Home / Installments
Back
Published: 04/06/2020
0
4
- 1 Appointment of a temporary manager at the observation stage
- 2 Appointment of a temporary manager at the observation stage
- 3 Manager’s action plan in the observation procedure
- 4 Rights and obligations of arbitration managers
- 5 Arbitration manager and membership in the self-regulatory organization of arbitration managers
- 6 Remuneration of the interim manager
- 7 Expenses of the temporary manager
Appointment of a temporary manager at the observation stage
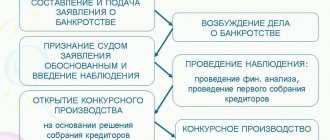
First, an application is submitted to the Arbitration Court to declare the debtor bankrupt.
This application indicates the name and address of the self-regulatory organization, from among whose members the arbitration manager must be selected.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrighten-GB
Next, the self-regulatory organization receives a ruling from the arbitration court to accept the application and provides the arbitration court with information about the candidacy of the arbitration manager.
After this, if the candidacy of the arbitration manager satisfies the established requirements, the arbitration court approves this candidate.
The activities of an arbitration manager can be divided into several stages.
Stage 1. Collection of information about the debtor.
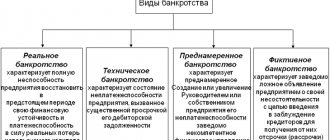
As part of the first stage, the main responsibility of the arbitration manager is to conduct an objective analysis of the financial status of the debtor for both legal entities and individuals. The arbitration manager checks the debtor's property assets, his activities and collects any other information necessary to make a decision. In addition, the arbitration manager is obliged to find out whether there are grounds to suspect the debtor of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy.
Stage 2. Notification of creditors.
At this stage, the bankruptcy trustee notifies creditors of the bankruptcy procedure. At the same time, the arbitration manager maintains a register of creditors, which takes into account all debt.
Stage 3. Drawing up an external management plan.
Stage 4. Meeting of creditors.
At this stage, the arbitration manager convenes the first meeting of creditors, at which the possibility of restoring the debtor's solvency is discussed and decisions are made between the creditor and the debtor. The meeting also discusses the external management plan or makes a decision to conduct bankruptcy proceedings.
Stage 5. Transfer of the approved plan to the court.
The plan for external administration or bankruptcy proceedings must be submitted to the arbitration court.
Stage 6. Court hearing and receipt of an arbitration court decision.
The arbitration court schedules a meeting at which the results of the arbitration manager’s activities are summed up and a determination is made on further actions in relation to the debtor.
Stage 7. Sale of the debtor's property.
The mechanism for appointing a temporary administrator is not defined in detail by law, which is why controversial situations often arise. Thus, it must begin its work simultaneously with the start of the observation procedure. But it is not entirely clear who should apply for his appointment: at this stage, not all creditors are aware of the beginning of the bankruptcy procedure, and the debtor is prohibited from indicating the candidacy of the manager.
Article 59 of the bankruptcy legislation provides for the following options for appointing a temporary manager:
- from among the candidates/SROs proposed by the creditors of the legal entity;
- from candidates registered with the court as managers, in the absence of proposals.
Since all creditors are not yet aware of the start of the insolvency procedure, any creditor, even those with small claims, can file a petition. As a result, the temporary manager often begins to act in the interests of the creditor who applied for his appointment. This in practice leads to abuse.
For your information
The observation procedure can last from three to five months. Accordingly, this is exactly the duration of work of this arbitration manager. It is therefore very important to appoint a manager as quickly as possible.
The following requirements apply to the candidacy of a temporary manager:
- no criminal record;
- non-participation in the management of the debtor company;
- non-bias in favor of the debtor or creditors.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytabouten-GB
The temporary manager begins to perform his duties until:
- appointment of a temporary/administrative manager;
- declaring the debtor bankrupt and moving to the stage of bankruptcy proceedings;
- a court decision approving a settlement agreement between creditors and the debtor;
- the arbitration decision to refuse to declare the debtor bankrupt.
The duties of a temporary manager arise from the peculiarities of the observational stage of bankruptcy of an enterprise. At this stage of observation, the company's management remains in place and continues to perform its official duties, but under the supervision of a professional manager. At the same time, certain restrictive measures are imposed on directors. Thus, they are prohibited from reorganizing the company, creating branches and representative offices.
The key goals of this observational stage, which determine the range of responsibilities of the manager, are:
- Organize the first creditors' meeting, which will resolve the most important tasks of the case on recognizing the financial insolvency of the debtor. The meeting must be held at least 10 days before the first court hearing in the case of declaring the insolvency of the enterprise.
- Compile a register of creditor claims in relation to a potential bankrupt. Consideration of the validity of complaints from the debtor about the illegality of including claims in the register.
- Analyze and evaluate the financial assets of a legal entity.
- Find the best ways to value assets.
In addition to these basic goals, the range of additional responsibilities of a temporary manager can include:
- determining the reasons for the impossibility of fulfilling one’s obligations;
- identifying the level of liquidity of the company’s property and assets;
- forecasting the return of the normal balance of payments when rehabilitation procedures are introduced at the enterprise: external management or recovery;
- assessing the market value of the enterprise as a complex;
- development of measures to restore solvency.
The observer should also analyze whether the company has signs of a fictitious bankruptcy. Indirect evidence of this fact is distorted financial statements, their absence; concealment of information about company-owned property; failure by a legal entity to take measures to collect receivables or assignment of rights to claim them on obviously unfavorable terms;
Information
The temporary manager is also obliged to monitor the work of the managers of the bankrupt enterprise. If management interferes with the normal performance of duties by the manager, then he must report the situation to the court and demand the temporary removal of management. Such a petition can be filed when management conceals documents, enters into transactions without the consent of the supervisor, etc.
When identifying signs of fictitious/deliberate bankruptcy, the observer assesses the possibility of bringing managers to subsidiary liability.
After completing the observation stage of insolvency, the temporary manager must provide reporting documentation to the court and the creditors' meeting. It should contain information about the results of work and information about the current financial situation of the debtor. In addition, the reporting must contain indications of the measures taken by the debtor to repay the debt.
Information
The manager’s tasks include developing a set of measures to restore the solvency of a legal entity, which are embodied in reporting.
The report reflects the following information:
- comprehensive financial analysis of the enterprise, assessment of investment and economic areas of work;
- measures taken to ensure the safety of property and identify creditors;
- petitions and statements presented to the court during bankruptcy proceedings;
- conclusion on identifying facts of deliberate/fictitious bankruptcy (if any);
- current list of creditor claims;
- minutes of the first and subsequent creditor meetings;
- justification for the possibility or impossibility of restoring the balance of payments;
- recommendations on the introduction of one or another bankruptcy procedure;
- other information about the performance of their duties.
Unlawful actions of a temporary manager or improper performance of his professional duties may be appealed in court. The complaint can be filed by the management of the enterprise, creditors or the Tax Inspectorate. If the complaint is satisfied, the manager may be subject to one of the penalties or removed.
Important
Not all actions of the observer can be appealed, but only those that violated the legal rights and interests of the plaintiffs in the bankruptcy case, provoked losses for creditors or worsened the financial position of the legal entity.
Thus, observation can be considered as a preliminary stage of the bankruptcy procedure. At this stage, the manager must form an objective picture of the financial situation at the enterprise and protect property from illegal withdrawal.
Procedure[ | ]
Monitoring is introduced from the date the arbitration court accepts the creditors' application for proceedings or based on the result of the arbitration court's consideration of the validity of the applicant's claims. Main content of observation:
- ensuring the safety of property
- compiling a register of creditors' claims
- holding the first meeting of creditors
The execution of enforcement documents on property penalties is also suspended; the allocation of the share of one of the shareholders of a legal entity is prohibited; a temporary manager is appointed; It is prohibited for the bodies of a legal entity to make a decision on the bankruptcy of a legal entity, etc.
In Art. 71 of the Bankruptcy Law 2002 provides that, for the purpose of participating in the first meeting of creditors, creditors have the right to present their claims against the debtor within 30 days from the date of publication of the notice of the introduction of the monitoring procedure. If creditors have filed claims against the debtor after 30 days from the date of publication of the notice about the introduction of the monitoring procedure, then these claims are subject to consideration by the arbitration court after the introduction of the bankruptcy procedure following the monitoring procedure. [1] In turn, the debtor has the right to submit his objections within 15 days from the date of expiration of the period for filing claims on the claims of creditors.
Having considered the claims presented by creditors, the arbitration court establishes the grounds for including these claims in the register of creditors and makes a ruling on inclusion or refusal to include the claims in the register of creditors' claims. In accordance with Article 72 of the Bankruptcy Law, the temporary manager sets the date for the first meeting of creditors and notifies all identified bankruptcy creditors, authorized bodies, representatives of the debtor's employees, as well as other persons who have the right to participate in the meeting of creditors. It should be taken into account that the first meeting of creditors must take place no later than 10 days before the end date of the observation procedure.[2]
At the first meeting of creditors the following issues are resolved:
- making a decision on introducing financial recovery and filing a corresponding petition with the arbitration court;
- making a decision on introducing external management and filing a corresponding petition with the arbitration court;
- making a decision to apply to the arbitration court with a petition to declare the debtor bankrupt and to open bankruptcy proceedings;
- formation of a creditors’ committee, determination of the quantitative composition and powers of the creditors’ committee, election of members of the creditors’ committee;
- determination of additional requirements for candidates for an administrative manager, external manager, or bankruptcy trustee;
- determining the candidacy of an arbitration manager or a self-regulatory organization from among whose members the arbitration manager should be approved;
- selection of a registrar from among registrars accredited by a self-regulatory organization;
- resolving other issues provided for by the Insolvency Law.
Appointment of a temporary manager at the observation stage
The responsibility of the temporary manager for failure to perform/improper performance of his professional duties may be expressed in his removal. This procedure is carried out at the initiative of the participants in the bankruptcy case. After the relevant determination is made (even if it is appealed), the manager is not subject to reinstatement.
The legislation also provides for other liability measures that may be applied to the manager:
- His exclusion from the SRO, which is designed to monitor the professional level of its members.
- Application of liability measures in the form of disqualification with publication of the corresponding mark in the Federal Register.
- Compensation for losses caused to the debtor and creditors.
- Additional measures of property liability.
- Criminal and administrative liability for causing damage on a large scale.
Manager's action plan in the observation procedure
After the temporary manager starts work, he needs to develop a list of activities that he plans to implement within the time allotted to him. Typically they are listed with a time frame for their implementation. The plan may include the following tasks:
- Analysis of financial statements for the last three years.
- Analysis of enterprise transactions completed over the past three years, taking into account the market conditions in which they were concluded.
- Inventory and valuation of legal entity assets.
- Analysis of the circle of counterparties of a legal entity, search among them for unreliable and fly-by-night companies, offshore companies.
- Analysis of the legality of creditors' claims received at this stage.
Also in his final report, the interim manager develops a brief action plan for the future, based on the results obtained during the analysis.
– external manager (the external management procedure is carried out). The main goal at this stage is to restore the debtor’s solvency. An external manager is an arbitration manager who actually manages the debtor after the introduction of external management. The peculiarity of this procedure is that the debtor’s previous management is removed from work. External manager:
- maintains a register of creditors' claims;
- develops an external management plan;
- maintains accounting, financial and statistical reports;
– administrative manager (the financial recovery procedure is being carried out). At the stage of financial recovery, the main function of the arbitration manager is the controlling function. The arbitration manager maintains a register of creditors' claims, monitors the implementation of the financial recovery plan, the debt repayment schedule, and the transfer of funds to creditors;
– temporary manager (observation procedure is being carried out). At the stage of the monitoring procedure, the arbitration manager is obliged to find out whether it is possible to improve the financial affairs of the debtor and restore his solvency;
– financial manager (bankruptcy procedures for citizens are carried out);
– bankruptcy trustee (the bankruptcy procedure is being carried out). The bankruptcy trustee manages the debtor. In the status of a bankruptcy trustee, the arbitration manager has the right:
- dispose of the debtor's property;
- dismiss employees;
- search, identify and return the debtor’s property, which is in the possession of third parties;
- demand repayment of debt to the debtor.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsen-GB
The responsibility of the arbitration manager in a bankruptcy case is provided for by the Law “On Bankruptcy”, as well as the Code of Administrative Offenses and, in some cases, the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Measures aimed at bringing the arbitration manager to account can be divided into categories.
- Suspension. Such a measure may be applied in the event of non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of the duties assigned to the insolvency administrator.
- Administrative responsibility. The basis for administrative liability may be concealment of property, information about property or its size.
- Criminal liability. In some cases, falsification of accounting or other accounting documents, alienation or destruction of property falls under criminal liability.
Bankruptcy and external surveillance
Temporary bankruptcy implies external administrative management if there is a high amount of accounts payable. The temporary stage of monitoring involves ensuring the storage of the debtor’s property and conducting analytics and accounting of his finances. Also attached to the bankruptcy case is a list of claims of all creditors. If, based on the results of observation, the possibility of restoring the solvency of a legal entity is discovered, the court at this stage may decide:
- carry out debt restructuring;
- draw up a debt repayment schedule.
The head of the company does not have the right to independently make decisions that could increase the debt without a meeting of creditors. There is an approved procedure for not charging fines, penalties and penalties, as well as other financial sanctions for improper fulfillment of payment obligations, except for current ones. This stage can last about two years. Temporary supervision in bankruptcy allows you to ensure the rights and guarantees of all parties and help resolve a difficult financial situation (with the exception of fictitious bankruptcy).
Rights and obligations of arbitration managers
The list of rights of a temporary manager includes:
- Submit to the court demands for recognition of transactions concluded by a legal entity as invalid, fictitious or void and their cancellation. We are talking about contracts concluded in violation of the requirements of 127-FZ. For example, those concluded with interdependent persons and on non-market conditions. Essentially, their goal is to deliberately worsen the financial situation of the debtor and withdraw assets.
- Coordinate the conclusion of certain transactions with the management of the bankrupt company. Agreements that require approval include transactions for the disposal of real estate, property with a price of more than 10% of the book value of all assets of the debtor legal entity, transfer of property into trust management; obtaining new loans and borrowings; on obtaining bank and government guarantees; attracting guarantors; assignment agreements.
- If the debtor enters into deliberately unprofitable transactions and management fails to take the necessary measures to restore the balance of payments, the temporary manager has the right to petition for the removal of the company's management from business.
- Request any information from the managers of a legal entity, including information that constitutes a trade secret. For example, information about property rights and obligations, etc. If management refuses to provide such documents, the manager can forcefully demand them in court. The observer also has the right to request the information he needs from the debtor’s counterparties when destroying primary documentation at the debtor enterprise.
- Appeal against unlawful claims of creditors.
- Take additional measures to ensure the safety of property.
The arbitration manager has the following rights:
- receive remuneration for your activities in accordance with current legislation;
- convene a meeting of creditors;
- apply to the arbitration court with demands and petitions;
- engage third parties or competent specialists to perform their duties, unless this contravenes the insolvency law;
- submit a petition for removal from the bankruptcy case to the court.
The responsibilities of the arbitration manager are as follows:
- analyze the financial activities of the debtor;
- draw up a register of creditors;
- identify signs of deliberate or fictitious bankruptcy, and if they are detected, report to the court about the identified offenses;
- protect the debtor's property;
- maintain the confidentiality of information that was obtained during the bankruptcy procedure while working with the debtor.
Consequences of the observation procedure
The consequences of introducing a monitoring procedure occur immediately after the court makes a decision on its appointment. They are defined by Article 63 of Federal Law No. 127. From the moment of introduction of supervision, a legal entity with debts loses its right to any transformation of the civil legal form, merger or division. All claims for debts of creditors can be brought upon the commencement of the procedure only in accordance with the procedure established by Article 134 of Federal Law No. 127.
All previously issued orders for the collection of the debtor’s property lose legal force. During the observation stage, encumbrances on property imposed as part of enforcement proceedings are removed. The work of bailiffs at this stage of bankruptcy ceases. During this period of insolvency, all creditors must have time to submit an application to the court to be included in the register, according to which their financial and property claims will be repaid.
The bankruptcy procedure requires very strict adherence to the deadlines specified by law. Creditors must have time to present their claims to the debtor no later than 30 days from the date of the court’s decision to introduce the procedure. The deadline for accepting objections to creditors' claims is 15 calendar days from the date of their presentation. At this stage, creditors, together with the interim manager, are the center of decision-making. The opinion of the founders of the bankrupt company in this situation is not decisive.
You cannot pay off a debt through mutual settlements, bypassing the repayment schedule approved by the court. New seizures of property of a legal entity are carried out only within the framework of the procedure established by law. Dividend payments are frozen. The sale of shares and property of a bankrupt is prohibited. A moratorium is imposed on the accrual of penalties and fines for late payments.
Arbitration manager and membership in the self-regulatory organization of arbitration managers
An arbitration manager - a citizen of the Russian Federation must be a member of only one of the self-regulatory organizations of arbitration managers (SRO).
To become a member of a self-regulatory organization of arbitration managers, an arbitration manager must meet the requirements that are established by the relevant organization of arbitration managers for each of its members, namely:
- presence of a positive result in passing the theoretical exam in the training program for arbitration managers;
- having at least 1 year of experience in management positions and at least 2 years of internship as an assistant to an arbitration manager in a bankruptcy case;
- availability of higher professional education;
- no criminal record for committing an intentional crime;
- absence of punishment in the form of disqualification for committing an administrative offense or in the form of deprivation of the right to occupy certain positions or engage in certain activities for committing a crime;
- not be excluded from the self-regulatory organization and arbitration managers for 3 years before submitting an application for membership;
- availability of timely and full payment of membership and other fees established by the self-regulatory organization of arbitration managers, including contributions to the compensation fund;
- availability of a compulsory liability insurance agreement.
In addition, the bankruptcy creditor, who is the applicant in the bankruptcy case, or the meeting of creditors has the right to present the following additional requirements to the candidacy of the arbitration manager carrying out the bankruptcy procedure, namely:
- having a certain amount of work experience as heads of organizations in the relevant sector of the economy;
- carrying out as an arbitration manager a certain number of procedures applied in a bankruptcy case;
- having a higher legal or economic education or education in a specialty corresponding to the debtor’s field of activity.
Interim manager's remuneration
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseen-GB
Based on the results of the observation stage of bankruptcy of a legal entity, the temporary manager has the right to receive remuneration for his work. It consists of the salary fixed by law, as well as accrued interest. Payments of remuneration are made from the debtor's funds and are made out of turn (before paying off creditor claims).
Information
The salary of an arbitration manager is specified in
127-FZ on bankruptcy
. Today it is set at 30 thousand rubles. monthly. The fixed part of the remuneration may be increased by a court decision at the request of creditors or other participants in the process. But such a decision can be appealed.
If the temporary manager resigns early, payments stop. When calculating the percentage of the manager's remuneration, it is calculated based on the book value of the debtor's assets and is:
- 4% for asset value up to 250 thousand rubles;
- 10000 rub. 2% - with an asset value of 250 thousand rubles. up to 1 million rubles;
- 25000 rub. 1% - if the value of assets is more than 1 million rubles;
- 45000 rub. 0.5% - for a cost over 3 million rubles.
Temporary manager's expenses
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressen-GB
In addition to remuneration, the temporary manager can count on compensation for expenses incurred during the supervision procedure. Moreover, such expenditure transactions must be economically justified and documented. Compensation is due to the manager if he was not removed from the business for improper performance of his duties.
The expenses incurred by the arbitration manager during the bankruptcy procedure are recovered from the debtor's funds. These may include costs for publishing information in the Federal Register, paying for the services of hired specialists, legal costs, organizing creditor meetings, etc.
End of the procedure
Observation ends from the date of commencement of financial recovery, external management, recognition of a legal entity as bankrupt by an arbitration court and the opening of bankruptcy proceedings or the adoption of a settlement agreement. At the same time, a certain period has been established during which the observation ends - 7 months from the date the court accepted the application for bankruptcy.
| ||||||||