Financial policy concept
The strengthening and distribution of power, based on relations between national and social groups, as well as classes, is called politics.
Politics penetrates into all spheres of human life. It can be social and financial, international and municipal, protectionist, monetarist, cultural, military, and so on. Note 1
Financial policy is a set of measures aimed at the most efficient use of financial reserves and assets.
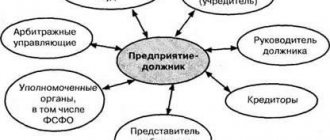
The subjects of financial policy are government bodies with appropriate powers. The objects are the relationships that develop regarding the turnover of finances. Functionally, financial policy is designed to perform the following tasks:
- Maintain the stability of the national currency.
- Ensure that the interests of all parties in the relationship are respected.
- Maintain the required budget level.
The impact on the financial system can be direct or indirect. The direct impact is licensing procedures, creating consistency in the work of budgetary, tax, monetary and investment policies. Indirect influence is exerted through the maintenance of fair competition and a set of mutual settlements between the participants in the relationship.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework Beaver's Scorecard 440 rub.
- Abstract Beaver Scorecard 260 rub.
- Test work Beaver's system of indicators 190 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
There are neoclassical, classical, monetarist, planned and regulatory approaches to the implementation of financial policy. In general, it exists to ensure the stability and independence of a business entity. If we are talking about a country, then financial policy helps support macroeconomic growth and economic development.
Forecasting the probability of bankruptcy based on the Beaver model
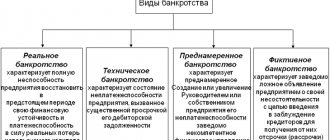
The probability of bankruptcy of an enterprise is one of the estimated characteristics of the current state and situation at the enterprise under study. By conducting a probability analysis on a monthly basis, the management of an enterprise can constantly maintain the probability at a low level. Well-known financial analyst William Beaver proposed his system of indicators for assessing the financial condition of an enterprise in order to determine the likelihood of bankruptcy - a five-factor model.
Table 13 – Beaver indicators
| Coefficient | Calculation formula | Probability of bankruptcy: |
| Beaver coefficient | (Net profit + Depreciation) / Average debt capital = (Page 2400 Form 2 + Line 5640 Form 5) / (Page 1400 Form 1 + Line 1500 Form 1) | insignificant - 0.4-0.45 (prosperous companies) average - less than 0.17 (5 years before bankruptcy) high (within the next year) - (-0.15) |
| Current ratio | Average value of current assets / (Most urgent liabilities (P1) + Short-term liabilities (P2)) = Page. 1200 Form 1 / (Page 1520 Form 1 + Page 1510 Form 1 + Page 1550 Form 1) | insignificant - less than 3.2 (prosperous companies) average - less than 2 (5 years before bankruptcy) high (within the next year) - less than 1 |
| Economic profitability ratio, % | Net Income / Average Asset Value = Page 2400 Form 2 / Page 1600 Form 1 | insignificant - 0.6-0.8 (prosperous companies) average - less than 0.4 (5 years before bankruptcy) high (within the next year) - (-0.22) |
| Financial leverage, % | Average cost of borrowed capital / Average cost of liabilities = (Page 1400 Form 1 + Page 1500 Form 1) / Page 1700 Form 1 | insignificant - 0.37 (prosperous companies) average - less than 0.5 (5 years before bankruptcy) high (within the next year) - less than 0.8 |
| Asset coverage ratio with own working capital | (Equity - Non-current assets) / Average value of assets = (Page 1300 Form 1 - Page 1100 Form 1) / Page. 1600 Form 1 | insignificant - 0.4 (prosperous companies) average - less than 0.3 (5 years before bankruptcy) high (within the next year) - less than 0.06 |
Weighting coefficients for indicators are not provided in W. Beaver’s model and the final bankruptcy probability coefficient is not calculated. The obtained values of these indicators are compared with their standard values for three states of the company, calculated by W. Beaver for prosperous companies, for companies that went bankrupt within a year, and for companies that became bankrupt within five years.
Table 14 – Beaver indicators
| Coefficient | For the beginning of the year | At the end of the year | Absolute change, (+,-) | Relative change, % |
| Beaver coefficient | ||||
| Current ratio | ||||
| Economic profitability ratio, % | ||||
| Financial leverage, % | ||||
| Asset coverage ratio with own working capital |
Diagnosis of the probability of bankruptcy of an enterprise using the Altman technique.
The degree of proximity of an enterprise to bankruptcy is determined using the methodology proposed specifically for Russian enterprises (Altman’s Z-score):
ZI = 8.38K1 + K2 + 0.054K3 + 0.64K4, (1)
where K1 is own working capital / assets ((Page 1300 Form 1 - line 1100 Form 1) / Page 1600 Form 1);
K2 - net profit / equity (Page 2400 Form 2 / Page 1300 Form 1);
K3 - revenue / assets (Page 2110 Form 2 / Page 1600 Form 1);
K4 - net profit / cost of production (Page 2400 Form 2 / Page 2120 Form 2).
The probability of bankruptcy of an enterprise in accordance with the value of the Zi model is determined as follows:
Z and less than 0 - the probability of bankruptcy is maximum (90-100%);
Zi = 0 - 0.18 - the probability of bankruptcy is high (60-80%);
Zi = 0.18 - 0.32 - probability of bankruptcy is average (35-50%);
Zi = 0.32 - 0.42 - the probability of bankruptcy is low (15-20%);
Z and more than 0.42 - the probability of bankruptcy is minimal (up to 10%).
Diagnosis of the probability of bankruptcy of an enterprise R.S. Saifullina, G.G. Sadykova
R.S. Saifullina, G.G. Sadykov proposed using a rating number (normative value 1) to assess the financial condition of enterprises:
R = 2K0 + 0.1Ktl + 0.08Ci + 0.45Km + Kpr, (2)
where Ko is the coefficient of availability of own sources of financing ;
Ktl—current liquidity ratio;
Ki - asset turnover ratio ( Proceeds from sale / Average assets = Page 2110 Form 2 / Page 1600 Form 1
);
Km - commercial margin (return on sales);
KPR - return on equity.
If the value of the final indicator R<1, the probability of bankruptcy of the enterprise is high, if R>1, then the probability is low.
Financial policy of the enterprise
The enterprise is part of the production process. It has its own assets and finances, which it strives to use as efficiently as possible. Financial management within the framework of the operation of a business entity is called financial policy. It allows you to maintain financial stability and independence, and continue successful functioning in the market.
The goal of an enterprise’s financial policy can be called the construction of a mechanism capable of achieving strategic and tactical goals, which may include optimizing capital, ensuring financial stability, increasing profits, achieving investment attractiveness, and creating new sources of raising funds. Tactical objectives depend on the main strategy of the enterprise. They are designed to solve problems step by step in order to achieve a strategic goal.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Development of an enterprise’s financial policy includes:
- Analysis of the financial and economic condition of the enterprise.
- Formation of accounting policies.
- Creation and implementation of the enterprise's credit policy.
- Cost management, including depreciation and costs.
- Management of all types of income.
- Dividend payment policy.
As in any other area of management, it all starts with a comprehensive analysis of internal and external factors that can influence the final result. For this purpose, accounting data, management reporting, as well as calculation of financial indicators are used. Having received comprehensive data on the current financial position of the enterprise and its potential, an accounting policy is then developed. Based on its main principles, they build relationships with creditors, shareholders, as well as government agencies.
Methods and models of analysis
The concept of “assessing the probability of bankruptcy” implies an algorithm specially developed by scientists. It is a formula that allows you to assess the risk of bankruptcy. Experts have developed approaches to help conduct a study of the situation at any given company.
Beaver model
The Beaver ratio is a rating used to assess the bankruptcy of an enterprise. The calculation involves the ratio of net profit and the total number of debts with payment obligations.
The author selected 5 out of 30 available analytical values that can effectively predict and characterize the onset of a crisis. The list is presented:
- assets or net financial turnover;
- income;
- liabilities or specific parameters of loans;
- level of liquidity;
- ratio of debts to profits received.
Important! Strengths include forecasting the timing of bankruptcy and the use of a payback rating. If it shows 0.2 units over 2 years, then the condition is assessed as a high risk of insolvency.
Beaver analysis
Altman methods
Two-factor modeling uses discriminant analysis to test business risks. The main purpose of the development was to try to find out how the method can be used in prosperous and problem companies.
The method uses two material parameters, the ratio of which allows one to draw conclusions about the state of the organization. These include:
- degree of liquidity at the time of inspection;
- the total amount of loans in passive circulation.
The simple and unique formula served as the basis for the development of other testing options. The technique remains popular in economic practice at the global level.
Important! The method allows you to accurately calculate development over the next 24 months. Its disadvantages include poor efficiency when trying to make calculations over a long period of time.

Two-factor modeling
Gordon-Springate model
The basis is the development of Altman, it was created to assess the viability forecast. The author chose to use four components, presented:
- enterprise assets or turnover index;
- the company's profit before taxes and interest on debts;
- short-term liabilities;
- net income.
Important! Profit before deduction to the treasury is important, which predetermines the final results of the calculations. The determining benchmark is the level of sales; if it is high, the organization is classified as successful; if it is low, the organization is classified as problematic.

Gordon-Springate model
Taffler's formula
The test means calculating the probability of ruin, which is based on the company’s financial indices. When calculating, attention is paid to four components, represented by the ratio of two material ratings. It is based on an integral assessment of the threat of insolvency; it uses certain ratios:
- income received from sales (before tax deductions) and the amount of existing liabilities;
- the volume of current savings to the total amount of debts;
- the amount of debt to the total ratio of assets;
- revenue to capital.
Important! The final figures allow us to make a verdict on the future of the enterprise. If the result exceeds 0.3 units, the situation is stable, and if it is not higher than 0.2, then the company is at risk of insolvency.

Taffler's formula
Fulmer's formula
Used by economists to identify the level of solvency and identify the likelihood of ruin. When creating the formula, the author used information from sixty companies, half of which showed stability, and the rest showed a critical situation.
Experts consider the formula to be accurate predictions. When calculating for the next year, the probability of the data obtained is 98%; when using the formula for two years, it is not less than 81%. To calculate the probability of entering a crisis state, the author used certain financial indicators:
- retained earnings for previous years and balance sheet;
- income before taxes and equity;
- stable cash income, long-term and short-term obligations;
- debts with a long audited payment period and balance sheet;
- short-term debts and total assets;
- material means;
- working capital and liabilities with long-term or short-term payment;
- profit before tax and interest paid.
Important! According to the results, insolvency occurs with negative quantitative values.

Fulmer's formula
Zaitseva formula
Uses Altman's development. The difference between the two types is the use of exclusively partial coefficients, individual for each enterprise. The formula includes the following information and ratios:
- net loss to equity;
- the ratio between payables and receivables;
- losses to the quantity of goods sold;
- revenue to assets ratio.
Important! Zaitseva’s six-factor development helps to identify signs of a bankrupt in the early stages of entering a critical state.

Six-factor calculation
IGEA model
Refers to the developments of domestic economists, which made it possible to spread it everywhere. The advantage is that the formula was created taking into account local realities and economic instability. Experts are confident that it is better for Russian companies to use the example of IGEA for accurate forecasting.
The basis is represented by partial indicators and a determinant method of analysis. During calculation, separate data is applied:
- working capital of the organization;
- the ratio of net income and the company's own assets;
- profit ratio and balance sheet of the enterprise;
- ratio of net income to costs.
Important! When receiving negative calculated figures, the risk of ruin ranges from 90 to 100%.
The practical application of the methodology has proven that it can be used to determine the onset of a crisis; if it is necessary to calculate a forecast, it is better to use foreign calculation methods.

IGEA model
Actions after risk analysis
An analytical study of the degree of potential and real risk of insolvency helps to completely eliminate the threat at the initial stages and preserve property. After diagnostic measures, measures must be taken to restore the stability of the organization and prevent subsequent problems.
The list of measures is presented:
- modernization of technologies and production techniques;
- studying the characteristics of the consumer market;
- payment of existing debts;
- increasing the rate of profit and economic growth - for implementation, you can sell assets and optimize sales.
The company must restructure its debts, and if after completion of the procedure the situation has not changed, then go through the bankruptcy procedure. Correct assessment of existing collateral and the application of certain evaluation criteria will help you pay creditors in a timely manner. A quick escape from ruin is achieved by reorganization or liquidation of a legal entity.
When searching for reliable suppliers, business managers are wondering how to choose the right financial organization that has the lowest risk of bankruptcy and which calculation is the most accurate. It is enough to use one of the above formulas online and make accurate measurements of the possible or existing risk of bankruptcy.
0
Author of the publication
offline 17 hours