A written application for bankruptcy of an enterprise can be submitted by: To whom the decision of the economic court on the liquidation of an enterprise is not sent: Help with studies and work About the project Contacts. Educational materials Work programs, workshops Methodological instructions, manuals Lectures How to write a thesis How to write a term paper Questions and tickets for exams, tests, tests. Tests and testing Cheat sheets and spurs By subject Technological Economic Accounting Labor protection Plant growing Livestock farming Land management Gardening, forestry and hunting Technical By type of work Examinations Laboratory work Abstracts Safety instructions Terms Miscellaneous Coursework Objectives Practice reports Diploma theses. Help with studies and work.
WATCH THE VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: IQ TEST with MMO
Who can go bankrupt? Only those who have debts of more than 500 thousand or perhaps with a smaller amount?
The Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” states that a citizen is obliged to apply for bankruptcy if the amount of his unfulfilled obligations is more than 500 thousand rubles. But the law also states that if the amount is less than 500 thousand, then the citizen has the right to do this, the main thing is to really prove to the court that he will not be able to fulfill his obligations.
Those. theoretically, you can declare yourself bankrupt with a debt amount of 100 thousand rubles, but our lawyers see the economic feasibility of going bankrupt with an amount of at least 300 thousand.
personal bankruptcy test
Should I go bankrupt or is there another way out? Should I start bankruptcy? Should you declare yourself bankrupt?
The appellate court overturned the first instance court's decision to refuse to recognize the debtor's transaction as invalid on the basis of clause 2 of Art. 61.3 of the Bankruptcy Law. However, when making its decision, the appellate court did not resolve the issue of applying the consequences of the invalidity of the transaction.
Which of the indicated determinations of the arbitration court considering a bankruptcy case are reviewed according to the general rules of Section VI of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation?
How much does bankruptcy cost? Is it profitable?
It must be remembered that bankruptcy proceedings are quite expensive. Below is a list of expenses that are mandatory during bankruptcy:
- the financial manager's remuneration is deposited with the court before filing a bankruptcy petition and amounts to 25,000 rubles.
- The state fee for considering a bankruptcy case is paid before filing a bankruptcy application and is 300 rubles.
In addition, during bankruptcy it is necessary to make publications in the Kommersant newspaper and in the Unified Federal Register of Bankruptcy Information about the progress of the bankruptcy procedure. Their cost may vary depending on the complexity of the case, but usually on average it is 15,000 rubles.
Those. 40,000 rubles will be only bankruptcy expenses.
The services of specialists from BashYurZashchita LLC to carry out the bankruptcy procedure will amount to 30,000 rubles.
Thus, the entire turnkey bankruptcy will cost the citizen 70,000 rubles.
Solving bankruptcy problems with answers for lawyers
D) the concept of “actual costing” is not used in accounting.
- Select from the following costs the costs that can be classified as basic (conditionally variable):
D) the cost of communication services (payment for telephone conversations).
- Why is the classification of costs by costing items most often used in accounting?
- Can general business expenses be classified as a comprehensive cost item and why?
- Define the total cost of production.
- According to the method of inclusion in the cost of production, expenses are divided into:
To perform the functions of an arbitration manager, an independent and objective person is needed. Let's see what functions are assigned to the bankruptcy manager: 1) study all the financial affairs of the enterprise that has fallen into bankruptcy in order to find opportunities to satisfy the claims of creditors, i.e.
Be sure to contact us, perhaps, having understood your question, we will be able to make you an interesting offer.
In a difficult situation associated with the onslaught of creditors, clients of the legal center will need:
- Professional advice and support for specific problems related to preparing for bankruptcy;
- The liquidation process has already been initiated and the client needs to strengthen its position before the judicial authorities;
- Typically, opponents pursue their own designated goals to obtain material benefits and use legal measures. In this case, effective protection of interests is needed;
- The bankruptcy procedure is not a guaranteed means of getting rid of debts, but it allows you to save on costs in a difficult situation.
Who is a financial manager? Where will I get it?
A financial manager is a person appointed by the Arbitration Court in a bankruptcy case of a citizen, whose participation in the case is mandatory.
Its task is to take into account the interests of creditors during bankruptcy - to challenge the citizen’s transactions, to replenish the bankruptcy estate. It is important to note that this is not a representative of a citizen, but an independent person, designed to help primarily creditors.
BashYurZashchita LLC has several SRO arbitration managers with whom we have been cooperating for a long time. In any case, we take care of all communication with the financial manager.
Tests with answers on the topic - Crisis management
The public has received mixed reactions to the law on bankruptcy of individuals. By declaring his financial insolvency, a citizen risks completely losing even minimal savings. Experts also expressed concern that this could result in financial insecurity for borrowers and losses for lenders. Nevertheless, the advantages are also obvious.
In other words, the second spouse (former spouse) is compensated in full for the value of his share in the joint property.
If the liquidation procedure is initiated by opponents, the likelihood of loss by both the debtor and the creditor increases. Included compression files are only those that have no conditions and are included on all devices and browsers.
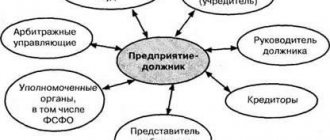
The debtor himself, the bankruptcy creditor (including on claims for the collection of alimony for minor children) and the authorized body.
D) the cost of electricity consumed by the enterprise.
- Can we say that actual costing is the actual costs associated with the manufacture of products?
Especially for teachers, educators and other employees of the education system, there is a 60% discount (only until the end of winter) when taking professional retraining courses (124 courses to choose from).
3.1.1 Test assignment on the topic “Diagnostics of the likelihood of bankruptcy”Based on the balance sheet data of Vostok LLC (Appendices 3 and 4), evaluate the structure of the balance sheet using the methodology established by Russian Government Decree No. 498 dated May 20, 1994 (as amended by Russian Government Decree No. 449 dated June 7, 2001). Calculate the ratios and compare them with the standard values of the current liquidity ratio, the ratio of own working capital, the coefficient of restoration (loss) of solvency and the degree of solvency for current obligations. Calculate the forecasted revenue for the next period. Give an economic interpretation of the results obtained. Present your calculations in a table.
3.2.1 Test assignment on the topic “Calculation of indicators, coefficients and analysis of the causes of insolvency”
Initial data
: Balance sheet and profit and loss statement of Vostok LLC (Appendices 3,4). The information necessary for making calculations, which is not contained in the financial statements, is as follows:
Information for calculations (rub.)
Indicator name
| To the beginning period | At the end of the period | |
| Overdue accounts payable | 2887891,5 | 1759387,5 |
| Gross revenue | 1086145,2 | 1863390,6 |
Exercise:
Calculate the indicators and coefficients of the debtor’s financial and economic activities in accordance with the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2003 No. 367, analyze the reasons for the loss of solvency and assess the current financial condition.
3.3.1 Test assignment on the topic “Analysis of the debtor’s assets and liabilities in order to identify reserves for settlements with creditors”
Initial data balance sheet and profit and loss statement of Vostok LLC (Appendices 3.4)
Exercise:
Conduct a horizontal and vertical analysis of assets and liabilities, give an economic interpretation of the results obtained. Determine the book value of assets involved in the production process, as well as the book value of assets that can be sold to restore the debtor's solvency.
Additional information for calculation:
| Name of assets | Book value |
| 1. Mothballed fixed assets | 301500 |
| 2. Non-production objects possible for sale | 1239000 |
| 3. Office decoration items, passenger vehicles, etc. | 78000 |
| 4. Long-term financial investments are impossible to return | 1500 |
| 5. Bad long-term accounts receivable | 6000 |
| 6.Technological standard for the cost of raw materials, materials and other similar values | 247500 |
3.4.1 Test assignment on the topic “Integral assessment of financial stability
»
Using the reporting data of Vostok LLC (Appendices 3,4), give an assessment of the risk of bankruptcy in order to summarize calculations for various indicators, using an integral assessment of financial stability, unfavorable current values, the current dynamics of which will indicate possible significant financial difficulties in the foreseeable future or bankruptcy. Give an economic interpretation of the results obtained.
3.5.1 Test assignment on the topic “Analysis of financial indicators when determining signs of deliberate bankruptcy”
Initial data: The bankruptcy case of Dalrybtekhsnab LLC was initiated in January 2008 at the request of creditors. The table shows data from financial statements for the period preceding the date of initiation of bankruptcy proceedings. Assignment: Based on the data presented in table. 25 calculate the indicators of financial and economic activity used to conduct an examination of the signs of deliberate bankruptcy and draw conclusions.
Table 25 Balance sheet of Dalrybtekhsnab LLC
| Assets | Code page | As of 01/01/08 | As of 04/01/08 | As of 07/01/08 | As of 10/01/08 | As of 01/01/09 |
| Fixed assets | ||||||
| Intangible assets | 110 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Fixed assets | 120 | 16500 | 16500 | 16500 | 6675 | 6675 |
| Construction in progress | 130 | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 |
| Long-term financial investments | 140 | 7500 | 7500 | 7500 | 18000 | 18000 |
| Total for section 1 | 190 | 25560 | 25560 | 25560 | 26235 | 26235 |
| Current assets | ||||||
| Reserves | 210 | 1395 | 1395 | 840 | 465 | 390 |
| Including: goods shipped | 215 | 45 | 45 | 90 | 30 | 15 |
| VAT | 220 | 300 | 300 | 150 | 225 | 240 |
| Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected more than 12 months after the reporting date) | 230 | 135 | 135 | 885 | 585 | 525 |
| Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected within 12 months after the reporting date) | 240 | 20482,5 | 21982,5 | 29482,5 | 36982,5 | 36900 |
| Short-term financial investments | 250 | 150 | 150 | 45 | 180 | 180 |
| Cash | 260 | 7,5 | 0 | 0 | 7,5 | 7,5 |
| Other current assets | 270 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Total for section 2 | 290 | 22500 | 23992,5 | 31432,5 | 38475 | 38272,5 |
| Balance | 300 | 48060 | 49552,5 | 56992,5 | 64710 | 64507,5 |
| Passive | Code page | As of 01/01/08 | As of 04/01/08 | As of 07/01/08 | As of 10/01/08 | As of 01/01/09 |
| Capital and reserves | ||||||
| Authorized capital | 410 | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 |
| Extra capital | 420 | 15000 | 15000 | 15000 | 15000 | 15000 |
| Reserve capital | 430 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 |
| Social Sphere Fund | 440 | 150 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Special-purpose financing | 450 | 7,5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Uncovered loss from previous years | 465 | -3000 | -3060 | -3360 | -4560 | -4560 |
| Uncovered loss of the reporting year | 475 | -60 | -300 | -1200 | -1350 | -1432,5 |
| TOTAL for section 3 | 490 | 14047,5 | 13665 | 12465 | 11115 | 11032,5 |
| long term duties | ||||||
| Loans and credits | 510 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 520 | 105 | 105 | 105 | 105 | 105 |
| TOTAL for section 4 | 590 | 555 | 555 | 555 | 555 | 555 |
| Short-term liabilities | ||||||
| Loans and credits | 610 | 300 | 150 | 60 | 0 | 15 |
| Accounts payable | 620 | 33120 | 35152,5 | 43897,5 | 52875 | 52740 |
| Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income | 630 | 22,5 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other current liabilities | 660 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 165 | 165 |
| Total for section 5 | 690 | 33457,5 | 35332,5 | 43972,5 | 53040 | 52920 |
| Balance | 700 | 48060 | 49552,5 | 56992,5 | 64710 | 64507,5 |
| Average monthly revenue | 7800 | 7050 | 3750 | 2235 | 3000 |
3.6 Identifying signs of fictitious bankruptcy
Signs of fictitious bankruptcy are detected if, on the date of filing the debtor’s application to the arbitration court, the debtor had the opportunity to fully satisfy the creditors’ claims for monetary obligations and (or) payment of mandatory payments. The calculation and analysis of the following indicators is carried out as of the last reporting date preceding the date of filing the debtor’s application.
If the degree of solvency for current obligations was less than or equal to 3 months (6 months for strategic organizations and organizations of natural monopolies), then the debtor had the opportunity to fully satisfy the creditors’ claims for monetary obligations and (or) payment of mandatory payments at the expense of its current economic activities. If the degree of solvency for current obligations exceeded the specified values, the value of the absolute and current liquidity ratios is checked. If the value of these coefficients is greater than or equal to their standard value, then the debtor had the opportunity to satisfy in full the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) payment of mandatory payments at the expense of its quickly liquid current assets without significant complications or termination of business activities.
If, as of the last reporting date preceding the date of filing the debtor’s application to the arbitration court, the debtor had the opportunity to satisfy in full the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) payment of obligatory payments at the expense of current business activities or at the expense of its quickly liquid current assets, then the signs fictitious bankruptcy are seen. Otherwise, there are no signs of fictitious bankruptcy.
Example: The bankruptcy case of Arsenal LLC in January 2008. at the request of the debtor. Table 26 shows the values of solvency indicators calculated for the period preceding the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings.
Assignment: Based on the data presented, draw conclusions about the presence or absence of signs of fictitious bankruptcy and about the period of analysis of the debtor’s transactions to determine the signs of deliberate bankruptcy.
Table 26 Calculated coefficients
| Indicator name | As of 01/01/08 | As of 04/01/08 | As of 07/01/08 | As of 10/01/08 | As of 01/01/09 |
| Absolute liquidity ratio | 0,08 | 0,06 | 0,03 | 0,02 | 0,003 |
| Current ratio | 1,2 | 1,1 | 0,6 | 0,5 | 0,4 |
| The indicator of the security of the debtor's obligations with its assets | 1,36 | 1,31 | 1,2 | 1,15 | 1,1 |
| Degree of solvency for current obligations | 2,2 | 2,4 | 5,7 | 6,1 | 6,7 |
Since the case was initiated at the request of the debtor, we will consider the values of the indicators for the last reporting period preceding the date of initiation of the bankruptcy case. The degree of solvency for current obligations is more than 3 months (6.7 months). Consequently, the debtor was not able to pay off his debts through his current activities. Absolute and current liquidity ratios less than 1 indicate that the debtor could not pay off debts using quickly liquid property. The indicator of the debtor's security with his assets exceeded 1, which means that by selling all his assets (including fixed assets and inventories), the debtor could pay off his debts. However, at the same time, its economic activities would stop. Thus, without stopping activities, the debtor was not able to pay off accumulated debts either through the sale of property or through income from its production activities. Therefore, there are no signs of fictitious bankruptcy.
We will analyze the debtor’s transactions to determine the signs of deliberate bankruptcy; for this purpose, we will calculate the quarterly and average rates of decline in the indicators in Table. 27
Table 27 Quarterly and average rates of decline in indicators
| Indicator name | As of 04/01/08 | As of 07/01/08 | As of 10/01/08 | As of 01/01/09 | Average pace |
| Absolute liquidity ratio | 0,75 | 0,5 | 0,6 | 0,15 | 0,44 |
| Current ratio | 0,9 | 0,55 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 0,76 |
| The indicator of the security of the debtor's obligations with its assets | 0,96 | 0,92 | 0,96 | 0,96 | 0,95 |
| Degree of solvency for current obligations | 1,09 | 2,4 | 1,07 | 1,1 | 1,32 |
If the average rate of change in the absolute and current liquidity ratios, the indicator of the debtor's security with its assets is less than one, and for the degree of solvency for current obligations is more than one, it means that during the period under study there was a decrease in the indicator. During the period under study, all solvency indicators worsened.
Comparing the average rate of decline with quarterly indicators, we note X quarters in which the rate of decline in indicators of absolute and current liquidity and the security of the debtor's obligations with its assets is below average, and the degree of solvency for current obligations is above average. Table. 28.
Table 28 Analysis of the debtor's transactions by period
| Indicator name | As of 04/01/08 | As of 07/01/08 | As of 10/01/08 | As of 01/01/09 |
| Absolute liquidity ratio | — | — | — | X |
| Current ratio | — | X | — | — |
| The indicator of the security of the debtor's obligations with its assets | — | X | — | — |
| Degree of solvency for current obligations | — | X | — | — |
3.6.1 Test assignment on the topic “Identifying signs of fictitious bankruptcy”
The bankruptcy case of Remflot LLC was initiated in January 2008 at the request of the debtor. Table 29 shows the values of solvency indicators calculated for the period preceding the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings.
Exercise:
Based on the data presented, draw conclusions about the presence or absence of signs of fictitious bankruptcy and about the period of analysis of the debtor’s transactions to determine the signs of deliberate bankruptcy.
Table 29 Calculated coefficients of Remflot LLC
| Indicator name | As of 01/01/08 | As of 04/01/08 | As of 07/01/08 | As of 10/01/08 | As of 01/01/09 |
| Absolute liquidity ratio | 0,12 | 0,09 | 0,045 | 0,03 | 0,0045 |
| Current ratio | 1,8 | 1,65 | 0,9 | 0,75 | 0,6 |
| The indicator of the security of the debtor's obligations with its assets | 2,04 | 1,965 | 1,8 | 1,725 | 1,65 |
| Degree of solvency for current obligations | 3,3 | 3,6 | 8,55 | 9,15 | 10,05 |
3.8.1 Test assignment on the topic of assessing the probability of bankruptcy: domestic and international practice"
Using reporting data (Appendix 3.4), assess the likelihood of bankruptcy using various methods of assessing domestic and international practice. The amount of accumulated depreciation for calculating the Beaver coefficient was: at the beginning of the year 70,455 thousand rubles; at the end of the year 63,738 thousand rubles.