General characteristics of bankruptcy procedures, their distinctive features.
Page 7 of 12 The law identifies the following main bankruptcy procedures: -observation; -financial recovery; -external control; -competitive proceedings; - settlement agreement. Supervision is a bankruptcy procedure applied to a debtor in order to ensure the safety of the debtor’s property, conduct an analysis of the debtor’s financial condition, compile a register of creditors’ claims and hold the first meeting of creditors. The monitoring procedure is introduced by a ruling of the arbitration court based on the results of considering the validity of the applicant’s claims.
The same court ruling appoints a temporary manager.
At the same time, the head of the debtor enterprise and other management bodies continue their work, but they can carry out a number of transactions only with the written consent of the temporary manager. In addition, during the observation period they cannot make a number of decisions (on reorganization, liquidation of a legal entity, creation of branches and representative offices, etc.).
From the date of introduction of financial rehabilitation, external management, declaring the debtor bankrupt by an arbitration court and the opening of bankruptcy proceedings or approval of a settlement agreement, supervision is terminated. Financial recovery is a bankruptcy procedure applied to a debtor in order to restore his solvency and repay debts to all creditors in accordance with the debt repayment schedule approved by the arbitration court.
The financial recovery procedure can be introduced by a meeting of creditors or an arbitration court at the request of the founders (participants).
The maximum period for financial recovery is 2 years. The arbitration court appoints an administrative manager who exercises his powers until the end of the financial recovery procedure or until he is removed by the arbitration court.
Recognition of bankruptcy of a legal entity in 2020: diagram of the main stages, features and consequences
/ / / Updated 07/12/2020 Author of the article: Reviewer: 2020-03-23T08:46:59+03:00 Has the company accumulated so many debts that the company will not be able to pay them off, even if it sells all its property?
External administration is a bankruptcy procedure applied to the debtor in order to restore his solvency. This procedure is introduced by the arbitration court on the basis of a decision of a meeting of creditors if a real possibility of restoring the debtor’s solvency is established. The management of the LLC has no other options other than bankruptcy. Various reasons can lead to such a disastrous result:
- sanctions and consequences of the economic crisis in the country;
- top managers chose the wrong development strategy;
- It was not a specialist who was put in charge of the company, but a thieves.
- inflation consumed all profits;
The law describes several signs of insolvency, upon the appearance of which the management of the LLC is obliged to file for bankruptcy:
- salaries to the company's employees, as well as other due payments, are also not made for a long period.
- over the past three months, the debtor company has not paid a penny to any of the creditors;
- the total amount of material obligations to all creditors (including the Federal Tax Service, Social Insurance Fund, Pension Fund) exceeds three hundred thousand rubles (in relation to each creditor, the debt is more than ten thousand rubles);
If there are signs of bankruptcy of an enterprise, and the management hesitates to apply to the arbitration court regarding the recognition of bankruptcy, it risks falling under the provisions of the articles -. When they talk about the legislation regulating the bankruptcy procedure in our country, first of all, they mean two documents: a rather voluminous , consisting of 12 chapters and 233 articles Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”; and short. Bankruptcy is the only legal way to get rid of a debt burden when there is nothing to pay the bills and there are no prospects that the situation will change for the better.
This is not a panacea for those who decided to take out loans and then declare bankruptcy, knowing that the law will write everything off. For such a vision of the essence of bankruptcy, you can go to jail for up to six years. The bankruptcy law gives the debtor a chance to pay off by changing loan terms to a more lenient side, attracting investors, reorganizing the company and other available methods.
The essence of bankruptcy and the features of its passage
Debtors try to declare themselves insolvent in order to get rid of the debt in a legal way. The court decides how and within what time frame the borrower will repay the debt, while interest, fines and penalties for late payments will no longer accrue.
The bankruptcy procedure is as follows:
- Drawing up an application and collecting additional documentation;
- Submitting a petition to the arbitration court at the place of registration (one of the following options is possible);
- acceptance of the application;
- denial of the application.
- Participation in a court hearing dedicated to the consideration of the case;
- Waiting for a court decision (one of the following options is possible);
- seizure of part of the property to pay off debt;
- decree to repay the debt from wages;
- debt write-off.
- Filing an appeal against court decisions (if there are claims)
Each stage must be considered separately so that individuals are not left with any questions.
Stage | Observation phase | Bankruptcy stage |
| Arbitration manager | Financial Manager | Competition manager |
| Types of activities carried out | conducting an assessment of the debtor's property; checking transactions made by the debtor for legality; analysis of the debtor’s sources of income; compilation of the bankruptcy estate | organizing an auction to sell the debtor’s property; sale of property; payment of received funds to creditors; return of the remaining funds (if any) to the debtor |
| Result | determining how the debt will be repaid | sale of property for the amount necessary to cover the debt |
Lawyer - Comparative analysis of bankruptcy stages
An important role among the general provisions on bankruptcy is occupied by its procedures.
The influence on the debtor at various stages of the insolvency process is carried out through various measures expressly provided for by law. Initially, at the stage of initiating proceedings in the case, these are interim measures (seizure of the debtor’s property, removal of him from management, analysis and establishment of the debtor’s financial situation, etc.); if it is possible to restore the debtor's solvency, these are restorative measures (measures to repurpose production, sell the debtor's enterprise, measures taken within the framework of a moratorium on satisfying creditors' claims, measures to invalidate a number of the debtor's transactions, etc.) and, finally, liquidation measures applied on the basis of a decision to declare the debtor insolvent (bankrupt), aimed at identifying the debtor's receivables, forming a bankruptcy estate, its implementation, as well as measures to satisfy the claims of creditors in the order of priority provided for by law. Thus, insolvency (bankruptcy) procedures are a set of measures provided for by law in relation to the debtor, aimed at restoring its solvency or liquidation.
The monitoring procedure is introduced based on the results of the arbitration court's consideration of the validity of the applicant's claims.
This is a bankruptcy procedure applied to the debtor in order to ensure the safety of the debtor’s property, conduct an analysis of the debtor’s financial condition, compile a register of creditors’ claims and hold the first meeting of creditors.
As a general rule, financial recovery is introduced by an arbitration court based on a decision of a meeting of creditors. Here the Law defines the procedure for filing a petition for the introduction of financial recovery, as well as the procedure for its implementation. External management is also introduced by the arbitration court based on the decision of the meeting of creditors, and
Main stages of bankruptcy - goals and relationships
Each of the stages of declaring a company insolvent is closely interconnected and is carried out in order to achieve its goals. The timing of the activities, their goals and objectives are listed in Law No. 127-FZ.
Stage 1. Observation
An analysis of the debtor's current financial situation is carried out at the preliminary observation stage (stat. 62-75 No. 127-FZ). For an independent assessment of the financial situation, a temporary manager is appointed, who publishes a notice of the introduction of supervision.
We invite you to read: Qualification Board of Judges of Moscow, complaint against a judge for violation of consumer rights
In relation to credits and loans, the rules will be as follows:
- As soon as the bank sends a demand to the debtor, a notice of delay - the statute of limitations begins to count from zero
- A call from a bank employee also “resets” the statute of limitations
- Partial repayment of a debt, a statement to the bank about the inability to pay, etc. will lead to a new limitation period.

It is not worth the risk of trying to determine the statute of limitations on a creditor. Simply list all creditors on your application. This way you will protect yourself from possible problems in bankruptcy.
Procedural deadlines in bankruptcy law table
However, if this action must be performed in an organization, then the period expires at the hour when the corresponding operations in this organization, according to established rules, cease. Thus, as a result of the announcement (not production! My note) by the court on April 24, 2013 of the operative part of the judicial act, the period for publication of information in accordance with Articles 28, 128 of the Bankruptcy Law began to run from April 25.
2013 and expired at 24 hours 00 minutes 05/06/2013″Question. Previously, everyone agreed that a notice of a meeting of creditors (Article 13 of the ZoB) is submitted to the EFRSB 14 working days before the date of the meeting of creditors (clause 4 of Article 13 of the ZoB). Even somewhere in the table about the publication of information it is indicated this way. /However, in Art.
Bankruptcy of a legal entity
Bankruptcy is a procedure that is carried out when the property and all assets of an enterprise (legal entity) are not enough to satisfy the claims of creditors.
To begin with, it does not matter to whom the debt arose - the bank, employees, clients, partners - legal entities, or to government agencies. In any case, it is in court that it is recognized that a legal entity is bankrupt, that is, it cannot fulfill all current obligations for more than 3 months, and the debt (over all assets) exceeds 100 thousand.
rub. In this case, conditions appear that the court designates, for example, the responsibility of the leaders of the legal entity in the current situation. Application for bankruptcy of a legal entity An application to the arbitration court for the insolvency of the debtor for a period exceeding 3 months can be filed by one of three parties:
- or the relevant body authorized to do so (prosecutor, tax authorities).
- the debtor himself,
- bankruptcy creditor,
If the volume of obligations already exceeds 100 thousand.
rub., while it is impossible to pay the funds for more than the specified period, company representatives are obliged to independently file a bankruptcy petition.
It is important to take into account that if a bankruptcy application is submitted by his creditors before the debtor himself, then they have the right to appoint a more suitable arbitration manager.
In some cases, property is sold at a price that is far from competitive, and the debtor is brought to so-called subsidiary liability.
This means that he is threatened with measures ranging from the alienation of personal property to liability under the Criminal Code for deliberate or fictitious bankruptcy. Insolvency (bankruptcy) of legal entities Insolvency is a synonym for the term bankruptcy regarding both legal entities and individuals. Designates the appropriately recognized financial condition of a legal entity when it is unable to satisfy the requirements:
- creditors (for existing obligations),
Stages of enterprise bankruptcy
Any modification and commercial distribution of the flowchart without the written permission of Russian Information Technologies LLC (www.russianit.ru) is prohibited. The diagram is provided on an “as is” basis; Russian Information Technologies LLC (www.russianit.ru) does not make any guarantees regarding the relevance, accuracy, completeness, or reliability of the information contained in the flow diagram.
Files for upload/download:
Special conditions for Courts, SROs and Training Institutions
If you are a representative of the Court, the head office of the SRO or an educational institution for training arbitration managers, write to us at and we will send a printed poster for free!
Share!
Share and show the scheme to your partners and friends, publish photos of the scheme on social networks and on your website, write to us how and why you use this scheme, what you would like to change in it. We do this work for you, and together we can make it even better!
We look forward to your feedback, suggestions and wishes in our VKontakte and Facebook groups and on the forum.
Bankruptcy of a legal entity: pros and cons of the procedure
Bankruptcy of a legal entity is certainly a tempting and often effective way to get rid of debts that, for example, a store cannot pay.
But there are certain risks, which we will discuss in our article.
Contents: Olga Yurievna Kirillova, managing director of the legal company Heritage Group Bankruptcy of a legal entity is certainly a tempting and often effective way to get rid of debts that, for example, a store cannot pay. However, the more the Federal Insolvency Law is improved, the more risks this procedure carries.
We recommend reading: Where to complain about the actions of the Rosreestr
For the debtor, the risks lie, first of all, in collecting losses from the director and participants, as well as in bringing them to subsidiary liability. For the creditor, the risks are that, having spent additional funds to finance the bankruptcy procedure, he will not be able to receive his money, since all the debtor’s property will be withdrawn. According to statistics, in 2020, bankrupt creditors received on average 5.5% of their debts.
The advantages for the debtor are that as a result of bankruptcy, all debts are written off, and the company is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Thus, the unprofitable company is liquidated, and neither creditors nor the tax authorities will subsequently be able to make any claims against it.
Advantages for the lender. If the debtor does not want to pay even if there is a writ of execution, in bankruptcy it is possible to obtain complete information about the financial activities of the debtor and challenge transactions that caused damage to creditors; return the property to the bankruptcy estate and bring the managers to subsidiary liability if the funds in the bankruptcy estate are insufficient. The bankruptcy estate is all property available at the time of the opening of bankruptcy proceedings and identified during bankruptcy proceedings. It is obvious that with such effective tools that bankruptcy legislation puts in the hands of the creditor, 5.5% of satisfied claims is very little. There is a simple explanation - it is not enough to have the tools, you also need to be able to use them.
Comparative characteristics of the concepts characterizing the category of “bankruptcy” and the legality of their use in domestic practice
, 09.03.2017
- , Candidate of Sciences, Head of Department
- Kaluga branch, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
- A CRISIS
- BANKRUPTCY
- CRISIS SITUATION
- INSOLVENCY
- ORGANIZATION
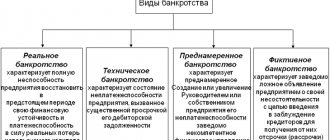
The article provides an analysis of theoretical information on the bankruptcy of organizations, which is considered from both a financial and legal point of view. The main features of the objective aspects of this phenomenon are analyzed. The characteristics of real, technical, intentional and fictitious bankruptcy are given.
The relationship between the depth and scale of the crisis and the danger of bankruptcy of the organization is reflected. The process of uneven economic development is characterized by a crisis situation and can be considered as a confluence of unfavorable situations and as a certain general pattern characteristic of a market economy. Currently, the problem of monitoring the financial condition of an organization for its management, choosing a lending priority, investment attractiveness, and identifying reliable partners is extremely relevant.
The development and tightening of competition, the fall in the effective demand of the population leads to the fact that many organizations are experiencing financial difficulties ranging from short-term to “protracted” in nature, leading in some cases to the development and deepening of the crisis situation, and in some cases to bankruptcy proceedings.
Crisis situations of an organization, as a rule, arise during the development of an economic entity, and during the period of expansion of production, and during the initial stage of decline in production. This is due to changes in production and sales volumes, an increase in accounts receivable and payable, and a shortage of working capital. Crisis phenomena of an organization go through several stages of development of a crisis situation: economic insolvency (hidden stage of bankruptcy), financial instability, insolvency (real bankruptcy) and the stage of official recognition of bankruptcy.
Bankruptcy of legal entities
The main legislative act on bankruptcy issues is the Federal Law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”.
This is the main source of regulatory information about all procedures, signs and consequences of bankruptcy. The law defines the concept of bankruptcy as follows: insolvency - recognition by an arbitration court of a person’s inability to fully satisfy demands for monetary obligations, for the payment of severance pay or wages, or to fulfill the obligation to pay obligatory payments. Each type of obligation can become an independent basis for initiating bankruptcy proceedings against an organization.
The first characteristic of the state of bankruptcy is included in the definition of the concept - specific types of debts, in the presence of which a legal entity can be considered insolvent.
The second important sign is that not every delay in repaying monetary obligations indicates the insolvency of the company, but only one that exceeds three months from the date when the obligations should have been fulfilled.
A debtor can file a bankruptcy petition against himself or his creditors. At the same time, for the director of the defaulter, filing a bankruptcy petition is an obligation in the following circumstances: · repaying a debt to a specific creditor will lead to the impossibility of settling obligations with other creditors; · the management body of a legal entity, authorized by the constituent documents, or by the owner of the property of the debtor - a unitary enterprise, decided to submit such an application; · foreclosure on the defaulter’s property will greatly complicate or make his further economic activity impossible; · the debtor meets the conditions of insolvency or insufficient property; · there has been arrears to employees for payment of wages or severance pay for more than three months.
The legislation provides
Bankruptcy in diagrams and tables
Moreover, inflated interest rates and prices are used. Penalties for late repayments of loan payments are taken into account, loans are attracted at significant interest rates (from friendly banks), property is purchased (again from friendly enterprises) at inflated prices, debt is formed, which is secured by the pledge of property (in this case, the creditor is placed in a privileged queue). They can “hang” accounts receivable, slowing down the flow of money in any way.
Stages of bankruptcy of a legal entity: diagram
In order to declare a debtor bankrupt, the concept of enterprise insolvency is used, that is, the inability to pay existing obligations on time.
Bankruptcy cases for legal entities are complex and multi-stage.
What are the stages of bankruptcy according to legal requirements?
What is the order of this judicial procedure? All legal nuances will be discussed further. The ability to declare oneself bankrupt is the only way to legally liquidate a business in cases where it is not possible to fulfill the obligations of creditors. In this case, as a rule, the amount of accumulated debts exceeds the value of the enterprise’s assets, and the period of delay is over 3 months.
(. In some situations, an analysis of the financial and economic condition of the company makes it possible to take preventive measures to normalize the organization’s activities in order to pay creditors. But if there are no prospects for business development, the owners have to file an insolvency petition with arbitration.
Clear regulations and mandatory stages of bankruptcy of a legal entity have been approved at the federal level in the already mentioned.
This regulatory document defines the algorithm of actions that are carried out in the process of declaring a company insolvent. The requirements are mandatory for all participants in the process, regardless of the organizational status of the organization and its industry affiliation.
Not all stages of bankruptcy are applied as the case is resolved, but preliminary observation is always carried out.
The decision to introduce monitoring measures is made by the court based on the results of consideration of the application (can be submitted by either the debtor or any of the creditors, as well as authorized government agencies). At the same time, the presented evidence of the debtor’s insolvency is carefully studied.
Based on the results of the observation, appropriate conclusions are drawn about the future fate of the enterprise - termination of bankruptcy proceedings or transition to the next stage.
The generally accepted procedure for declaring a legal entity bankrupt includes five mandatory stages.
5 stages of bankruptcy of a legal entity (diagram and table)
Evgeniy Malyar 5 The state is interested in the success of all business entities operating on its territory.
The budget is formed through the taxes received from them. For this reason, Russian legislation clearly defines all possible stages of the procedure for recognizing financial insolvency. A legal entity or one that has declared its inability to pay debts, on the basis of Law 127-FZ, goes through the stages of bankruptcy, the description of which this article is devoted to.
The first procedure, called observation, is carried out after the filing of an application by the insolvent debtor or him (one or more) to the arbitration court. How this stage will end is still unknown.
If, during the consideration of the circumstances, it turns out that the debt could have been repaid, but the debtor, based on some of his own considerations, did not pay, a decision will be made to terminate the bankruptcy proceedings. Second option: the parties reach a settlement agreement.
In other words, if the creditors and the debtor independently find a solution that suits everyone, the lawsuit stops.
By the way, such a solution is possible at all stages of bankruptcy, except the first. Monitoring consists of the objective financial condition of the debtor in accordance with the provisions of Articles 127-FZ, starting from the 62nd and ending with the 75th. A temporary manager appointed by the arbitration court performs a number of duties:
- notifies interested parties that he is monitoring this business entity;
- ensures the inviolability of assets and property of a legal entity;
- preliminary estimates the current financial results of the enterprise as unprofitable or profitable;
- draws up a preliminary register of financial claims against the debtor.
The manager and financial director are not prohibited from carrying out most business transactions if they are not related to the alienation of property in favor of third parties.
Deadlines under bankruptcy law
Type of legal act or code article | What is regulated |
| Bankruptcy Law of 2002 | The Basic Law, according to which the procedure for recognizing financial insolvency of all categories of citizens takes place |
| Federal Law No. 476 of December 29, 2004 | Amends the Law “On Bankruptcy”, regulating the process of recognizing the insolvency of individuals |
| Article 65 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation | Establishes the right of all categories of citizens to recognize their insolvency in court |
| Article 446 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation | Regulates which categories of property cannot be seized from the debtor |
| Article 196 and 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation | Penalties for deliberate and fictitious bankruptcy |
Law The bankruptcy procedure is carried out in the manner prescribed by Federal Law No. 127 “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”.
And if the debtor is found to have property, the location of which needs to be established, the process may drag on for years. Do you want to calculate the terms of the bankruptcy procedure taking into account your events? Come visit us for a free consultation.
So, let's look carefully at the diagram of the stages of bankruptcy.
From the presented diagram, the mechanism for considering insolvency cases by the court becomes clear. More details about what tasks are pursued at the stages of the bankruptcy procedure are in the next section.
EFRSB)
Register of creditors
Action Deadline Entering data about the creditor into the register From the moment the court made a ruling on entry into the register Informing the manager or registrar about changes in data Timely
Observation
Bankruptcy proceedings
Action Deadline Inclusion in the EFRSB of information on the price of the collateral, the procedure and conditions of trading, etc.
Automatic signing of the consent implies a complete termination of the insolvency procedure. What information is included in the agreement? First of all, this is the exact procedure for repaying creditors' obligations; also indicates the settlement format, including terms and interest rates. Additionally, the document may include other conditions that do not contradict legal requirements.
One of them, namely the settlement agreement, is allowed to be renewed at any time, and some of the others (except for monitoring) are not always carried out and for the intended purpose of the bankruptcy creditors participating in the proceedings. The right of influence is directly provided for by the provisions of Law No. 127-FZ. So, let's take a closer look at the diagram of the stages of bankruptcy.
FREE CONSULTATIONS ARE AVAILABLE TO ALL CITIZENS AT THE SPECIFIED PHONE NUMBERS OR VIA CHAT MODE
It’s not worth the risk of trying to find the statute of limitations on a creditor.
Simply list all creditors in full on your own application. This way you will protect yourself from possible problems in bankruptcy.
The procedure is carried out in accordance with legislative norms in accordance with Art. 76-92 of Law No. 127-FZ. This stage is not assigned in all cases, but only when hidden potentials for business resuscitation are identified. The decision to apply is approved at the first creditors' meeting together with the development of a preliminary debt repayment schedule.
Among the consequences of reorganization, the following steps should be highlighted:
- Cancellation of absolutely all pre-trial actions to repay debts, including already issued collection orders.
- Suspension of dividends, ban on payment of interest on shares.
- Prohibition on carrying out any transactions with obligations (barters, offsets, etc.).
- Removal of seizures from the debtor's assets, suspension of the accrual of sanctions on debt amounts.
An independent manager is appointed responsible for the implementation of the adopted financial recovery plan.
The maximum period is one and a half years; as an exception, it can be extended to 2 years. If no actions bring results, debts are not repaid, the court makes a decision to introduce bankruptcy proceedings, or rather, the free sale of the legal entity’s assets.
The completion of recognition of the debtor's insolvency is the introduction of bankruptcy proceedings. The procedure itself is carried out strictly in accordance with the regulations of Law No. 127-FZ (stat. 124-149) and means the inevitability of business bankruptcy. As before, at this stage the parties are allowed to enter into a settlement agreement. The main goal of the production is the fullest possible repayment of creditor claims through the sale of company assets at free auction.
- Closing a financial insolvency case;
- Introduction of external management based on the financial report submitted to the administrative manager;
- Initiation of bankruptcy proceedings in case of unsuccessful reorganization.
We suggest you read: How to record the provision of study leave to an employee in accounting
Bankruptcy of legal entities
Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Adopted by popular vote on December 12, 1993.
(as amended on December 30, 2008) // Russian newspaper. 01.21.2009. 2. Arbitration Procedural Code of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2002 No. 95-FZ (as amended on July 12, 2011) // Rossiyskaya Gazeta. July 27, 2002; 07/15/2011. .Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Part one dated July 31, 1998 No. 146-FZ (as amended on July 19, 2011) // Russian newspaper. 06.08.1998; 07/22/2011; Part two dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ (ed.
dated 07/19/2011) // Parliamentary newspaper. 08/10/2000; Rossiyskaya gazeta.07/22/2011.
We recommend reading: Deadline for including claims in the register of creditors during monitoring
.Federal Law of December 2, 1990 No. 395-1 (as amended on July 11, 2011) “On Banks and Banking Activities” // Rossiyskaya Gazeta. 02/10/1996; 07/15/2011. .Law of the Russian Federation of November 27, 1992 No. 4015-1 (ed.
from 07/18/2011)
“On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation”
// Rossiyskaya Gazeta. 01/12/1993; 07/22/2011.
.Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ (ed.
dated September 28, 2010) “On accounting” // Russian newspaper. November 28, 1996; 09/30/2010. .Federal Law of February 25, 1999 No. 40-FZ (ed.
from 02/07/2011, as amended. from 06/27/2011)
“On the insolvency (bankruptcy) of credit institutions”
// Rossiyskaya Gazeta.04.03.1999; 02/11/2011; 06/30/2011. .Federal Law of 08.08.2001 No. 129-FZ (ed.
from 07/01/2011)
“On state registration of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs”
// Rossiyskaya gazeta.10.08.2001; 07/04/2011. .Federal Law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ (as amended on July 12, 2011, as amended on July 18, 2011) “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” // Rossiyskaya Gazeta. November 2, 2002; 07/15/2011; 07/22/2011.
.Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 296-FZ (as amended on December 28, 2010) “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” // Rossiyskaya Gazeta. December 31, 2008; 12/31/2010.
.Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 6/8 of 07/01/1996
“On some issues related to the application of part one of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation”
// Bulletin of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation. 1996. No. 9.
How to legally write off debts if the creditor does not intend to forgive them
A person crushed by the burden of debt ceases to feel like a full-fledged citizen. He constantly needs to look for money to survive; he loses interest in work and self-development.
This situation is fully applicable to a legal entity. The obvious solution in this situation is bankruptcy. After going through this procedure, the debtor will completely get rid of debts.
In simple terms, the meaning of bankruptcy is to clear a legal entity or individual from the burden of debt and start a new life - free from debt dependence.
Important! If debts are written off through bankruptcy proceedings, the debtor is considered completely exempt from paying them. If the debtor anticipates the onset of insolvency (the inability of a legal entity to pay creditors for an amount of more than 300,000 rubles), and in the case of an individual (for an amount of more than 500,000 rubles), then it is worth thinking about the need to carry out a bankruptcy procedure in order to write them off completely .
At the same time, the grounds for the occurrence of debt (unrepaid loan, credit, unjust enrichment, surety agreement, other business agreements) have no legal significance. In some cases, you also have to pay for other people’s debts, for example, if a citizen acts as a guarantor for a loan agreement of his friends or relatives.
In this case, the question arises whether the guarantor can declare bankruptcy. He has such a right if he meets the criteria of insolvency. Our Company provides full support for the bankruptcy procedure, achieving the desired result - complete freedom from debt.
Call us and we will help you get rid of bad debt!
Insolvency of legal entities
Bankruptcy of legal entities is often considered one of the options for possible liquidation of an organization. But according to existing legislation in this industry, during the procedure itself there is an opportunity to breathe new life into the enterprise.
In any of these options, the insolvency procedure entails complete relief from debts. But only the presence of compelling reasons can serve as an argument in declaring a legal entity bankrupt. The law states that if within three months an enterprise cannot repay its debt to creditors, then there is a basis for declaring a legal entity bankrupt.
The arbitration court will initiate a case if the debtor claims more than 300,000 rubles. In view of these grounds, authorized bodies, creditors of the legal entity, as well as the insolvent debtor himself have the right to file a bankruptcy petition. An on-site tax audit can also become the basis for declaring an enterprise insolvent. Documentary confirmation will be:
- acts of reconciliation with debtors;
- accounts receivable of a legal entity;
- bank accounts with statements;
- inventory statements;
- financial statements as of the latest date.
- debtor's account;
Negative results of an on-site inspection confirm the grounds for the insolvency of a legal entity. The right to declare an enterprise bankrupt is possible only by an arbitration court. For the head of a legal entity, initiating a bankruptcy case is both a right and an obligation. Within a month after identifying the first signs of bankruptcy, the head of the debtor enterprise is obliged to file an application with the arbitration court.
Each company manager bears criminal liability for knowingly leading an enterprise to bankruptcy. The manager of a legal entity is given a month to file an insolvency application if appropriate signs are identified.
Otherwise, he is subject to subsidiary liability to creditors. For creditors of a legal entity and authorized bodies, filing for bankruptcy is an inalienable right.
General characteristics of bankruptcy procedures Text of a scientific article in the specialty “State and Law. Legal Sciences"
foreign currency) direct participants in the movement of goods across the customs border.
In addition, they monitor compliance by individuals with the rules for transporting cash currency across the customs border of Russia, established by the currency legislation of our country. The function of customs currency control is carried out by a system of customs authorities, which includes the Federal Customs Service, the Currency Control Department of the Federal Customs Service, currency control units of regional customs administrations, departments and offices of customs currency control. The tasks, functions, and rights of these customs authorities are enshrined in the Regulations on these authorities, approved by orders of the Federal Customs Service and issued on the basis of federal regulatory legal acts on currency regulation and currency control.
In conclusion, I would like to note that currency control in customs, being a type of state currency control, is characterized by the fact that it is one of the functions of customs authorities; the forms and methods used by customs authorities are defined in the legislation on currency regulation and the Customs Code of the Russian Federation; Violators of currency legislation are subject to administrative coercive measures provided for by current legislation. UDC 343.535:343.85 E.A. Lebedeva (Moscow, Moscow State Law Academy) GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BANKRUPTCY PROCEDURES The legal foundations of bankruptcy are considered, and characteristics of its individual procedures are given.
Federal Law of October 26, 2002
No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”1 provides for a plurality of procedures applicable to insolvent debtors, the introduction of which depends on the specifics of their legal status, the possibility (impossibility) of restoring their solvency and other circumstances.
In accordance with the said Law, when considering a bankruptcy case of a debtor-legal entity, the following bankruptcy procedures are applied: - observation (Chapter IV); - financial recovery (chap.