Bankruptcy proceedings can affect almost any company facing financial problems, both a huge production facility and a small company with a dozen employees. The key issue in the bankruptcy process most often becomes the formation of a clear priority from the list of creditors (debtors). This procedure is fixed by law and is not subject to “free interpretation”. The article discusses the general scheme for declaring a company bankrupt through court and the order of payments in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise.
Features of the debt repayment procedure
When the court finds that the company is unable to pay off its debt obligations, the bankruptcy trustee begins work. He is appointed by the arbitration court considering the bankruptcy case of a specific object, on the recommendation of the debtor himself or the organization of insolvency practitioners.
The first stage of the hired employee’s work is observation. The manager studies accounting and tax reporting and compiles a list of creditors.
It is this person who will subsequently be involved in the formation and management of the bankruptcy estate, i.e. the totality of resources that is intended for settlements with lenders. The manager, at his own discretion, determines the procedure and amount of payments for applications. If he does not accept any requests, then they are considered completed. Requests for debt collection are satisfied gradually. As soon as the debtor pays off the payments of the first stage, it is time for the next one.
There is a guarantee of fulfillment of obligations on the part of the debtor, even if the requests were not considered by the bankruptcy trustee. It is contained in the provision of the Bankruptcy Law, which states that the involved employee is obliged to maintain the necessary amount of funds to cover all requests.
A bankruptcy trustee may be appointed to pay off all debts.
When submitting applications after the registry is closed or during office work, there are two options for solving the problem:
- If a creditor whose request belongs to the first priority applies after the completion of payments of his category, but before the completion of settlements with the second, then his application is considered out of turn.
- Since there is a time interval between the payments of the first and second stages, a request received before the completion of the priority payments will be considered after their completion.
After satisfying the requirements, the responsible person is obliged to provide reports on the transactions performed to the arbitration court. In addition, you will need documents confirming the fact of sale of the property and a list of persons whose requests were satisfied (indicating the amount of payments).
Within five days from the end of bankruptcy proceedings, the manager is obliged to submit documents to the state register confirming the fact of repayment of all debts.
Thanks to knowledge of the law, there are no questions about what to do in the event of bankruptcy of an organization and what is paid first. There are clear regulations defining the procedure and priorities for payments to creditors. It is described in the latest publication of the Law “On Bankruptcy” dated October 26, 2002, and by 2020, most likely, no changes are expected.
Payments in case of bankruptcy will be discussed in the video:
Primary and secondary obligations
All actual obligations of the debtor are divided into primary and secondary:
Information provided by the legal portal BukvaPrava https://bukvaprava.ru/
- current payments are of primary importance;
- Secondary obligations include regular payments.
Current payments have priority because they allow for bankruptcy proceedings.
Current payments
Current expenses, claims for payment of which arose before the recognition of the enterprise's insolvency, are subject to repayment out of turn.
The sequence of repayment of current expenses is regulated by law.
The following are paid in priority order:
- costs of carrying out bankruptcy measures, including payment of legal expenses and services of the arbitration manager and the specialists involved;
- outstanding obligations under employment contracts, severance pay;
- the work of specialists involved by the arbitration manager to perform his duties in the insolvency case, including for the collection of funds;
- communal payments;
- other current expenses.
Payment obligations included in one queue are repaid according to the calendar order.
The procedure for repaying debts to creditors
Law of the Russian Federation No. 127 “On Insolvency” can be considered as a tool for protecting the interests of all participants in economic relations. The provisions of the document regulate the order of satisfaction of creditors' claims upon the occurrence of bankruptcy, and it is illegal to independently change the prescribed order.
Circumstances indicating the insolvency of the enterprise and preceding the commencement of bankruptcy proceedings are:
- the total amount of debt obligations is more than 300 thousand rubles;
- the period of delay in payment of debts exceeds 3 months.
This gives grounds for declaring the enterprise insolvent.
Current payments in bankruptcy include salaries
Extraordinary payments
There is an established sequence of debt payments in accordance with Article 134 of Federal Law No. 127. Before the start of settlements with creditors in a certain order, the bankrupt enterprise is obliged to make extraordinary (or current) payments.
Debts incurred by the enterprise from the moment it was declared bankrupt are repaid out of turn. These costs, in fact, support the progress of the case according to calculations.
Current payments include:
- payment of costs caused by the bankruptcy procedure: state fees, fees for employees participating in court proceedings.
- wages to employees of a bankrupt enterprise who continued to work from the moment the liquidation procedure began.
- remuneration of persons who were involved in the implementation of activities within the framework of the bankruptcy case.
- payments for consumed utility resources - electricity, water supply, etc.
- current costs.
If stopping the company's activities could lead to loss of life or environmental or man-made emergencies, then funds from the debtor's accounts are primarily used to prevent undesirable consequences, despite other debt obligations.
The order and priority of debt repayment is controlled by the bank, which receives payment orders. The loan obligation is considered fulfilled at the moment the funds are credited to the account of the creditor company. An important condition for repaying the debt is making a payment with notification to a notary.
Basic payments
The previous version of the law provided for 5 stages of fulfillment of debt obligations, and with the latest publication the order of priority was reduced to 3 main stages:
- Settlements with citizens who are entitled to compensation for causing moral or physical harm.
- Salaries of personnel registered under an employment contract, severance pay, royalties for intellectual activity.
- Other creditors.
Compared to the previous version of the law, items that refer to transfers to the state budget and mandatory funds, as well as on a competitive basis, have been excluded from the list of priority payments.

Last in line are loan payments.
Last round of payments
The third group includes consideration of requests from authorized bodies or from creditors who are in line on a competitive basis.
In this case, a special scheme is provided for satisfying applications with the collection of penalties and fines for late payments. In this case, the claims of creditors are entered into a special register and are considered after the main debts are repaid.
This list also includes the following payments:
- wage arrears, vacation pay and sick leave;
- taxes and insurance payments;
- debt on bank loans and advances;
- payment of utilities and rent.
Bondholders are also creditors on the bankruptcy list, so their claims are among the last to be satisfied. The timing of payments is determined by the court depending on the financial condition of the debtor enterprise, as well as the actions taken to reorganize the business.
Sequence of payments
Federal law provides for the following order of payments in case of bankruptcy of an enterprise:
- First of all, the expenses for court costs, wages of the arbitration manager, as well as those persons whom he involved in the performance of his duties are covered.
- In the second, the claims of persons who worked under a contract, employment contract, etc. to receive wages are paid.
- Then the requirements for payment of utility bills are met, as well as all other expenses that need to be incurred to ensure the normal functioning of the debtor enterprise.
- All remaining creditor requirements are fulfilled last.
It is necessary to note that repayment of debt to creditors is carried out in order of priority, while taking into account the rule: payment of money to persons who are in the next queue begins only when all the claims of creditors in the previous one are repaid.
Requests that belong to the same queue are executed in the order they are received.
The queue of creditors in bankruptcy must also be observed:
- First, obligations to citizens whose life or health the debtor caused harm are repaid. This may be the payment of moral compensation, compensation in addition to damages.
- Then wages, vacation pay, severance pay, as well as all other expenses related to wages are paid. This also includes paying authors compensation for intellectual achievements.
- Thirdly, all obligations to other creditors are repaid.
Legislative regulation
The main regulatory act regulating the priority of creditors is Federal Law No. 127. All actions of a legal entity are regulated in accordance with the law.
But to protect the rights of creditors in bankruptcy, there are separate regulations:
- First of all. The procedure for compensation for moral damage is determined by Articles 134 and 135 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- Second stage. Article 136 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes the amount and terms of debt repayment.
- Third stage. Penalties and additional penalties for creditors are prescribed in Article 137 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Debt can only be collected in accordance with the procedure established by law.
If the debtor has no money
Since the very fact of bankruptcy presupposes the insolvency of the legal entity, it is not surprising that there are often not enough funds to satisfy all the claims of creditors. The procedure for satisfying creditors' claims in bankruptcy first involves repaying the debt using the organization's existing accounts. If the available funds are insufficient, then valuable property is put up for auction for sale, and the money received is sent to organizations that have claims. Funds can be sent to the account of the lender or an authorized notary.
If there are not enough funds, then the attacker’s personal property is sold at auction. If this is not enough for calculations, then a penalty may be imposed on the share in the family’s joint property.
The company's financial resources are used to pay creditors, but if during the trial it turns out that the owner deliberately brought the organization to bankruptcy, then responsibility for repaying debts becomes individual
If the amount of funds available to the company is not enough to pay off all debts, then write-off occurs in the following order:
- payment of alimony, compensation for damage to the life and health of victims;
- wages, benefits, bonuses for intellectual work;
- settlements with contracted employees;
- contributions to non-budgetary organizations;
- settlements with applicants whose claims were not satisfied earlier;
- distribution of funds to the accounts of remaining creditors.
When forming a payment schedule, the order in which claims from lenders are received is taken into account.
Payment of taxes
In the process of bankruptcy of an enterprise, payment of taxes can relate to both current payments and accounts payable.
The order and amount of payment of tax debts depends on the correct qualification.
Demands for repayment of tax payments made after the start of bankruptcy proceedings are qualified as current payments of the 4th stage.
Collection of this category of debts is carried out on the basis of a collection order sent by the tax authority to the bank and subject to execution based on the priority given in Federal Law No. 127.
Important nuances
In addition to all of the above, the new edition of 127-FZ put an end to one more issue, which before its adoption caused a lot of controversy. We are talking about the problem of the need to withhold wages of employees of a bankrupt company.
The text of the described document contains information about the ability of the manager (or other responsible person) to withhold money from the bankrupt’s accounts to pay salaries to people who continued to work after the start of the bankruptcy process, as well as to those who were hired after this point.
Also, it was in the new edition that the debtor’s obligation to compensate for moral damage caused to him appeared. The amount of financial compensation in this case is established by the court.
Payments in foreign currency
Quite often there are situations when a bankrupt company has debts in one of the foreign currencies, for example, dollars. From now on, to determine the amount of such debt, it will be converted according to the current exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia).
Maintaining sequence
The claims of creditors of a particular priority are satisfied only after obligations to persons belonging to the previous priority have been repaid. But there is an exception to this rule: the order may be violated when there is a case secured by a mortgage on property.
Unrecognized claims
Quite often a situation arises when the manager refuses to recognize the legitimacy of the creditors’ claims. In this case, if the responsible person acts strictly within the framework of the law, they are considered fulfilled.
Addition to the register of creditors' claims
You should also talk about situations where, after the registry of creditors' claims is closed, new requests are made. If new claims relate to the first priority and are presented before the final settlement with creditors, but after settlement with this priority, then they must be satisfied out of turn. In this case, before payments to other persons are continued, the process is suspended for the required period of time.
If these requests are submitted before the repayment of obligations to the primary creditors, then they are subject to satisfaction after completion of work with this queue.
Terminating the manager's work
The final stage of the manager’s work is drawing up a report on the work he has done and submitting it to the court for consideration. If the judge does not make any comments on the case, then the manager completes his work.
After the court hearing, he has 5 working days to notify the relevant government authorities that the company that was under his control is no longer a debtor.
An example of drawing up the order of payments in bankruptcy (for current payments)
Flagman PJSC voluntarily declared itself bankrupt and, with the help of an arbitration manager, determined the existence of the following debts that arose after going to court:
- payments for electricity and water necessary for the operation of the company’s office and plant;
- remuneration to the external manager;
- arrears of wages to accounting department employees who worked after the declaration of bankruptcy;
- bankruptcy court costs;
- withheld personal income tax from the wages of those employees who continued to work after bankruptcy;
- expenses for environmentally safe shutdown of the company's plant;
- remuneration for specialists hired by an external manager who carried out work on the “preservation” of production.
In accordance with Article One Hundred Thirty-four, paragraphs one and two of the Federal Law “On Bankruptcy”, these payments must be made in the following order:
- expenses for environmentally safe shutdown of the company's plant;
- remuneration to the external manager;
- bankruptcy court costs;
- arrears of wages to accounting department employees who worked after the declaration of bankruptcy;
- remuneration for specialists hired by an external manager who carried out work on the “mothballing” of production;
- payments for electricity and water necessary for the operation of the company’s office and plant;
- withheld personal income tax from the wages of those employees who continued to work after bankruptcy.
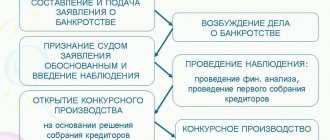
Stages of the bankruptcy procedure
Bankruptcy is established in the Arbitration Court, where either the company itself can apply voluntarily (using the bankruptcy procedure as a kind of protection from creditors), or one of the creditors, demanding payment of debts in court.
A company in bankruptcy either sells off its assets to pay off debts, or, in a more optimistic version, improves its financial condition through effective external management and pays off creditors without liquidation.
Stage #1 - applying to the court to declare the company bankrupt (either by the company itself or by any of the creditors or government authorities). The court considers all the circumstances (including the presence of outstanding debts in the amount of at least three hundred thousand rubles) and makes or does not decide to initiate one of the procedures related to bankruptcy.
Stage #2 - observation. A temporary manager appointed by the court at this stage assesses existing debts and the possibilities of paying them off without losing all property. The manager refers to the company’s accounting and tax records, and also compiles a list of all creditors indicating the amount of debt (“register of claims”).
Stage #3 - financial recovery. It is possible if the interim manager suggested ways out of the crisis and found ways to pay off debts. The company continues to remain under the control of its owners, albeit with some restrictions.
Stage #4 - external control. If financial recovery is not successful, then the company’s management is transferred to an arbitration manager, who can impose a temporary moratorium on debt payments. During this “deferment” period, the manager takes steps to improve the company (through the sale of illiquid divisions, reorganization of the organization, etc.).
Stage #5 - bankruptcy proceedings. Introduced if it is not possible to save the company at the previous stages. The organization is liquidated, its property is subject to sale, all proceeds are transferred to creditors according to the established priority.
| Sequence | Types of creditor claims | Reason: Law “On Bankruptcy” (Federal Law No. 127) |
| 1. Payments outside the main priority (current payments arose after the organization began bankruptcy proceedings) | ||
| 1st stage | Various costs associated with the prevention of man-made/environmental disasters that may result from the cessation of activities of a bankrupt company | Article one hundred thirty-four, paragraph one |
| 2nd stage | 1. legal expenses for the current bankruptcy, payment of monetary remuneration to the external manager, payment for the work of employees involved in the work of the arbitration manager (whose work is mandatory under current legislation) | Article one hundred thirty-four, paragraph two |
| 2. payment of wages to employees (under employment contracts) working after the declaration of bankruptcy | ||
| 3. payment of wages to employees who were hired by the arbitration manager (except for those indicated in the first and second paragraphs) | ||
| 4. payments for utility expenses, if they are absolutely necessary for the operation of a bankrupt company | ||
| 5. other current payments | ||
| 2. Principal payments (occurred before the organization began bankruptcy proceedings) | ||
| 1st stage | Requirements related to liability for causing harm to the life and health of individual citizens | Article one hundred thirty-four, paragraph four |
| 2nd stage | Requirements for payments upon dismissal and arrears of wages to employees working under employment contracts, as well as payment of arrears under copyright contracts | |
| 3rd stage | Settlements with all other creditors (net liabilities, taxes and fees, etc.) | |
This group of creditors includes persons to whom the actions of the debtor caused harm to their life or health. The amount of payments to such citizens is calculated by capitalizing temporary payments established by the arbitration court on the date of the insolvency decision. The following time frames apply:
- the age of an individual must not exceed 70 years;
- the calculation of temporary payments should not be less than 10 years;
- if an individual is 70 years old, then the period of capitalization of temporary payments is 10 years.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Compensation in case of bank bankruptcy amount
The amount of moral damage caused is determined on the basis of a judicial act. Compensation in excess of damages is paid in the amounts provided for by the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation.
An important rule for satisfying the claims of creditors in bankruptcy is the repayment of debts to creditors of one priority after all payments to persons from the previous one. Thus, persons from the second priority of creditors in bankruptcy will receive funds only after the claims of creditors from the first priority are satisfied, and creditors from the third priority - after persons from the second.
The following are considered second creditors in order of priority (Article 136 of Law No. 127-FZ):
- employees signed under an employment agreement awaiting payment of severance pay or salary;
- authors of the results of intellectual activity awaiting payment of royalties.
In addition to the amount owed, they are also paid interest for failure to meet deadlines for salary transfers, vacation compensation, amounts due upon dismissal, and other payments.
Settlements with second-priority creditors are carried out as follows:
- First, the debt is paid to persons registered under an employment agreement, but in an amount not exceeding 30 thousand rubles. for 1 month;
- then their remaining claims are settled;
- Lastly, the royalties are transferred to the authors of the results of intellectual activity.
More information about what the minimum salary a manager should have is described in the article “Minimum salary of the CEO of an LLC in 2020.”
All other persons to whom the debtor has outstanding obligations belong to the third priority of creditors in bankruptcy (Article 137 of Law No. 127-FZ).
In this case, settlements with them are carried out in stages:
- the principal and interest are repaid first;
- then (upon full settlement of the first part) amounts of penalties, lost profits and other monetary sanctions are paid.
The third priority also includes creditors whose obligations to whom are secured by collateral, but they have not received full compensation for their funds through the sale of the collateral.
This situation is possible due to the fact that the creditor can receive no more than 70 or 80% (if it is a bankruptcy creditor under a loan agreement) from the sale of the collateral. The rest of the funds goes to settlements with first and second priority creditors, payment of legal expenses and settlements with the arbitration manager.
Thus, the law provides for 3 stages of creditors in bankruptcy. First of all, there are persons who suffered physical harm as a result of the debtor’s activities. The second stage includes employees registered under an employment agreement and the authors of the results of intellectual activity. The remaining creditors are included in the third priority.