When, during the liquidation process, an organization has paid off its debts, its owners must perform another important procedure - divide the remainder of the property among themselves. Despite its apparent simplicity, the operation causes difficulties for many company founders.
Distributing the authorized capital during the liquidation of an LLC is not so simple. This is a complex process, the implementation of which can lead to disputes and mutual grievances between the founders of the company.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (Saint Petersburg)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
To avoid negative consequences, it is necessary to know in advance how to distribute the authorized capital of the Company.
The essence of the concept
Authorized capital is the amount of funds required to start the operation of a company. It is formed from the contributions of participants. From a legal point of view, the authorized capital represents the amount of property within which a legal entity will be liable to creditors.
Availability of authorized capital is mandatory. The amount is a guarantee of fulfilling the interests of creditors. The attractiveness of an organization for investment and its prestige in business circles depend on the amount of capital. The larger the amount, the safer creditors feel and are happy to make deposits.
The founders must form the capital of the Company. It consists of contributions that the owners of the company make at the time of its creation. Legislation allows you to contribute both cash and property that has undergone a preliminary assessment to capital.
The main functions of the authorized capital include:
- guarantee of loan interests;
- determining the share of participation of the owner of the enterprise;
- increasing the prestige of the organization;
- starting opportunity to begin functioning.
The amount of profit that the founder will receive depends on the size of contributions to the authorized capital.
If the debtor is a participant in a legal entity:
- Sale of property
All property of a citizen available on the date of the decision of the arbitration court to declare the citizen bankrupt and introduce the sale of the citizen’s property and identified or acquired after the date of adoption of this decision constitutes the bankruptcy estate, incl and shares in the authorized capital of legal entities.
Please note that a share in the authorized capital can be excluded from the bankruptcy estate if it does not represent material value (if the organization does not operate).
The rights of a participant in a legal entity belonging to a citizen are exercised by the financial manager during the procedure for the sale of property (including voting at the general meeting of participants).
What documents are needed for this? To exercise the powers of a participant, a judicial act by which it was approved is sufficient for the financial manager.
Are changes being made to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities? No changes are made.
- Restructuring of debts of a participant in a legal entity
Despite the fact that the debt restructuring procedure does not imply the consequences of bankruptcy (including, after restructuring, you can be a manager or otherwise participate in management), during the procedure itself, some restrictions are still imposed on the debtor-participant: acquisition/alienation of shares in authorized capital is allowed only with the consent of the financial manager.
Initial estimate
Availability of authorized capital is a prerequisite for passing the procedure of state registration of a legal entity. Not all companies can afford to have a large amount of money at the start. For this reason, the state has established a minimum, upon entry of which it carries out the registration procedure.
Today, the minimum amount of capital is legally fixed at the level of 10,000 rubles . It consists of contributions from participants, which are carried out in accordance with established rules.
The amount of the authorized capital is divided proportionally between the founders of the company. However, in practice, there are cases when 3 owners contributed 10% of the amount, and the rest was paid by the last founder.
The state reserves the right for the owners of the company to independently distribute the amount of contributions among themselves.
It should be remembered that the amount of profit received and the share upon termination of the company’s operation depend on the size of the deposit.
Section order
The division of the authorized capital between the founders is carried out last.
First you need:
| First step | Pay off the debt. Only the balance after settlement of the company's debts is subject to division. |
| Second step | When the debts are repaid, the due part of the property can be received by the founders, who had the right to a part of the profit at the time the organization functioned. When an organization ceases operations, there is always a small amount of profit left that must be distributed among the participants within a specified period. |
| Third step | And only lastly does the division of the organization’s capital occur. Founders who made contributions can hope to receive funds equal to the size of their share. If after distribution there is property or money left, it is divided among the participants of the organization. |
All sections performed during the liquidation of a company are carried out in a certain order prescribed by law. If there is not enough profit to pay the share to the participants, they have the right to claim part of the property in the 3rd priority order.
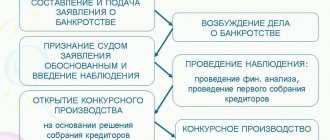
Bankruptcy funds
If a company is declared bankrupt, all available funds will be used to repay debts to creditors. The authorized capital is no exception to the rule.
The operation is carried out in bankruptcy proceedings, which are ordered by the court. The operation is performed by an arbitration manager. The specialist will carry out all operations for the sale of property and the distribution of its parts among creditors in order of priority.
If there are funds remaining after the sale of the organization’s property and settlement of existing debts, they will be distributed among the founders. The amount that the owner of an organization can count on depends on the size of the contribution to the authorized capital.
Actions with the authorized capital during the liquidation of an LLC
Termination of the functioning of an organization is a process that must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of current legislation. The authorized capital is distributed among the founders of the company in accordance with the size of their share. However, the operation is performed only after the company's debts are paid off.
If an organization is declared bankrupt, all funds are used to pay off debts. If after this a certain amount of funds remains, they are distributed among the founders of the organization in accordance with the size of their share.
The amount of payments is affected only by the amount of funds invested by the founder, which was recorded in the organization’s Charter. If the contribution has not been officially registered, its size does not affect the amount of funds that the founder will receive from the authorized capital upon liquidation of the organization.
The distribution procedure can only be carried out after drawing up the liquidation balance sheet of the company.
If a company has a debt to creditors that exceeds the amount of property available for sale, an amount with a negative value is formed on the balance sheet. In this case, the bankruptcy procedure begins. Payments from the authorized capital in favor of the founders of the company will not be made.
How to dismiss a director during the liquidation of a municipal unitary enterprise without violating the law is explained here.
Nuances of calculations
Not always the presence of debt can lead to the liquidation of an enterprise and the distribution of authorized capital among its founders.
When thinking about the advisability of terminating the activities of an organization, an entrepreneur must remember that if there is debt, the amount of which does not exceed 100,000 or 1,000,000 rubles, depending on the size of the company, it is not necessary to liquidate the company and distribute the authorized capital.
As a way out of the situation, the following measures can be taken:
- change of management of the Company;
- reorganization;
- exit of participants and sale of existing shares;
- execution of bankruptcy proceedings.
Increasing the authorized capital in case of bankruptcy
In order to prevent the bankruptcy of the debtor, the general meeting of its participants (shareholders) before the start of the bankruptcy procedure or during rehabilitation procedures may make a decision to increase the authorized capital[1]. In this case, various sources of formation of additional authorized capital are allowed, among which the following should be highlighted:
— additional contributions from participants;
— contributions from third parties to whom shares (shares) are transferred;
— reducing the debt of creditors through the transfer of part of the shares (shares).
In the event of an increase in the authorized capital during bankruptcy, state registration of the corresponding changes in the constituent documents (and information in the register of legal entities) of the debtor must be carried out before the date of the court hearing to consider the bankruptcy case.
In relation to a debtor - a joint stock company, an increase in the authorized capital can be carried out exclusively through an additional issue of ordinary shares distributed by private subscription[2]. This measure cannot be included in the external management plan by the external manager on his own initiative. To initiate it, a corresponding petition from the debtor’s management body is required.[3]
When placing additional shares in bankruptcy, a number of features are applied, established by clauses 2-5 of Art. 114 of the Insolvency Law. These features include:
— limited period of issue (no more than 3 months);
— the need to carry out state registration of the report on the results of the placement no later than a month before the end date of external management;
— shareholders have the right of pre-emptive acquisition, valid for 45 days from the date of commencement of the placement of shares;
— the possibility of paying for issued shares exclusively in cash[4];
— the existence of the right of persons who purchased shares to demand the return of paid funds out of turn if the issue is declared invalid.
[1] The possibility of increasing the authorized capital by the debtor is provided, for example, clause 5 of Art. 64, Art. 109 of the Insolvency Law.
[2] Art. 114 of the Insolvency Law.
[3] This power of the debtor’s management bodies when introducing external management is provided for in clause 2 of Art. 94 of the Insolvency Law. Moreover, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 39 of the Law on JSC, in order to place shares through a closed subscription, a decision of the general meeting of shareholders on increasing the authorized capital of the company by placing additional shares is required, adopted by a three-quarters majority vote of shareholders - owners of voting shares participating in the general meeting of shareholders, if a larger number of votes is needed for making this decision is not provided for by the company's charter.
[4] In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 34 of the Law on Joint-Stock Companies, payment for shares upon the establishment of a joint-stock company, as well as additional shares, can be made not only in money, but also in securities, other things or property rights or other rights that have a monetary value.
Correct distribution
The authorized capital of the Company does not disappear without a trace. During the liquidation procedure, funds are distributed among the founders of the organization depending on the size of the share they contributed when creating the organization.
If an enterprise has a debt to creditors, then the authorized capital will be used to repay debts to them, and its balance will be distributed among the owners of the organization.
The law provides for the possibility of creating an enterprise without contributing the authorized capital in full. The owners of the company can pay only part of the amount, and pay the rest of the money later. However, in practice, cases arise when there is unpaid authorized capital during the liquidation of an LLC.
In this case, the liquidation procedure is carried out in accordance with the established procedure. However, founders who have not promptly fulfilled their obligations to pay the authorized capital within a certain period regulated by law may be held liable.
The interim balance sheet form for the liquidation of an LLC is filled out and submitted for approval to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Read more about the consequences of forced liquidation of an LLC here.
The list of necessary documents and forms when liquidating a public organization is given at the link.
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
That's why FREE expert consultants work for you around the clock!
- via the form (below), or via online chat
- Call the hotline:
- Moscow and the Region
- St. Petersburg and region
- Regions
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
Questions and answers on the topic
Question
How does it affect and what happens to the authorized capital during bankruptcy of an LLC? The debtor's authorized capital is 46,000,000 rubles. The company was registered in 1999 (as far as I understand, at that time the participant was obliged to pay the authorized capital and provide confirmation of its payment to the tax office, if I’m wrong, please correct me). Since the debtor does not have property or bank accounts, we plan to file for bankruptcy for this debtor. What will happen to its authorized capital? In my understanding, the concept of Authorized Capital is abstract, and besides, we now do not know how it was contributed - in cash or other assets, and whether it was contributed at all. Does the founder of an LLC (who owns a 100% share of the management company) take any risk if the company goes bankrupt?
Answer
The authorized capital is an asset and, therefore, cannot be an asset used to repay debts to creditors. Thus, the authorized capital does not play any role in bankruptcy.
The founder may be held vicariously liable on the grounds provided for by the Bankruptcy Law.
The debtor himself has the right to file an application for bankruptcy; as for liability, it may arise if it is established that the debtor did not file such an application within the period established by law. The costs associated with the bankruptcy procedure are borne by the applicant; perhaps this is the only risk of filing such an application.
Additionally, you can read the recommendation: How to challenge a fine for failure to file a bankruptcy petition.
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the “Lawyer System”
.
«Article 7. Right to appeal to the arbitration court
1. The debtor, bankruptcy creditor, and authorized bodies have the right to apply to an arbitration court to declare a debtor bankrupt.
2. The right to appeal to the arbitration court arises from the bankruptcy creditor, the authorized body for monetary obligations from the date of entry into force of a court decision, arbitration court or judicial act on the issuance of writs of execution for the forced execution of decisions of the arbitration court to collect funds from the debtor. The right to apply to an arbitration court arises for a bankruptcy creditor - a credit organization from the date the debtor shows signs of bankruptcy established by this Federal Law.
The right to appeal to the arbitration court arises from the authorized body for obligatory payments after thirty days from the date of the decision specified in paragraph two of paragraph 3 of Article 6 of this Federal Law.
2.1. The right to apply to the arbitration court arises for a bankruptcy creditor - a credit organization in the manner established by paragraph two of paragraph 2 of Article 7 of this Federal Law, subject to prior publication, at least fifteen calendar days before applying to the arbitration court, of a notice of intention to apply to the arbitration court. an application to declare the debtor bankrupt by including it in the Unified Federal Register of Information on the Facts of the Activities of Legal Entities.
3. Partial fulfillment of the demands of a bankruptcy creditor or an authorized body is not a basis for the arbitration court to refuse to accept an application to declare a debtor bankrupt if the amount of unfulfilled claims is not less than the amount determined in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 6 of this Federal Law.
Article 8. The right to submit an application from the debtor to the arbitration court
Bankruptcy of an OJSC by decision of the director
Does its general director have the right to apply to the court to declare a joint stock company bankrupt if the corresponding decision of the general meeting of shareholders has not been adopted and the share of state participation in the authorized capital of the company is 49%? Nadezhda Verkhova and Alexey Alexandrov, experts from the GARANT Legal Consulting Service, explain.
49% of the JSC's shares are owned by the state. Can the general director of an open joint-stock company, without a corresponding resolution of the shareholders, initiate bankruptcy proceedings for the joint-stock company?
The debtor, bankruptcy creditor, and authorized bodies have the right to apply to an arbitration court to declare a debtor bankrupt (Clause 1, Article 7 of Federal Law No. 127-FZ of October 26, 2002 “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 127 -FZ).
The circumstances that constitute the grounds for filing an application with the arbitration court to declare the debtor bankrupt by the debtor himself are listed in Articles 8 and 9 of Law No. 127-FZ. These articles describe cases in which filing an application to declare a debtor bankrupt is, respectively, the right and obligation of the debtor.
So, according to Art. 8 of Law N 127-FZ, the debtor has the right to file an application with the arbitration court in case of foreseeing bankruptcy in the presence of circumstances clearly indicating that he will not be able to fulfill monetary obligations and (or) the obligation to pay mandatory payments on time.
Article 9 of Law No. 127-FZ provides that the head of the debtor is obliged to submit the debtor’s application to the arbitration court if:
1) satisfaction of the claims of one creditor or several creditors makes it impossible for the debtor to fulfill monetary obligations or obligations to pay obligatory payments and (or) other payments in full to other creditors;
2) the body of the debtor, authorized in accordance with its constituent documents to make a decision on the liquidation of the debtor, made a decision to apply to the arbitration court with an application from the debtor;
3) the body authorized by the owner of the property of the debtor - a unitary enterprise, made a decision to apply to the arbitration court with an application from the debtor;
4) foreclosure on the debtor’s property will significantly complicate or make impossible the debtor’s business activities;
5) the debtor meets the signs of insolvency and (or) signs of insufficient property;
6) Law No. 127-FZ provides for other cases.
As can be seen, the adoption by the debtor’s body of a decision to apply to the arbitration court with an application to declare the debtor bankrupt is an independent basis for the debtor’s manager to become obligated to apply to the court with a corresponding application. In other listed cases, such an obligation arises from the manager due to the very fact of the occurrence of the conditions provided for in Art. 9 of Law No. 127-FZ of circumstances, regardless of the decision of the general meeting of shareholders or other body of the debtor, as well as the state’s share of participation in the authorized capital of the debtor. The above is, in particular, confirmed by the provisions of paragraph four of clause 2 of Art. 38 Law No. 127-FZ, according to which, the debtor can submit an application without making a decision of the founders (participants) of the debtor, as well as another authorized body of the debtor about the debtor filing an application with the arbitration court.
At the same time, neither Law No. 127-FZ, nor Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies” indicate that the decision on filing such an application in court should be made by the general meeting of shareholders. Therefore, unless otherwise provided by the charter of the joint-stock company, the issue of making such a decision falls within the competence of the sole executive body - director, general director (clause 2 of article 69 of the JSC Law).
Thus, regardless of the presence of a decision of the general meeting of shareholders of the company, the general director in the case established by Art. 8 of Law N 127-FZ, has the right, and in cases established by Art. 9 of Law N 127-FZ, is obliged to apply to the court with an application to declare a joint stock company bankrupt (including with a state share in the authorized capital). This is also confirmed by judicial practice (see, for example, paragraph 5 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 15, 2004 N 29, the decision of the Twelfth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated July 1, 2011 N 12AP-4185/11, the Third Arbitration Court of Appeal dated October 8, 2009 N 03AP -3760/2009, Nineteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated December 22, 2008 N 19AP-5004/08, ruling of the Twelfth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated August 20, 2013 N 12AP-7127/13).
The texts of the documents mentioned in the experts’ response can be found in the GARANT legal reference system.
Distribution of authorized capital upon closure of an LLC
The distribution of any property of the company occurs strictly in accordance with the norms of the law, according to the established rules of priority. Participants take and withdraw funds only after settlements with all creditors.
If an organization does not have the ability to pay off all external debts due to insufficient own funds, then its own property must be sold, which in turn is accountable and cannot go anywhere in violation of the liquidation procedure.
The authorized capital is also the property of the LLC; it should be withdrawn to pay off and repay the company’s debts.
As such, there is no mandatory return of the authorized capital. The founders are not recognized as creditors of the company and take assets only after the distribution of property according to the company’s obligations.
The authorized capital may go to the participants in a smaller amount than was contributed due to insufficient funds during liquidation.
Distribution always occurs in proportion to the contributions of the founders, since the original ratio of shares does not go away.
Is return of capital possible only upon liquidation?
The return of the authorized capital to the founders is most often discussed in the context of the termination of the company’s activities, but you can get your share not only during liquidation. Another opportunity to return funds is to voluntarily leave the founders. In order to exercise their right to withdraw, a member of the organization will need to submit an application. In it you need to indicate the size of your share and specify in what form you want to receive it.
It must be borne in mind that it is only possible to withdraw from membership if such a possibility is provided for in the charter. If the voluntary withdrawal of the founders on the basis of an application is not stipulated in it, then it will not be possible to receive their share of the authorized capital in this way.
Important! The legislation does not prohibit amendments to the charter regarding the withdrawal of founders. Even if such a right was not initially provided for, nothing prevents the document from being supplemented with relevant provisions (i.e., the founders will have the right to voluntary exit and return of the authorized capital). True, this is only possible if all participants agree to make changes.
As for the direct payment of the share, it must be taken into account that by law it is carried out in cash. If, when creating a company, you contributed property to the management company, then there is no guarantee that it will be returned to you. You may be returned either the cash equivalent or other property if you consent. You can also receive your share in the form of property when you contributed money, but agree to return it in the form of a property.
Write-off of a share in the authorized capital upon liquidation
So, having carried out a completely multi-stage procedure for closing an LLC, the liquidation commission has the right to write off the remaining funds in favor of the founders in proportion to their contributions. Then the owners withdraw and collect the payments assigned to them.
If the company’s debt obligations are too large and lead to liquidation through bankruptcy, then the founders, of course, should not count on receiving the share contributed during creation. In such situations, the remaining funds are used to pay for the services of the manager and support of the procedure.