or cancel the performance fee?
- Legal nuances of collecting the enforcement fee
- Recovery amount
- Conditions for payment
- How not to pay?
- Procedure
- What you need to dispute
- Preparation of an administrative claim
- Documentation
- Instructions
According to Art. 112 Federal Law No. 229 “On Enforcement Proceedings” the enforcement fee is the amount of collection that the debtor is obliged to pay in case of untimely fulfillment of the obligation specified in the executive document. If the obligation must be fulfilled immediately, then the fee is collected within 1 day after receiving a copy of the resolution on the commencement of enforcement proceedings.
The enforcement fee is collected by the bailiff. The decision to collect the fee is agreed with the senior bailiff.
Resolution
As stated above, the debtor can appeal the decision to impose the enforcement fee (an administrative claim against the actions of the bailiff), and can file a claim with the court for a deferment or installment plan for the collection of the enforcement fee, for a reduction in its size or for exemption from its payment. To do this, you must follow the rules for going to court.
Evidence of the existence of grounds for deferment or installment payment of the fee is provided by information about the difficult financial situation. The degree of guilt in failure to comply with requirements also matters. In any case, the court will reduce the fee by no more than 25%.
The debtor can provide evidence of the absence of guilt in failure to fulfill obligations under the writ of execution (this is the only basis for exemption from paying the fee). Such rules are contained in paragraph 74 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2015 No. 50.
After accepting the claim for proceedings, the court will suspend the collection of the enforcement fee until a decision is made.
An interesting issue from a practical point of view is the collection of legal costs with the participation of a representative in the case. And if you remember, in administrative claims only a person with a higher legal education can be a representative. Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Pension Fund dated January 21, 2016 No. 1 (on reimbursement of costs associated with the consideration of the case) establishes the rule.
Costs are not distributed between the parties if the dispute does not involve a violation or challenge of the rights of the plaintiff. And only the court can reduce or exempt the fee according to the law. The bailiff does not have such a right. Therefore, it will be difficult to recover legal costs in cases related to the enforcement fee (except for declaring its appointment illegal).
A resolution is a document of an executive nature. This means the following: the debtor is obliged to fulfill all the requirements specified in the document, and within the specified period. It is worth noting that informing the debtor about the imposition of a fee is the duty of the bailiff. In this case, the court controls the receipt of notifications by the citizen.
The debtor is given 10 days after the bailiff’s decision to appeal the decision to impose a fee. In case of delay, in exceptional cases, a citizen has the right to restore the deadline, but only if there are good reasons.
It is possible to challenge the bailiff's decision only within 10 days. In case of delay, citizens in exceptional cases have the right to restore the deadline, but this will require valid reasons.
The court considers a citizen's complaint within 10 days. The grounds for a positive decision on the debtor’s request may include:
- premature issuance of a decision;
- violations when making a decision;
- collection of fees in cases in which they are not allowed;
- incorrect calculation of the fee amount;
- refusal of the bailiff to recognize the validity of the reasons due to which the citizen did not repay the debt.
Proof of the legality of actions falls on the FSSP employee. However, the applicant citizen is also obliged to prove the bailiff’s violation of legal norms.
Collection of the enforcement fee is carried out by decision of the senior bailiff. He can make this decision on the basis of the debtor’s failure to comply with the court decision on the principal debt, because there are certain deadlines for the writ of execution and the fulfillment of its instructions.
If the service does not see payments for enforcement proceedings, it gives a day to resolve the issue, after which a decision on collection is made. The preparation of the document and its application is regulated by Article 112 of Federal Law 229 “On Enforcement Proceedings”.
The defendant must be warned about the existence of such a law and the possibility of charging an enforcement fee when opening enforcement proceedings. Not only will he not be able to avoid repaying the debt, but he will also add to it the amount of the executive debt.
The resolution is drawn up according to a specific model and must contain several main sections with information:
- The name of the branch of the bailiff service, which is engaged in debt collection under enforcement proceedings, is indicated.
- Date of the decision.
- Information about the official approving the document.
- Production number, its title.
- Grounds for collecting the enforcement fee, for which the bailiffs charge a fine.
- Reference to the Federal Law regarding enforcement proceedings.
- There must be resolution language indicating the assessed rate of fees.
- The resolution also provides details for paying the fee.
This document should also contain information about the possibility of appealing the decision and its regulations. The defendant can challenge the fine if he has compelling evidence that he is right. But it is still not recommended to bring the matter to the issuance of this resolution.
The document must have the signature of the head of the FSSP department and a seal. The debtor personally gets acquainted with the drawn up and signed resolution, according to which he is now obliged to pay both the principal debt and the fee.
A copy for the debtor is sent to his residence address. If the debtor receives this decree, then the bailiffs had grounds for issuing a fine. Such a reason may be failure to comply with a court decision or
The basis for the debtor to receive a decree to collect an additional enforcement fee may be his failure to voluntarily comply with a court decision on the debt or his failure to provide information about why he cannot comply with this decision.
After receiving notice of the commencement of proceedings, you must either voluntarily repay the debt within the prescribed time frame, or prove that measures are being taken to comply with payment requirements.
Employment may be considered such measures (if the debtor did not work before). The bailiff service must notify the debtor about the opening of enforcement proceedings.
Several methods are used for this - a postal letter with notification of delivery, a telephone call, a personal meeting between the bailiff and his ward.
If the defendant does not want to confirm receipt of the notification, he is still considered informed, but in the column about receipt of the document there will be an o.
You should not expect that it will be possible to cancel the court decision to pay the debt in this way, by concealment; the bailiffs will still find a way to contact you and serve the notice. And now, after paying the principal debt, you will need to spend more money on fines and fees.
How to cancel the enforcement fee of bailiffs
Conditions for payment According to the requirements of the letter of the FSSP of the Russian Federation dated July 8, 2014 No. 0001/16, there are 4 mandatory conditions for collecting the enforcement fee:
- If the voluntary deadline for complying with the court decision has expired.
- If there is information in the case that the debtor is aware of the commencement of proceedings, but ignores the fulfillment of the legal requirements of the court or officials in an administrative manner.
- The applicant did not provide information about the impossibility of fulfilling the legal requirements of the bailiff.
If a decision to initiate enforcement proceedings is made, then you will have to pay. To cancel the payment, it is advisable to appeal the decision itself.
Arbitrage practice
Judicial practice regarding exemption from payment is in favor of applicants in cases where it is possible to prove the absence of guilt in failure to comply with a court decision. Circumstances confirming the grounds for exemption from payment may be:
- A postmark on the envelope indicating when the order to initiate enforcement proceedings was served on the applicant;
- Medical documents confirming the applicant’s presence in a medical institution during the period when the decision was received at his address,
- Other evidence that the applicant did not have the opportunity to execute the court decision on time.
Exemption from the performance fee has many nuances that cannot be discussed in one article. Contact a lawyer and get an answer to your question.
How to write an application to cancel the enforcement fee
However, it often happens that the Debtor was not properly notified of the initiation of enforcement proceedings and, for good reasons, could not voluntarily fulfill its requirements within the prescribed period. There are cases when both envelopes with documents such as: The resolution to initiate enforcement proceedings and the Decree to collect the enforcement fee arrive at the same time! In this case, the collection is clearly illegal, since the debtor simply physically could not have known about it and taken the necessary actions in time. In this case, you need to at least contact the bailiff in person and write an application to cancel the enforcement fee, a sample of which is located just below.
What to consider
The defendant in court proceedings and his lawyer can appeal the actions of the bailiff by submitting an appeal to his management if they do not agree with the accrual of the fee. An application to reduce this amount is also submitted to the court. The collection itself is carried out as a payment according to its own budget classification code (KBK).
When considering a case in court regarding a debt, the defendant immediately needs to consider whether it is possible to reduce this debt or defer it. When the bailiffs open enforcement proceedings, and payment according to the court decision is never made, they have every right to charge an enforcement fee taking into account the procedure.
This will be a punishment for the irresponsible debtor and will significantly increase the already existing debt. Also, the threat of receiving additional penalties in the form of a fee additionally encourages you to comply with the court’s order to collect the debt on time.
Application to the bailiffs for the cancellation of the enforcement fee
The chances of a positive decision are small, but this should be done in order to confirm in court the applicant’s desire to resolve the dispute without resorting to litigation.
- Prepare a statement of claim with a simultaneous application for the suspension of enforcement proceedings or individual procedures within the framework of debt collection through the court.
- Participate in the meeting, form a solid evidence base. The time frame for resolving a case depends on the complexity of the specific situation.
Protection can be carried out already at the administrative stage of the proceedings, with further transition to the courts.
What is an enforcement fee
An enforcement fee is a monetary requirement that is imposed on the debtor in a situation where he has not fulfilled the court decision within the time frame established for voluntary compliance. For voluntary execution of a court decision, bailiffs give five days from the moment the debtor received a decision to initiate enforcement proceedings (excluding non-working days).
If the five-day period has passed and debt obligations have not been repaid, the bailiff has the right to begin forced collection measures - from foreclosure on a bank account and a ban on traveling outside the country to deductions from wages and enforcement fees.
There are decisions that are subject to immediate execution. In such situations, a citizen in debt is given only a day to fulfill the decision. If the decision is not implemented during this period, FSSP employees issue an act imposing an enforcement fee.
The procedure for debt collection by bailiffs.
How not to pay enforcement fees to bailiffs
If the request to suspend the proceedings is granted, the bailiff is obliged to postpone the collection until the court makes a decision on the merits of the case. The operation of certain enforcement procedures may be suspended.
A request to suspend compulsory enforcement measures must be submitted along with the statement of claim. Preparation of an administrative claim An administrative claim is drawn up in accordance with the rules of Art. 125 CAS RF. It is submitted in writing. The document must contain:
- the name of the court to which the application should be filed;
- information about the administrative plaintiff - name of the organization, full name. an individual, his place of registration or stay;
- FULL NAME.
Law Club Conference
If such an opportunity was not presented, then the second resolution can be considered illegally issued. for example, you were familiarized with the resolution to initiate an individual entrepreneur on the date of 23, and obviously you were not given time for voluntary execution, etc. etc. (see Resolution of the Constitutional Court)
I’m not entirely sure of the 100% legality of the following, but I’m retelling my personal experience. Was a collector under an individual entrepreneur. The IP lasted a very long time. In the end, a third party transferred money to the Claimant on behalf of the Debtor, bypassing the SSP accounts, with the wording “To pay off the debt under the Debtor’s IL.” I revoked the IList (you don’t have to specify the reason) - the IP was stopped. As far as I know, the Debtor did not pay any enforcement fee.
Appealing a decision to collect an enforcement fee (sample)
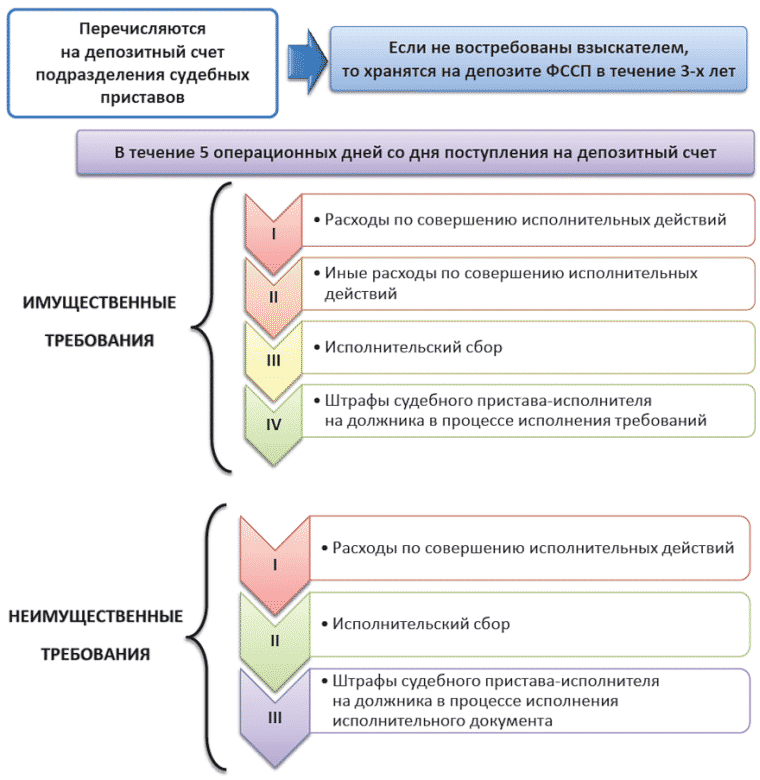
Federal Law; 2) upon repeated presentation for execution of a writ of execution, according to which a resolution of the bailiff to collect the enforcement fee was issued and not cancelled; 3) by order of the bailiff on the collection of expenses for carrying out enforcement actions and the enforcement fee imposed by the bailiff in the process of executing the enforcement document; 4) according to judicial acts on interim measures; 5) according to executive documents containing requirements for the forced expulsion from the Russian Federation of foreign citizens or stateless persons; 6) according to executive documents containing requirements for serving compulsory labor; 7) at the request of the central authority to search for a child. 6.
How to pay and where to get details for individuals and legal entities
Reimbursement of expenses for enforcement proceedings.
An enforcement fee is a type of penalty imposed for refusal to voluntarily pay debts within the framework of a valid court order. The amount is determined in Article No. 112, Part No. 3 of Federal Law No. 229 and is 7% of the amount of arrears. However, the amount cannot be less than 1000 rubles for citizens and individual entrepreneurs, as well as 10,000 rubles. for organizations.
You can find out about the presence of an imputed fee by visiting the official website of the FSSP. The amount of the fine is indicated in the third column next to the debt. You can also pay the resulting arrears on the bailiff service portal. However, the online system accepts the entire amount along with the fee for payment at once. To complete a payment transaction, you must use the instructions described in a special section of the site.
Details for partial repayment of the debt can be obtained from the supervising bailiff, including paying the debt on the spot. After securing the fine, you must hand over the receipt to the FSSP employee.
How to correctly and quickly cancel the collection of the enforcement fee?
The final decision on the claim will take place at the final hearing. During the analysis process, additional evidence and facts may be required - extracts, documents and opinions of independent experts. On average, the processing time for a case can take from one to six months. Options for solving the problem Based on the results of the meeting, a court decision will be made. It may partially or fully satisfy the plaintiff's demands. But due to the specifics of the cases under consideration, there are certain restrictions on the court's decision. They are described in detail in paragraph 7, article 113 of law No. 229-FZ. When making a final verdict, assessors have the right to choose one of the following decisions:
- Postpone the collection of the enforcement fee. This practice is applicable if the plaintiff is unable to pay the compensation amount within the required time frame.
5000 rubles – for legal entities.
The latest figures indicate the minimum amount of the fee if the court case was considered as a non-property one. This amount takes into account the costs of carrying out measures to satisfy the requirements of the writ of execution, carrying out additional measures to search for real or movable property, and the defendant’s funds.
To pay the performance fee, the following conditions must be met:
- notify the defendant of additional costs;
- provide confirmation of expenses and the need to generate a fee;
- the debtor did not present supporting documents, according to which he was not able to satisfy the requirements of the writ of execution.
If the description of the case does not directly indicate compensation for enforcement costs, they can be requested by forming a new judicial appeal.
What is the size of the FSSP enforcement fee?
The specified fee represents the responsibility of the debtor in the form of an obligation to pay money to the budget for failure to fulfill the requirements of the writ of execution within the appropriate period.
The fee is 7% of the amount to be recovered from the debtor or the value of the property. But the amount of the corresponding fee cannot be:
- less than 1,000 rubles, if the debtor is a citizen or individual entrepreneur, and
- less than 10,000 rubles, if the debtor is an organization.
If the debtor is obliged to fulfill a non-property requirement, the amount of the fee in case of failure to fulfill the requirements on time will be:
- 5,000 rub. for citizens and individual entrepreneurs;
- 50,000 rub. for organizations.
Let us consider in more detail individual issues related to the enforcement fee below, but now watch the VIDEO on the topic of protecting the rights of the debtor in enforcement proceedings, because there are problems not only in the issue of collection:
Application to the bailiff to cancel the enforcement fee
To evaluate it, you need to contact professional lawyers. They will help you find inaccuracies, inconsistencies with current rules or other gross violations of the law.
Appealing a decision to collect an enforcement fee First, the preparatory stage is carried out. It consists in clearly forming a claim, indicating violations committed by the bailiff.
This is the most important part of the process, since the outcome of the future case depends on the correctness of the information provided. Therefore, it is recommended to follow certain rules. The preliminary stage of preparing a challenge to the decision to collect an enforcement fee:
- Compile a correct evidence base. The content of Article 33 of Law No. 229-FZ is preliminary studied. Even if the errors were minor, they will become a reason for challenging.
Cancellation of the enforcement fee - judicial practice and grounds
At the time of receiving the bailiff’s order to collect the fee, the debtor has a reasonable question: are there any cases of complete cancellation of the enforcement fee. The law directly provides for the grounds for cancellation and return of collected funds, in particular in accordance with Part 10 of Art. 112 Federal Law dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ, the following cases of cancellation of the following documents are considered as grounds for the return of funds collected by the bailiff:
- collection orders, including by virtue of a court decision to cancel the enforcement fee;
- judicial acts on the basis of which collection is carried out;
- document presented for collection.
The specified grounds for canceling the enforcement fee represent an exhaustive list and cannot be supplemented by participants in the proceedings. Within the framework of this article, we will dwell in detail on the first two cases, for the implementation of which it is necessary to challenge the bailiff’s decision or a judicial act.
Let us note that there are quite a lot of cases from judicial practice in terms of satisfying the requirement to appeal on specified grounds. As an example of a challenge in the absence of notification of the initiation of proceedings, we highlight the Appeal ruling of the Judicial Collegium for Administrative Cases of the St. Petersburg City Court dated January 12, 2016 in case No. 33a-750/2016. In the case of an appeal against a judicial act, as a rule, a court order (in connection with the simplified procedure for challenging), judicial practice in 2020, in 2019 and in the current 2020 in all cases is in favor of the debtor.
The cancellation of collection of the enforcement fee in the absence of notification to the debtor about the initiation of proceedings is guaranteed by the legislator and follows from the concept formulated in Part 1 of Art. 112 Federal Law dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ. The analyzed type of fines is applied if the debtor voluntarily does not pay the debt to the creditor within the prescribed period, the bailiff carrying out forced collection has the right to make a demand for payment in the amount established in Part 3 of Art. 112 of the specified Federal Law.
Is it possible to challenge the performance fee?
According to Art. 112 Federal Law No. 229 “On Enforcement Proceedings”, an enforcement fee is a monetary penalty imposed on the debtor due to his violation of the deadline for voluntary fulfillment of the requirements contained in the executive document. This period is:
- 5 days after receiving a copy of the document on the opening of production;
- 1 day after receiving a copy of the document, if the document is subject to immediate execution: on the collection of alimony, payment of wages to an employee.
The amount of the fee is 7% of the collection amount or the value of the seized property, but not less than 1 thousand rubles for individuals, 10 thousand rubles for organizations, 5 and 50 thousand rubles for individuals and legal entities, respectively, if the document contains a non-property claim.
Note!
Collection of the fee is carried out on the basis of a resolution issued by the bailiff and approved by the head of the OSP. According to paragraph 6 of Art. 112 Federal Law No. 229, the debtor has the right to cancel this decision through the court.
Cancellation of the fee is possible in cases where the order to collect it is made in violation or in violation of the law, including in the following cases:
- issuing a decision without evidence of receipt by the debtor of a decision to open proceedings;
- collection of fees, despite the court granting the debtor payment in installments before the commencement of proceedings;
- incorrect determination of the terms of voluntary execution or the amount of the fee in the resolution;
- re-issuing a decision if the original decision is not cancelled;
- collections on claims in respect of which no fee is collected;
- issuing a resolution after the actual and complete fulfillment of the obligation imposed on the debtor;
- recovery on the basis of a resolution not approved by the head of the PCB.
In what cases can the court reduce the enforcement fee or grant a deferment?
Reducing the amount of the fee and providing a deferment (installment plan) for collection provide the same grounds. Moreover, at the same time you can ask the court to reduce the fee and delay (spread out) its collection.
The grounds for a positive court decision are such significant circumstances that the court will accept as valid. The reasons for non-fulfillment of the requirements, the degree of guilt of the debtor, the measures taken by him for execution or the circumstances for which they were not taken, as well as the financial situation of the debtor are taken into account.
How to reduce the performance fee
A reduction in the amount of the fee is possible only within 25%, no more. If the bailiff collected, for example, 5 thousand rubles, the court can reduce this amount only to 3,750 rubles.
To reduce the amount, you can refer to a poor financial situation, lack of money, including in the context of the size of the principal debt. Any arguments that will justify why the assigned amount is too large and unaffordable are suitable here.
The main opportunity to reduce the amount of the fee is to refer to a poor financial situation and confirm this in court. If the court accepts the arguments, you can save up to 25% of the fee.
How to cancel the enforcement fee of bailiffs
The enforcement fee can be challenged by the debtor in court, in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 112 Federal Law No. 229. There is no possibility of challenging the decision in the order of subordination. According to Art. 128 Federal Law No. 229, an application for cancellation is submitted to a court of general jurisdiction in the manner prescribed by administrative proceedings. In accordance with Art. 218 CAS, going to court is carried out by filing an administrative claim to challenge the decision.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 22 CAS, the claim is filed in the district court at the address of the location of the OSP, the decision of the employee of which is being challenged. According to paragraph 3 of Art. 219 CAS, such a claim can be filed within 10 days from the moment the debtor learned of the violation of his rights and legitimate interests. Violation of the specified deadline is not grounds for refusal to accept the claim; the reasons for missing it are studied individually.
After filing an administrative claim, the debtor must:
- Appear at the appointed time and place yourself or send your representative to the meeting.
- Support the stated demands, insist on checking the legality of the order issued by the bailiff to collect the fee.
- Provide arguments and evidence of the illegality of the decision made or violations that were committed during its adoption.
- Prove the fact of violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, as well as compliance with the deadline for filing a lawsuit.
- Receive a positive court decision, and, if necessary, appeal it in the manner prescribed by Art. 228 CAS.
Note!
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 226 CAS, a case challenging a decision to collect an enforcement fee must be considered by the court within 10 days of the debtor’s application.
Assistance from a lawyer regarding enforcement fees
Resolving issues related to performance fees is not a simple matter, as it might seem at first glance. The debtor does not always know what to do correctly under a given set of circumstances, or what evidence to provide to the court.
Our lawyers are ready to provide highly qualified legal assistance in resolving issues related to the collection of enforcement fees from debtors, including:
► consulting on issues of collection, release, reduction of enforcement fees, reduction of the amount of collection under a writ of execution, and other issues of enforcement proceedings;
► drawing up procedural documents in court to challenge bailiffs’ decisions to collect enforcement fees, to exempt from enforcement fees, to reduce the amount of enforcement fees;
► legal support in the process of court consideration of submitted applications, representation of the interests of the principal in court hearings;
► representing the interests of the principal directly before the bailiff service.
Call today and together we will begin to fight for the observance of your rights and legitimate interests!!!
How to write an application to cancel the enforcement fee
The statement of claim for the cancellation of IP is drawn up in accordance with the requirements of Art. 220 CAS and contains the following information:
- name of the court to which the administrative claim is filed;
- Full name of the applicant, his address, contacts;
- name, position of the administrative defendant;
- the name of the bailiff department whose bailiff issued the decision;
- date and details of the issued and contested decision;
- an indication of the rights of the debtor that are violated by the resolution;
- an indication of the provisions of the legal acts violated by the bailiff’s decision;
- requirements for invalidation of the resolution, cancellation of the enforcement fee, its return, in the case of preliminary retention of IP.
Note!
The application is submitted in 2 copies, one of which is sent to the bailiff whose decision is being disputed. The same applies to the sent package of documents attached to the application.
What is the enforcement fee for bailiffs?
There may be several reasons for this:
- The debtor repaid part of the debt after the court decision, but before the initiation of proceedings based on the writ of execution.
- The debtor repaid part of the debt during the voluntary repayment period.
- By the tribunal's decision.
The court has the right to reduce the amount of the fee. To do this, you will need to prove that there were reasons that prevented you from paying the debt on time.
For example, serious illness, injury. It is important to know that the debtor is obliged to pay immediately after treatment.
A difficult financial situation is not a significant reason for reducing the amount of the fee.
Conclusion So, we have examined the concept of enforcement fees and determined the amounts for property and non-property disputes. They explained which cases are exempt from the fee.
How can you cancel the enforcement fee without going to court?
As far as I understand, the enforcement fee of the bailiffs can be appealed to the head of the bailiff within 10 days from the date of receipt of the decision. The point is that I was not notified of the proceedings against me due to the incorrect address in the court order. The money and the performance fee were withdrawn from the card without warning. Is it normal that I was not notified, that no one bothered to check my address (I live and have been registered at my current address since birth) about this and can I contact the prosecutor’s office?
Regulatory regulation
The enforcement fee is described in Article No. 112 of Federal Law No. 229 and is a penalty in monetary terms. A fine comes into force if the debtor fails to pay the arrears specified in the court order on time. The order is subject to immediate execution in the cases described above. The period for voluntary repayment is five working days after receipt of the documents by the citizen. The collection is credited to the account of the federal service with further transfer to the budget.
- making a decision by a judicial authority;
- To appeal the decision, a period of 30 calendar days is provided;
- in the absence of a complaint, the order comes into force at the end of the specified period;
- if there is an application, the document acquires legal status upon consideration;
- after the start of production, a writ of execution is issued to the collecting party;
- the creditor has the right to transfer papers to the FSSP even if the debtor voluntarily repays the arrears;
- the bailiff initiates a case and gives the citizen 5 days to secure financial obligations;
- If there is no action on the part of the person at the specified time, the levy is activated.
At the same time, execution in administrative and criminal cases is different. In the first case, up to 3 months are provided for voluntary deposit of funds for the fine; in the second situation, 30 or 60 days - depending on the penalty. Accordingly, if the debt is not paid on time, the executors take control of the matter.
What is the enforcement fee for bailiffs?
- The debtor repaid part of the debt after the court decision, but before the initiation of proceedings based on the writ of execution.
- The debtor repaid part of the debt during the voluntary repayment period.
- By the tribunal's decision.
The court has the right to reduce the amount of the fee. To do this, you will need to prove that there were reasons that prevented you from paying the debt on time.
For example, serious illness, injury. It is important to know that the debtor is obliged to pay immediately after treatment.
Answers from lawyers (33)

Good afternoon. The period for voluntary execution of a decision of an administrative body is indicated in the resolution on the initiation of enforcement proceedings.
RUSSIAN FEDERATION FEDERAL LAW ON ENFORCEMENT PROCEEDINGS
Article 30. Initiation of enforcement proceedings
Advertisement from him the enforcement fee and expenses for carrying out enforcement actions provided for in Articles 112 and 116 of this Federal Law.
12. The period for voluntary execution cannot exceed five days from the date the debtor receives the resolution to initiate enforcement proceedings, unless otherwise established by this Federal Law.
The Law does not talk about any notifications by telephone.
Since you received them on June 28, the bailiffs are acting illegally.
It is necessary to appeal the actions of the bailiff to the senior bailiff or to the court
02 July 2013, 19:20
Client clarification
Please tell me, if I had not come at all and had not received these decisions, then they would never have been able to impose an enforcement fee on me, because Couldn't they prove that they handed me the orders? Or, in this case, would they send me the orders by mail and upon return with a postal stamp indicating non-receipt, they could calculate the period from this date?
02 July 2013, 19:34









