What it is?
Bankruptcy prevention is a set of measures whose main goal is to prevent financial collapse. During the implementation of a plan to save an organization from collapse, all possible methods developed by specialists are used.
Control and combating the insolvency of business entities is regulated by the legislation in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
It is very important to determine the reasons and dominant factors that influenced the solvency of representatives of small, large and medium-sized businesses.
Then it will be possible to take the necessary measures to prevent bankruptcy of credit institutions and other business entities.
After this, it will be possible to choose the most effective strategy for the further development of the company, which will help it not only get out of the crisis and begin economic growth.
External control
External management is reflected in the sixth chapter of the insolvency law. This process of stabilizing the economic situation of the company involves the removal of persons involved in the management of the company from their duties and the redirection of their powers to an external manager approved by the court.
External management is approved by the judicial authority through a petition from a meeting of lenders for a temporary period of up to 18 months. If such a need arises, the period of this process can be extended by another 6 months. During this time period, the manager draws up a plan of actions necessary to restore solvency, which must be approved by a meeting of lenders. The purpose of this planning is to restore the company's stable, solvent financial position.
In addition to the implementation of the external management plan, the resumption of stable activity of the debtor enterprise is facilitated by the introduction of a moratorium on the debtor’s fulfillment of obligations to lenders.
There are special organizations that are included in the register approved at the federal level, operating in areas of strategic importance for the country, for example, in the military-industrial complex.
To prevent their bankruptcy in accordance with Article 91 of the Federal Law on Insolvency, the Russian government promotes the implementation of the following measures:
- Analysis of the solvency and economic situation of the enterprise.
- Implementation of company reorganization.
- Restructuring of debt for tax payments, government fees. budget and payments to extra-budgetary funds.
- Rehabilitation before the judicial stage.
- Finding ways (including issuing a state guarantee) to implement an agreement between these enterprises and their lenders on restructuring the accumulated debt.
- Repayment of government debt authorities to enterprises operating in the field of state defense procurement, if the resulting insolvency arose for this reason.
- Other measures.
External control is approved in a lawsuit. To prevent the insolvency of these enterprises, in accordance with Article 189.9 of the same law, the following measures are being implemented:
- financial recovery of the company at the pre-trial stage;
- approval of the temporary administration, in addition to situations that are interconnected with the deprivation of licenses to perform banking operations.
- implementation of enterprise reorganization;
- an event that is being implemented jointly with the Deposit Insurance Agency, which assumes the obligations of a bankruptcy trustee in situations of insolvency of credit companies.
All of the above measures must be carried out before the license to carry out banking operations is revoked.
Thus, destabilization of the financial position of an enterprise is not an unsolvable situation. There are numerous methods for improving the solvency of a company, including at the stage after the start of litigation. Lawyers and financial advisors can offer significant assistance in such a situation.
Modeling
The modeling method is most often used by specialists who make forecasts for the financial development of representatives of small, large and medium-sized businesses. In the process of conducting research, only verified facts are used, which are subject to detailed analysis.
To carry out these surveys, special software is used, and the following techniques can also be used: statistics and mathematical models.
The modeling method allows you to analyze a large amount of data obtained from the demographic, economic and social spheres.
Based on the results of the analytical and research work, specialists are able to choose directions for the company’s further development, make a forecast, and also predict the behavior of certain individuals whose actions could cause financial collapse.
Financial recovery
Financial recovery is regulated by the fifth chapter of the Federal Law “On Bankruptcy”. The start of the process of improving the financial condition of the enterprise is decided by a meeting of lenders and approved in court. Also, representatives of the debtor company can send a petition for its implementation.
A mandatory procedure for starting this process is the formation of planned actions and a debt payment schedule. This documentation is approved at a meeting of lenders. The financial recovery of a debt-ridden enterprise can last no more than two years.
An important feature of the procedure is the limitation of the actions of the managers of the debtor company. An arbitration manager is appointed in court, and candidates for this position are considered at a meeting of lenders.
If the managers of a debt-ridden company do not carry out the planned financial recovery actions, then, based on a decision of a meeting of lenders or an arbitration manager, they may be deprived of management rights in court.
Enterprise managers, without the consent of the meeting of lenders, do not have the right to:
- carry out transactions in which they have an interest, or transactions that involve the acquisition of more than five percent of the value of the assets of the debtor enterprise or involve the provision of guarantees, loans, or the transfer of the debtor’s property into trust;
- carry out procedures that entail additional obligations if the debts generated after the implementation of the process of financial rehabilitation of the company have reached twenty percent of the amount reflected in the list of claims against the debtor.
In addition, without the approval of lenders and persons providing security for debt obligations, managers do not have the right to implement the reorganization of the enterprise. And they also do not have the right to enter into transactions related to:
- provision of financial resources to the debtor company;
- with the transfer of debt or transfer of rights of claim;
- with the acquisition or alienation of property (in addition to the sale of products);
- with a loan debt of more than 5% of the share of the amount reflected in the list of requirements for debtors at the time of the start of the recovery process.
Extrapolation
It is advisable to use this method in cases where the cause of bankruptcy of a business entity is caused by instability of the financial market or an unfavorable political microclimate in the country.
Using the extrapolation method, experts give a forecast regarding the financial viability of a company for a short period of time. In the process of collecting and analyzing information, statistics are created, the indicators of which change under the influence of various external factors.
See this article for a sample register of creditors during liquidation.
What requirements must be observed when liquidating a company with debts? Read at this address.
Features of the problem of bankruptcy of enterprises in Russia
The problem of bankruptcy of enterprises can be called very relevant in the Russian economy due to huge mutual non-payments, wage arrears, etc. The prerequisites for these problems include the wrong strategy of the enterprise and the poor performance of the crisis management system.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Methods of preventing bankruptcy of enterprises 420 rub.
- Abstract Methods for preventing bankruptcy of enterprises 280 rub.
- Test work Methods for preventing bankruptcy of enterprises 220 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Let us note the strong differentiation of the situation depending on the industry of the enterprise:
- a significant increase in the maximum number of bankruptcies in the construction and mechanical engineering sectors;
- reducing the number of bankruptcies in the food production, forestry and agriculture sectors, as well as the electric power industry;
- The largest bankruptcies in terms of revenue are from the trade sector.
Note 1
Among the main reasons for the increase in the number of bankruptcies in recent years, experts cite the stagnation of effective demand and the slowdown in the recovery of investment activity. Based on Russian statistics, starting from 2020 to this day, more enterprises have been liquidated than new ones are registered.
Factors influencing the number of business bankruptcies:
- Cost of lending for business representatives.
- Changes in the income that the population actually has.
- The rate of change in investment demand in the country as a whole.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
The increase in the number of bankrupt enterprises is a negative indicator that makes people reluctant to engage in entrepreneurship and open new jobs.
Sanitation
The procedure, during which financial insolvency is prevented by the method of reorganization, is regulated by the Federal legislation of Russia. An appeal is sent to the owner of the organization that he must take measures to prevent bankruptcy and normalize the financial situation.
It is worth noting that government bodies cannot exert any pressure on a business entity, despite the fact that the reorganization method is a mandatory norm for preventing bankruptcy.
The rehabilitation method, legislation in force on the territory of the Russian Federation, allows the use of the following persons and representatives of small, large and medium-sized businesses:
- founders of enterprises of any form of ownership;
- unitary organizations that legally own the debtor’s property;
- creditors (both private financial institutions and banking institutions);
- legal entities and individuals capable of preventing the bankruptcy of companies and restoring its solvency.
The main advantage of this method of preventing bankruptcy is the possibility of applying reorganization at any stage of consideration of this issue.
Rehabilitation can be provided to Russian companies (Article 575 of the Civil Code in force in Russia and Article 3 of the Federal Law) in a certain amount, which is determined based on the requirements of creditors.
When making calculations, authorized persons take into account the enterprise’s need for funds, which will be spent on repaying debts to the budget, suppliers and contractors, as well as on paying current expenses.
Rehabilitation can be provided to business entities at the stage of bankruptcy (the corresponding legal procedure is carried out until the bankruptcy case is closed in court) in two ways:
- as return assistance;
- on a non-refundable basis.
1.3 Criteria for the need for rehabilitation
The Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” specifies three, as it were, equal measures that should prevent the bankruptcy of an organization: financial recovery; appointment of a temporary administration; reorganization. According to this undifferentiated approach, the criteria under which an organization will be considered in need of financial rehabilitation (rehabilitation) are, in principle, the same as in cases when a temporary administration may be sent to it or when a requirement for reorganization may be presented to it, and also contradictory.
— introduction of new forms and methods of management;
— conversion, diversification, transition to the production of new products, improving their quality;
— increasing marketing efficiency;
— reduction of production costs;
— reduction of receivables and payables;
— increasing the share of own funds in current assets through part of the consumption fund (especially funds allocated for the payment of dividends) and the sale of short-term financial investments;
— sale of excess equipment, materials, work in progress, finished products, as well as subsidiaries and shares in the capital of other enterprises;
— temporary stop of capital construction;
— debt conversion by converting short-term debt into long-term debt;
— expansion of exports;
- reduction in the number of employees, etc. When assessing the financial condition of enterprises and establishing the balance sheet structure, an analysis of the financial condition is carried out, the purpose of which is to determine the degree of its solvency based on the balance sheet structure. [12]
— provision of financial assistance to the organization by its founders (participants) and other persons;
— change in the structure of the organization’s assets and liabilities;
— change in organizational structure;
other measures carried out in accordance with laws.
If there are grounds for reorganization, the manager, based on an analysis of the financial condition and solvency of the debtor, must develop a reorganization plan and submit it for approval to the meeting of creditors no later than seventy days from the date of his appointment.
The rehabilitation plan must provide for measures to restore the debtor's solvency and the period for its restoration.
The debtor's solvency is recognized as restored in the absence of grounds for initiating bankruptcy proceedings established by Article 41 of the Law “On Economic Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”.
If there are no grounds for reorganizing the debtor, the manager develops a plan for liquidating the debtor - a legal entity or a plan for terminating the activities of the debtor - an individual entrepreneur and releasing him from debts (hereinafter referred to as the liquidation plan) within the period provided for in part one of this article.
We invite you to read: Nuances of bankruptcy of individual entrepreneurs with tax debts
The manager can develop both an alternative reorganization plan and a liquidation plan.
The reorganization plan and liquidation plan include a conclusion on the financial condition and solvency of the debtor. [15]
The reorganization plan and (or) liquidation plan are considered at a meeting of creditors, which is convened by the manager no later than eighty days from the date of publication of the notice on the opening of bankruptcy proceedings. The manager notifies all creditors in writing of the date and place of the meeting of creditors and provides them with the opportunity to familiarize themselves with the reorganization plan and (or) liquidation plan at least ten days before the date of the said meeting.
The reorganization plan or liquidation plan approved by the meeting of creditors, as well as the minutes of the meeting of creditors, are submitted by the manager to the economic court no later than five days from the date of the meeting of creditors.
In the event that a meeting of creditors makes a decision to approve a reorganization plan or a liquidation plan, which provides for a reorganization or liquidation period exceeding the originally established one, the economic court extends the reorganization or liquidation period if there are sufficient grounds to believe that the extension of the reorganization or liquidation period will lead to to restore the debtor's solvency or increase the total amount of satisfied creditors' claims.
Rehabilitation is introduced by the economic court on the basis of a decision of a meeting of creditors or on its own initiative in cases provided for by this legislation.
The decision of the economic court on reorganization is subject to immediate execution.
Rehabilitation is introduced for a period not exceeding eighteen months from the date of the decision to carry it out. [eleven]
The reasons for the insolvency of an enterprise can be both objective and subjective: unprofessional management, worn-out equipment, falling demand for manufactured products, losses, disproportionate consumption fund, diversion of funds into short-term financial investments, incorrect choice of forms of non-cash payments, large accounts receivable and payable, etc. .
2 Analysis of financial condition
2.1 Organizational and economic characteristics of OJSC GAZ
Open Joint Stock Company "GAZ" (hereinafter "GAZ OJSC" or "Company") is a legal entity operating in accordance with the Charter approved by the State Property Committee of the Russian Federation dated November 26, 1992 No. 913-R, registered by the Resolution of the head of the Avtozavodsky district of Nizhny Novgorod, decision dated December 21, 1992 No. 2614-R. The authorized capital of the enterprise is 1,000,000 rubles.
The main activity of OJSC GAZ is the production and sale of trucks and cars, automotive components and assemblies, spare parts, consumer goods and other products.
Table 1
Type of products of OJSC "GAZ"
| Indicator name | Unit | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
| change | ||||
| Revenue from the sale of goods, products, works, services – total | million rubles | 508,90 | 29 131,00 | 34 026,90 |
| Trucks | million rubles | 119,80 | 15 147,30 | 17 968,30 |
| % of total revenue | % | 40,2 | 41,3 | 38,5 |
| Passenger cars | million rubles | 8 064,20 | 7 644,40 | 10 214,30 |
| % of total revenue | % | 40,3 | 39,2 | 42,4 |
| Buses | million rubles | 5 324,90 | 6 339,30 | 5 844,30 |
| % of total revenue | % | 19,5 | 19,5 | 19,1 |
The company also owns a number of social facilities. In accordance with the agreement between the management of GAZ OJSC and the administration of Nizhny Novgorod, the housing stock and local roads were transferred to the municipal balance in 2007. This caused a significant reduction in the Company's social costs.
In 2008, OJSC GAZ produced commercial products totaling 24.4 billion rubles. Sales volume amounted to 25.7 billion rubles. 191.5 thousand cars were assembled, 198.6 thousand cars were sold, of which 318 were shipped for export.
In 2008, the total number of vehicles sold decreased by 10% compared to the level of 2007, including trucks by 5% and cars by 29%. The number of buses sold increased by 34%.
The production facilities of OJSC GAZ are characterized by a high degree of physical and moral wear and tear. Thus, the share of technological equipment older than 20 years is 57.8%.
The total investment in 2008 amounted to 1.2 billion rubles. In 2010, investments are expected to grow to 1.4 billion rubles. The company is actively engaged in the modernization of manufactured cars, restyled versions of which will be presented on the market in the near future.
The company has also allocated significant funds for scientific, technical and development projects. During the reporting period, 0.8 billion rubles were spent for these purposes.
The tightening of the conditions for the import of used foreign-made cars into Russia, as envisaged by the Government of the Russian Federation, will have a favorable effect on the market conditions of the Company's main products.
The total amount of payments for environmental pollution amounted to 819,022 thousand rubles. At the same time, no penalties were imposed on the Company for violation of environmental legislation in 2008.
In 2008, the average number of employees of the Company was 85.9 thousand people, which is 19.9% less than last year, of which industrial and production personnel amounted to 79.8 thousand people.
In the reporting year, GAZ OJSC allocated 3.4 billion rubles to pay for labor. At the same time, the average monthly salary increased by 62% and amounted to 13,324 rubles.
The general management of the Company’s activities is carried out by the Board of Directors, an executive body elected by the general annual meeting of shareholders, whose competence includes determining the priority areas of the Company’s activities.
2.2 General assessment of the property and financial condition of OJSC GAZ
To carry out the analysis of GAZ OJSC, an analytical balance sheet should be drawn up for aggregated items. (Annex 1)
Based on the comparative analytical balance, the following important criteria for the financial condition of the enterprise can be determined.
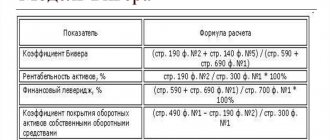
Firstly, the total value of the enterprise’s property, which is equal to the balance sheet currency at the beginning and end of the analyzed period. At the beginning of the reporting period, this figure was 24417677.0 thousand rubles, at the end of the period - 42426625.0 thousand rubles, change - 18008948.0 thousand rubles, or 73.754% of their value at the beginning of the period.
Secondly, the value of the immobilized property of the enterprise, equal to the total of the section - non-current assets. At the beginning of the reporting period, this figure was 21443625.0 thousand rubles, at the end of the period - 34229149.0 thousand rubles, change - 12785524.0 thousand rubles. or 59.624% of their value at the beginning of the period.
Thirdly, the cost of mobile (current) assets. At the beginning of the reporting period, this figure was 2974052.0 thousand rubles, at the end of the period - 8197476.0 thousand rubles, change - 5223424.0 thousand rubles. or 175.633% of their value at the beginning of the period.
Fourthly, the cost of inventories. At the beginning of the reporting period, this figure was 1112705.0 thousand rubles, at the end of the period - 1466805.0 thousand rubles, change - 354100.0 thousand rubles. or 31.823% to their value at the beginning of the period.
We invite you to read: Life after bankruptcy: what is possible and what is not
Methods for preventing bankruptcy in organizations of strategic importance
Federal Russian legislation (Article 191 of the Federal Law) regulates the procedure for preventing financial collapse in strategic enterprises and organizations.
The Government of the Russian Federation assumes responsibility for preventing the bankruptcy of such business entities.
They carry out a certain set of measures (first of all, a detailed analysis of the financial condition of the organization is carried out, an audit of its assets is carried out and solvency is determined):
- a decision is made regarding the reorganization of the enterprise;
- reorganization is carried out (pre-trial) or other financial methods are used;
- repays debt incurred on completed government orders (both industrial and defense);
- carries out a reorganization of the organization's tax obligations that arose in the course of its economic activities to regulatory authorities, extra-budgetary funds and the federal budget;
- acts as an intermediary between the enterprise’s creditors, and, if necessary, provides government guarantees regarding debt payment, etc.
Find out whether liquidation through an offshore company is considered the most legal alternative method, or does it have its disadvantages? What are the obligations for the retention period of documents after the liquidation of an LLC, read here.
What is the procedure for liquidation by merger? Details in this article.
Measures to prevent bankruptcy
The bankruptcy procedure does not mean that the company will necessarily be liquidated.
The law provides for measures aimed at preventing bankruptcy or, in other words, recovery procedures.
Their timely application can change the financial situation of the debtor.
Credit organizations
The insolvency procedure of credit institutions ends with the revocation of the license to carry out the relevant activity.
To avoid this situation, the following measures can be taken:
- appointment of a temporary administration;
- financial recovery;
- reorganization.
These measures can be applied by a credit institution (except for the appointed temporary administration) or the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation has the right to demand that a credit institution develop and implement a plan for implementing financial recovery.
Such a plan may include:
- cost-cutting measures;
- measures to obtain additional expenses;
- assessment of the general financial condition of the credit institution;
- measures aimed at changing the organizational structure, etc.
Measures aimed at preventing bank bankruptcy are regulated by paragraph 4.1 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”.
Enterprises
The Bankruptcy Law establishes that timely measures must be taken in relation to enterprises to prevent the onset of their insolvency.
Such measures include:
- providing financial assistance;
- change in the composition and structure of management bodies;
- collection of accounts receivable;
- attracting investments;
- assistance in reaching agreements between the debtor and his creditors;
- provision of credits, loans and other types of financial support;
- application of the enterprise reorganization procedure.
Measures to prevent bankruptcy of an enterprise are aimed at creating effective management of its finances and production, developing strategic goals and methods for their implementation.