Prices for lawyer services in business disputes
Bankruptcy is an integral element of business activity, from which even the largest enterprise or successful entrepreneur cannot be insured. Bankruptcy - what is it? The concept and signs of bankruptcy are contained in Federal Law No. 127-FZ, within the framework of which the legal regulation of insolvency procedures is carried out.
Bankruptcy is the officially recognized inability of a legal entity, an entrepreneur without the formation of a legal entity, as well as a citizen, to repay in full debt to creditors or to fulfill obligations for mandatory payments provided for by law.
What is bankruptcy
As a legal procedure, bankruptcy, including the bankruptcy of a legal entity, is a strictly regulated process, consisting of mandatory and additional procedural stages, during which:
- Formal signs of the debtor's insolvency are established.
- Bankruptcy proceedings are initiated.
- Official procedures provided for by law are carried out.
- The debtor’s ability to repay debts to third-party organizations or government agencies in full is established.
- The order of payments is established.
- An opportunity is being taken to stabilize the financial position of the debtor.
- The debtor's property assets are identified and sold at auction to repay debts to creditors.
- The debtor is declared insolvent (bankrupt).
Establishing signs of insolvency allows you to officially begin the bankruptcy procedure. The legislation considers the inability of a debtor to satisfy monetary obligations to creditors for three or more months in a row as signs of insolvency.
Monetary obligations include: debts to the workforce for wages, severance pay and other payments; overdue debt on mandatory payments.
3 ways to get a free legal consultation 01
-consultant in online chat bottom right
02
Free call 8 (free consultation in Russia)
03
Request a call back (bottom left button), a lawyer will call you back in 10 minutes
Free consultation with a lawyer on business disputes Prices for lawyer services on business disputes
General information about bankruptcy
Definition 1
Bankruptcy is the inability of an enterprise or organization to make payments to creditors on monetary obligations.
Reasons for bankruptcy:
- Objective reasons:
- Dissatisfaction with the regulatory and legislative framework;
Rapid growth of inflation.
- Subjective reasons:
- Reduction in production volumes;
Decrease in sales volumes;
- Decrease in the quality of products;
- Reducing the price of a product;
- Dumping;
- High production costs;
- Decrease in profitability of finished products;
- Long production cycle.
Signs of enterprise insolvency:
- The debtor's inability to satisfy in full all the creditor's demands.
- The debtor's inability to make obligatory payments.
- The insolvency of an enterprise can only be recognized by an arbitration court.
To determine the signs of bankruptcy, it is necessary to take into account:
- The amount of monetary obligations for goods provided, work performed or services performed.
- The amount of mandatory payments excluding penalties and interest.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework Bankruptcy indicators 470 rub.
- Abstract Bankruptcy indicators 270 rub.
- Test work Bankruptcy indicators 190 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Types of bankruptcy
The legislation does not formally contain a description of the types of bankruptcy, however, based on the conditions for the emergence of the grounds and the purpose of its implementation, the following types of bankruptcy can be distinguished:
- Real bankruptcy: a legal entity has complete insolvency caused by objective circumstances, and any measures to financially improve its activities cannot bring results.
- Technical bankruptcy: the inability to repay existing debt is temporary, caused by an increase in accounts receivable.
- Criminal bankruptcy: falls under the elements of crimes provided for by criminal law.
Only technical bankruptcy retains the opportunity for the enterprise to return to normal economic activity. To achieve this, a set of financial recovery measures is being implemented under the guidance of persons appointed by the arbitration court in the process of considering a bankruptcy case.
Real bankruptcy can be initiated both at the request of the debtor himself and at the request of creditors. To initiate a bankruptcy case, a submitted application from at least one creditor is sufficient. The owner of the debtor enterprise may initially file bankruptcy for the purpose of liquidating the legal entity.
Criminal bankruptcy pursues specifically defined goals - achieving economic or other benefits through a deliberate criminal violation of the law to the detriment of the economic interests of other persons or the state. A separate category of insolvency can also be simplified bankruptcy, which is a subtype of real bankruptcy and is aimed at liquidating a legal entity.
Types of enterprise bankruptcy
The bankruptcy of an organization does not always end with exclusion from the state register and the end of economic activity. Under certain circumstances, financial recovery can actually revive the debtor and return the enterprise to normal functioning. But in some cases, only recognition of insolvency allows you to legally deal with debts and avoid pressure from creditors.
In accordance with stat. 2 of Law No. 127-FZ of October 26, 2002, insolvency means a judicially recognized inability of a debtor to meet its obligations, including transactions with counterparties and payment of tax payments. Regardless of the organizational and legal status of the company, the essence of the procedure is to repay debts and make full settlements with creditors, sell off assets if there is a shortage of funds to fulfill claims, or carry out rehabilitation measures aimed at fully restoring solvency.
The main sign of bankruptcy according to stat. 3 No. 127-FZ is the inability of a legal entity to repay claims within 3 months from the date of proper fulfillment of obligations. The minimum total amount of debts is 300,000 rubles. The decision to declare a company bankrupt is made by an arbitration court. At the same time, the amount of unfulfilled obligations is confirmed by documents - with the presentation of decisions, demands, contracts, shipping notes, invoices, acts, etc.
Types of bankruptcy of legal entities:
- Real is the absolute insolvency of the enterprise, implying a complete inability to fulfill obligations and return to profitable operation. As a rule, such organizations are in a deep financial crisis, characterized by loss of initial capital, lack of funds and the presence of a large amount of debt. Even the implementation of rehabilitation measures does not bring results, bankruptcy proceedings are inevitable, and all assets are sold off in order to at least partially pay off creditors. For business owners, declaring bankruptcy remains the only opportunity to get out of the current situation, liquidate the company and avoid subsidiary liability. Among the reasons for the ruin of a company are most often ineffective management, theft of funds and excessive lending.
- Technical - this type of bankruptcy is also called conditional or temporary by economists for the reason that it is caused by an excess of the accumulated amount of overdue receivables and excessive overstocking of warehouses. But at the same time, the amount of debts still remains much lower than the total assets of the enterprise, and with competent anti-crisis management, the situation can really be corrected. As a rule, bankruptcy is successfully prevented already at the stage of financial recovery; skillful reorganization allows the company to quickly return to a stable financial position with profit from its activities. With the help of the arbitration manager, resuscitation measures are carried out aimed at restoring the solvency of the legal entity, including, if necessary, reorientation of work taking into account current market requirements.
- Intentional - this deliberate type of bankruptcy represents fraudulent actions aimed at simulating the insolvency of a legal entity. At the same time, the lack of funds is not considered obvious, and the situation of insolvency is created artificially with the involvement of third-party dummies and companies. Through complex multi-stage money transfers, finances are withdrawn from circulation, assets are sold in advance (usually to their own subsidiaries), liabilities are not repaid, and the founders deliberately initiate bankruptcy, falsify documentation and manipulate facts in order to evade compliance with tax and commercial payments.
- Fictitious is another type of deliberate “false” bankruptcy, when the founders submit deliberately false information in order to avoid settlements with creditors. The initiation of insolvency proceedings is carried out with the aim of obtaining installment payments or a legal discount on the total amount of claims.
Note! All criminal types of bankruptcy insolvency are strictly prosecuted in accordance with the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (Articles 195, 196, 197, etc.).
Types and procedures for bankruptcy procedures
The procedure for declaring a legal entity insolvent is carried out in accordance with the requirements of Law No. 127-FZ. The initiator can be both business founders and creditors, as well as authorized government agencies. Documents are submitted to the arbitration court at the official location of the enterprise. In addition to the application indicating the required data, the package of forms must include documentation confirming the amount and period of non-fulfillment of obligations.
The judicial procedure itself can be performed in a simplified form or in full. The stages of measures include the stages of observation, external management, preventive financial recovery, final bankruptcy proceedings and a settlement agreement, which can be concluded at any time. Following the results of bankruptcy and if it is impossible to return the enterprise to sustainable functioning, the company is legally liquidated with exclusion from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, complete cessation of work, closure of r/accounts, public publication of an announcement, etc.
Bankruptcy check
As part of the economic activity of any legal entity, it becomes necessary to verify the solvency and legal integrity of the counterparty. One of the effective ways to avoid risks when making transactions and protect your own economic interests is to check bankruptcy.
You can check a legal entity or entrepreneur for an insolvency case using the electronic resource EFRSB (Unified Federal Register of Bankruptcy Information), available at: https://bankrot.fedresurs.ru/
This resource allows you to search by the following parameters:
- By region of location of the legal entity or individual.
- By name of legal or natural person.
- By category of debtors.
- According to the obligatory details of the debtor (TIN, OGRN, OKPO).
In the event of initiation of bankruptcy of an individual and the introduction of certain procedures, information about them falls into the EFRSB and is available to any interested party. In the event of a change in the status of the debtor and termination of the insolvency procedure, information from the EFRSB in relation to a specific legal entity or individual must be deleted.
Bankruptcy of citizens and companies.
Main differences
It should be noted that today, in order to initiate bankruptcy proceedings against a legal entity, it is necessary to have unfulfilled obligations in the amount of 300 thousand.
rub. Often, these individuals include those with significant credit obligations or business owners who incur obligations personally as part of the operations of their companies. Before the introduction of the bankruptcy procedure for an individual, it was quite difficult to collect debt from persons who ensured the fulfillment of the obligations of companies they owned, or persons who were responsible for the activities of the company.
Often, at the time of filing claims against such persons (guarantors, joint debtors, managers), they no longer had any property, and the law did not establish a mechanism for receiving funds from such individuals (often the amount of debts of business owners is measured in millions).
Application for bankruptcy
After establishing formal signs of insolvency, it is necessary to officially initiate proceedings to declare the debtor insolvent (bankrupt). This occurs by sending a bankruptcy application to the arbitration court at the location of the debtor, including in the case of bankruptcy of an LLC.
In accordance with the law, the following entities can file a bankruptcy petition:
- The debtor, if he establishes formal signs of insolvency and the inability to pay off debts.
- A bankruptcy creditor who has an overdue debt of at least three months.
- Authorized bodies, for example, the Federal Antimonopoly Service.
The bankruptcy application is subject to consideration in a court hearing of the arbitration court, and information about the beginning of the insolvency procedure and the procedure for accepting creditors' claims is subject to official publication.
Concept, criteria, signs of insolvency (bankruptcy)
The main legislative acts containing rules on insolvency (bankruptcy) include the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Articles 25, 61, 65), the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2002 “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, the Arbitration Procedural Code of the Russian Federation.
Insolvency (bankruptcy)
there is an inability of the debtor recognized by the arbitration court to fully satisfy the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) to fulfill the obligation to make obligatory payments.
A citizen is considered unable to satisfy the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) fulfill the obligation to make mandatory payments (i.e. payments to budgetary and extra-budgetary funds - taxes, fees, insurance and other contributions and payments), if the corresponding obligations and (or) obligations are not fulfilled within 3 months from the date of their fulfillment and if the amount of obligations exceeds the value of the property owned by it, and a legal entity - if the corresponding obligations and (or) obligations are not fulfilled within 3 months from the date of their fulfillment.
The minimum amount of debt is indicated as one of the signs of bankruptcy:
- for a legal entity – at least 100 thousand rubles;
- for an individual – 10 thousand rubles.
Legal significance is attached only to monetary debt obligations.
The right to apply to an arbitration court to declare a debtor bankrupt is vested in: the debtor, bankruptcy creditors, as well as authorized bodies (Federal Tax Service,
Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, etc.). The Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities, and the liquidation commission can also act as creditors for monetary obligations.
Cases of insolvency (bankruptcy) of legal entities and citizens, including those registered as individual entrepreneurs, are considered by the arbitration court. Jurisdiction is exclusive.
A court hearing to verify the validity of the applicant’s claims against the debtor is held no less than 15 days and no more than 30 days from the date of the decision to accept the application to declare the debtor bankrupt. In addition, the arbitration court may order an examination in order to identify signs of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy.
Criteria, signs of insolvency of a business entity:
- the presence of a monetary debt nature of the debtor's obligations;
- failure of a citizen or legal entity to satisfy the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) to fulfill the obligation to make mandatory payments within three months from the date of their execution;
- the presence of a debt in relation to a citizen in the amount of at least 10 thousand rubles, and a legal entity - at least 100 thousand rubles;
- official recognition of insolvency by an arbitration court.
The legislation establishes an additional sign of insolvency (bankruptcy) of a citizen, namely: the excess of the amount of his obligations over the value of his property.
Reasons for bankruptcy
Determining the causes of bankruptcy, for example, bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur, in some cases helps to improve the financial, economic and production activities of the debtor and can help avoid bankruptcy and termination of the activities of a legal entity or entrepreneur.
The main causes of insolvency can be classified into the following groups:
- Ineffective management in the process of carrying out the current activities of the enterprise.
- Objective economic circumstances that do not depend on the will or discretion of a legal entity (economic crisis, changes in legislation, etc.).
- Ineffective servicing of accounts payable, which leads to a sharp increase in penalties for systematic delay in fulfilling obligations.
- Ineffective servicing of receivables: lack of real measures and actions aimed at collecting them.
- Illegal actions of persons leading to insolvency.
In specific cases, there may be other reasons for bankruptcy, caused by both objective and subjective circumstances. Establishing the cause of bankruptcy will allow us to pay special attention to it at the initial stages and insolvency procedures and take measures to eliminate them.
Goals and objectives of bankruptcy
Contrary to the misconception that bankruptcy is always the liquidation of a company, this procedure also has the following tasks:
- Protecting a company that finds itself in a difficult financial situation from ruin and providing assistance in restoring its solvency in order to subsequently return to the market.
- Satisfying the claims of creditors that have become due, but which the company is not able to cover in the normal course of business.
- Liquidation of a company with debts.
The procedure for declaring a company bankrupt, the rules for filing and the process of considering a bankruptcy application are fully regulated by a special regulatory act - the Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy”).
Currently, the practice of applying this law has developed in such a way that a debtor company extremely rarely independently applies to the court to declare it bankrupt, holding out until the last minute and waiting for the initiation of insolvency proceedings by its creditors. The role of creditors can be either counterparties to whom obligations have not been fulfilled within the framework of the company’s activities, as well as other interested parties - banks, tax services, and other government funds.
Misconduct
Criminal legislation contains a number of crimes, the commission of which is directly related to the bankruptcy procedure. Among them are:
- Intentional bankruptcy.
- Fictitious bankruptcy.
- Illegal actions in bankruptcy.
All of these situations arise as a result of violation of specific legal norms, pursue economic benefits for the violator and entail negative economic or other consequences for business entities or legal relations protected by law.
Committing illegal actions during bankruptcy includes:
- Concealment of property assets, destruction and falsification of debtor's documentation, concealment of property rights.
- Illegal repayment of debts to creditors to the detriment of other creditors at any stage of insolvency.
- Obstructing the legitimate activities of an arbitration manager or other officials appointed by the courts in the bankruptcy process.
These actions entail criminal liability and the application of punishment in the form of sanctions provided for in the articles of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Signs of bankruptcy
The main sign of bankruptcy is the inability of the enterprise to make payments within 3 months from the deadline for payment of mandatory payments.
Types of bankruptcy:
- Fictitious bankruptcy is false information from the manager about his insolvency.
- Intentional bankruptcy is the deliberate creation of insolvency.
- Real bankruptcy is the inability of the head of an enterprise to restore his solvency.
- Technical bankruptcy is characterized by overdue accounts receivable. In this case, accounts receivable exceed the amount of accounts payable.
Consequences of bankruptcy
The consequences of declaring a legal entity and individual bankrupt are provided for by law. The consequences of bankruptcy of an enterprise may include the following possible options:
- Full or partial repayment of debts to creditors.
- Declaring the debtor bankrupt and terminating the legal entity (liquidation).
- Restoring the financial condition of a legal entity and returning it to normal business activities.
- Conclusion of a settlement agreement between the debtor and all creditors.
The insolvency of an individual has special consequences:
- Write-off of debts to creditors that were not repaid during bankruptcy.
- Inability to take part in the management of legal entities for three years after the completion of bankruptcy.
- When receiving a credit or loan, it is necessary to indicate information about the insolvency that has occurred within five years after the citizen is declared insolvent.
In a number of cases, the insolvency procedure entails negative consequences for the owners and managers of the legal entity, who will be liable for the organization’s debts if their guilty actions led to the formation of debt and the initiation of bankruptcy, including bankruptcy of the enterprise.
Bankruptcy filing procedure
Bankruptcy proceedings take place in cases where:
— there are no payments for mandatory payments for more than 3 months (90 days); — the amount of debt to creditors exceeds 100 thousand rubles.
It is more profitable for business owners to file an application to court before the creditor company does. In this case, it is possible to relieve yourself of the burden of loan repayments. If time is lost, and the creditor was the first to declare the debtor bankrupt, then court proceedings will be aimed at returning the debt by any legal means.
The calculation of the total debt includes penalties, penalties and accrued interest.
How to file for bankruptcy
To know how to file for bankruptcy, you need to thoroughly study the rules and regulations of the Insolvency Law. However, knowledge of legal acts does not always help in carrying out legally significant actions.
It is quite possible to carry out an insolvency procedure on a legal entity’s own, but it is unlikely to be effective. The best way to file insolvency is to provide qualified assistance from specialists from legal, auditing or consulting companies. They will provide the debtor or creditor with a full set of necessary documents, represent their interests at each stage of bankruptcy, appeal against illegal actions or decisions of the arbitration manager, and provide protection of rights and interests at the stage of selling property and repaying debts to creditors.
Bankruptcy is like a rebus: it cannot be liquidated, it can be revived
The main ones are indicated in Article 3 of the above-mentioned Federal Law:
- Failure to fulfill requirements within three months from the date on which the obligations should have been fulfilled.
- Inability to fulfill the demands of creditors (in fact, this sign is obvious).
We recommend reading: Certificates for old-style international passports
: conditional, supervisory and actual. In addition, there are special or additional signs of bankruptcy inherent in certain types of legal entities:
- natural monopolies,
- strategic enterprises,
- financial (credit) organizations,
- peasant (farm) households. about the bankruptcy of the agro-industrial complex.
They are defined in the relevant paragraphs of the federal insolvency law.
What are the risks of bankruptcy?
What are the risks of bankruptcy? Different negative consequences may occur for different subjects of bankruptcy proceedings:
- Termination of activities of a legal entity (liquidation during bankruptcy).
- Causing property damage in the event of incomplete repayment of a debt to a specific creditor.
- Causing property damage to the debtor as a result of unlawful actions of the arbitration manager.
- Bringing to criminal or administrative liability in case of unlawful actions during the implementation of the insolvency procedure.
The most serious consequences are criminal prosecution with the imposition of specific types of punishment: a fine, disqualification of the convicted person, suspended or actual imprisonment.
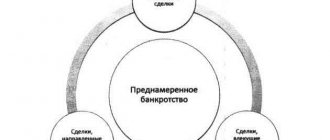
Fictitious bankruptcy of the debtor
In some cases, the company's management decides to file an application with the court with deliberately false information about the welfare and financial position of the enterprise. The most common reason for such fraud is evasion of debt payments, removal of tax burden (tax evasion), deferment of payments.
Such manipulations are a violation of current legislation. If the fact of deliberate or fictitious bankruptcy is recorded, the organizers will be held criminally liable until the actual period of limitation or release of will.
How to file for bankruptcy
How to file for bankruptcy? The legislation provides for the only way to initiate insolvency proceedings - filing an application to initiate bankruptcy proceedings with the arbitration court. Only after this formal procedure has been followed can an insolvency case be initiated by the court with the measures provided for by law.
The fact of establishing signs of insolvency, in the absence of a submitted application, has no legal consequences.
You can file for bankruptcy on your own or with the help of experienced bankruptcy lawyers. If the execution of the application and the documents submitted with it meet the requirements of the law, the court will decide to initiate insolvency proceedings against the debtor.
Natural monopolies
Natural monopolies are understood as organizations that sell goods or perform work (provide services) in the absence of competition in the region.
The criteria for a natural monopoly are:
- the ability of an enterprise to set price limits for manufactured goods (works, services) in the region;
- the inability to replace goods produced by the enterprise with similar ones produced by another enterprise.
Based on these criteria, natural monopolies are usually classified as:
- oil refineries;
- gas companies;
- railway companies;
- communications enterprises (post office, telegraph, etc.);
- energy companies;
- companies providing water supply and sanitation services;
- organizations involved in nuclear waste disposal.
A bankruptcy case is initiated against the listed organizations if they have overdue obligations in the amount of at least 1,000,000 rubles, and the minimum period of overdue is six months.
It is possible to suspend the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings even if the above signs are present if you formulate a pre-trial debt repayment plan, secured by a guarantee from local authorities or the property of the founders.
Bankruptcy support
To fully protect the rights and interests of the debtor or creditor at each stage of bankruptcy, legal support for bankruptcy is required, which will be provided by qualified specialists from legal or consulting firms.
Legal support includes:
- Representation of a creditor or debtor at all stages and procedures of insolvency.
- Preparation in the interests of the debtor or creditor of any documents necessary at any stage of insolvency.
- Appealing actions and procedural decisions made by the interim manager at certain stages of insolvency.
The services of a lawyer will not only help to avoid problems at all stages of bankruptcy, but also guarantee the most effective protection of the economic interests of all participants in the case.
Fictitious bankruptcy of a FL debtor: consequences and responsibility
Fictitious bankruptcy according to the elements of the crime is fraud causing material damage. Punishment for fictitious bankruptcy is provided for by the administrative and criminal codes . The amount of liability assigned will depend on the amount of damage caused.
Administrative liability for fictitious bankruptcy
If the amount of damage caused is not classified as large, then for this offense the citizen will face administrative liability under Part 1 of Article 14.12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The Administrative Code provides for a fine of 1 to 3 thousand rubles.
Criminal liability under Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
If the amount of damage caused is considered large, then the citizen bears criminal liability. In accordance with the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, damage of 2 million 250 thousand rubles is considered major.
If it is proven that FB caused major damage, the perpetrator may suffer the following punishment:
- monetary penalty in the amount of 100 thousand to 300 thousand rubles;
- involvement in forced paid labor for a period of up to 5 years;
- or imprisonment for a term of up to 6 years with a monetary penalty in the amount of up to 80 thousand rubles or in the amount of salary for a period of up to 18 months.
A criminal case can be initiated by:
- Financial manager . Since it is this participant in the procedure who analyzes and assesses the financial condition and makes decisive conclusions about the presence or absence of signs of fictitious bankruptcy.
- Creditors . The creditor is the main person who benefits from eliminating any risks of concealing the debtor’s property - the amount of debt that can be repaid depends on this.
It is important to consider that the financial manager does not conduct an analysis of the FB if a creditor has filed for bankruptcy. Since Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that an application for recognition of bankruptcy must come from the debtor.
Challenging transactions
In order to prevent cases of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy, as well as infringement of the interests of creditors, the law allows for challenging transactions in bankruptcy.
According to the law, at the stage of bankruptcy, any suspicious traces of the debtor that occurred within one year before the initiation of insolvency proceedings can be challenged. Challenging such transactions of the debtor is carried out by filing an appropriate application and considering it in arbitration courts.
How does liquidation of a legal entity differ from bankruptcy?
In addition, there are alternative options for closing a company when it is purchased by another legal entity, or if a reorganization of a business entity, merger with a third party, division or spinoff is possible. However, in Russia, business activities are often liquidated through the bankruptcy process.
Its goal is to find a way to repay debts to creditors and budgetary institutions.
As a rule, an application to declare an organization bankrupt is submitted to the Arbitration Court by its counterparties or employees.
But a business owner can also initiate bankruptcy proceedings when the inability to meet debt obligations becomes obvious.
Cost of bankruptcy
The concept of “bankruptcy cost” includes both the direct costs of carrying out all procedures provided for by insolvency legislation, and the cost of services to support the interests of the debtor or creditor from legal or consulting companies.
The total cost of bankruptcy can be determined only after a thorough forecast of upcoming procedures and activities, analysis of the object of work and the complexity of the case. An insolvency practitioner acting as a representative of one of the parties to a bankruptcy case may exercise all actions and powers permitted by law.
Of particular importance is the determination of the cost of the remuneration of the arbitration manager appointed to carry out established insolvency procedures. The amount of his remuneration is determined by the arbitration court when making a decision to initiate bankruptcy proceedings. Payment of remuneration for the work performed by the bankruptcy or external administrator is the responsibility of the debtor and is classified as current payments of the first priority.
Assistance during the bankruptcy procedure will be provided by a qualified specialist with practical experience in supporting such cases.
A bankruptcy specialist, as part of the provision of services to support the activities of a debtor or creditor, can perform the following actions:
- Protection of the interests of the owners of the enterprise - the debtor, as well as protection of the rights of creditors at all stages and stages of bankruptcy (in court proceedings, at meetings of creditors, when identifying property assets and selling property at auction).
- Legal support at the stage of preparation for bankruptcy: forecast and analysis of the debtor’s financial condition, optimization of current payments and restructuring of debts to creditors.
- Registration and presentation of any documents in the interests of the client.
- Appealing unlawful actions and procedural decisions of participants in an insolvency case at all stages of this procedure.
On the issue of the relationship between the concepts of “insolvency” and “bankruptcy”
The legislative codification of the concept of insolvency (bankruptcy) is contained in Art.
2 of the Federal Law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” (hereinafter referred to as the Bankruptcy Law), which states that insolvency (bankruptcy) is the inability of the debtor recognized by the arbitration court to fully satisfy the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) fulfill the obligation to pay mandatory payments. Our analysis of the issue of the relationship between the definitions of “insolvency” and “bankruptcy” showed that the problem of the interconnectedness of these concepts has been repeatedly studied in the legal literature.
In the history of state and law of Russia, various options for the content of these terms are proposed.
The famous Russian civil specialist G.F. Shershenevich defined bankruptcy as the careless or intentional infliction of damage to creditors by an insolvent debtor by reducing or concealing property.
Diagnosis of bankruptcy
Bankruptcy diagnostics is a comprehensive analysis of the financial, economic and production state of a legal entity with the aim of objectively predicting unfavorable developments of events that could lead to insolvency (bankruptcy) of the enterprise.
Bankruptcy diagnostics allows us to identify indicators that create the most likely threat of signs of insolvency. For diagnostic purposes, various methods are used, and the method of determining the current threat of bankruptcy is of greatest practical importance.
This method uses a number of objective solvency ratios of a legal entity, and above all, the absolute liquidity ratio. A number of other coefficients make it possible to determine the factors of the upcoming threat of insolvency (financial stability of a legal entity).
Diagnosis of bankruptcy is of great importance at the stage of identifying signs of insolvency, as it can show specific options for increasing the efficiency of the enterprise and reducing the level of accounts payable to acceptable values.
Bankruptcy is a consequence of the emergence and increase of insolvency
In 2012, a Law on Bankruptcy appeared, based on the provisions of which it can be concluded that one of the signs of economic insolvency is the inability to make payments, which already has or is just becoming sustainable. It turns out that in order to determine the concept, types and causes of bankruptcy, it is necessary to find out how the financial situation of the debtor has evolved and when exactly insolvency occurred, recognized by the court dealing with economic affairs as a legal fact with consequences established by the Law.
The assessment of the ability to carry out financial transactions is carried out in accordance with Council of Ministers Resolution No. 1672, dated 2011. The analysis of the company's condition is carried out on the basis of the Instruction, the purpose of which is to standardize the procedure for calculating solvency ratios and study the financial situation of business entities, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Economy No. 140/206 (2011).
When analyzing and assessing solvency to identify the causes of bankruptcy of enterprises, you may encounter difficulties associated with the lack of financial statements in full or doubts about their reliability. It is worth remembering that one of the fundamental principles of financial and economic analysis is to operate exclusively with verified facts. Therefore, there may be a need to determine the degree of compliance of the data from the debtor’s accounting records with the information of its accounting, confirming the actual presence of these assets and liabilities. The correctness of their reflection in the relevant documentation is of great importance.
The research is carried out using methods of formal, logical, arithmetic, normative and mutual verification, which in the vast majority of cases is possible only through economic examination .
A decrease in the ability to make payments and the financial stability of a business entity occurs due to a decrease in the liquidity of assets, a reduction in sources of financing (and therefore an increase in the share of borrowed funds) and a disproportionate change in the value of assets/liabilities.
The latter, when carrying out business activities, is usually due to expenses, which is understood as a decrease in the volume of assets or an increase in the number of liabilities, leading to a decrease in equity capital. Moreover, this situation should not be associated with the transfer of financial resources to the owner of the property or their distribution among the participants.
Based on this, the reasons for the bankruptcy of organizations are identified, the activities of the debtor are examined - all significant points relating to the recognition of a person as economically insolvent are determined.
Recognition of transactions as invalid due to bankruptcy
Recognition of transactions as invalid in bankruptcy is an effective mechanism aimed at protecting the interests of the debtor's creditors. The causes of bankruptcy can be single incorrect decisions of the debtor's managers, systemic errors in carrying out economic activities, as well as obviously illegal actions of the owners and managers of a legal entity aimed at deliberate or fictitious bankruptcy.
A transaction made by the debtor within one year before the filing of a bankruptcy application with the court, or after the acceptance of this application, may be declared invalid in the following cases:
- In case of obviously unequal counter-performance of obligations by the counterparty under the contract (suspicious transaction).
- In case of deliberately illegal actions that resulted in an unreasonable increase in wages, payment of bonuses and other payments within the framework of labor relations (such cases, for the purpose of challenge, are equated to contested transactions of the debtor).
Recognizing a transaction as invalid does not entail legal consequences of its completion.
Author of the article: Petr Romanovsky, lawyer Work experience 15 years, specialization - housing disputes, family, inheritance, land, criminal cases.
Useful information on business disputes
- Bankruptcy Bankruptcy of individuals
- Initiation of bankruptcy proceedings
- Intentional and fictitious bankruptcy
- Bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur
- Bankruptcy of credit institutions
- Debtor bankruptcy procedure
- Bankruptcy of the developer during shared-equity construction
- Bankruptcy supervision
- Bankruptcy procedure
- Bankruptcy LLC
- Company bankruptcy
- Bankruptcy of tour operators
- Homeowners association bankruptcy
- Insurance company bankruptcy
- Bankruptcy of SNT
- Stages of bankruptcy
- Subsidiary liability in bankruptcy
- Bank bankruptcy procedure
- Current payments in bankruptcy
- Bankruptcy of legal entities
- Company reorganization
- Alternative liquidation of LLC
Agricultural organizations
Agricultural organizations include persons engaged in the production, sale and processing of agricultural products, provided that the income from the sale of such products is at least half of the total income of such an organization (Article 177 127-FZ). Agricultural enterprises also include fishing firms, the total profit of which from the sale of water resources and agricultural products is at least 70% of the total profit received.
To initiate bankruptcy proceedings, a company must meet the following criteria:
- have arrears in payments to the budget, as well as to banks and employees in a total amount of at least 500,000 rubles;
- be at least 3 months overdue on such payments.
When considering the application by the court and assessing the presence of signs of bankruptcy, the court takes into account seasonal fluctuations in the agricultural market and financial forecasts.
For example, if a bankruptcy petition for an agricultural enterprise is filed by a creditor, the court may refuse to initiate the case if it is obvious that with the onset of the harvest season, future profits will cover all current obligations. The upcoming seasonal profit is regarded by the court as the future income of the debtor, which will help avoid bankruptcy.
Signs of bankruptcy of legal entities
The main signs of bankruptcy of an enterprise are two criteria: insolvency and the presence of unpaid debts. Insolvency implies the inability of a legal entity to make payments on its obligations for 3 months from the date on which they were required to be paid. In order for the arbitration court to begin bankruptcy proceedings for an enterprise, the debt must grow to a specific size. Article 3 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” indicates in Part 2 only the general condition for starting an insolvency case. But right there, in Part 3 of Art. 3 states that it is applicable only in cases where other provisions of the Law do not provide otherwise.
Non-payment of debts means a situation in which the total amount of debt obligations of an organization becomes higher than the value of its property; at the same time, the debtor does not have the opportunity to pay existing obligations.
The existence of debts must be confirmed by the relevant decisions of the arbitration court that have entered into force. In turn, creditors can apply to the court to declare the debtor bankrupt after receiving a writ of execution and filing it with the bailiff service. 30 days after the application, creditors can submit an application to the arbitration court.