Crimes related to bankruptcy
If the management could not foresee the situation in advance and the insolvency of the organization is caused solely by objective reasons, then the bankruptcy procedure is carried out legally on the basis of the paragraphs of Law No. 127. As a result, the debts of the legal entity are written off in full, and it is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
If the insolvency was caused by unprofessional orders of the manager or orders of the founders, then they must cover part of the obligations themselves, i.e. they bear subsidiary liability.
- Illegal actions in the course of true (legal) bankruptcy:
- concealment of property (rights to it and obligations), information about it, transfer of assets to other persons, their alienation, as well as destruction of papers with information about the economic activities of an economic entity, if these actions caused major damage and were carried out due to signs of insolvency;
- fulfillment by the debtor of the demands of some creditors to the detriment of the interests of others;
- illegal creation of obstacles to the work of the temporary manager of the debtor financial company, refusal to transfer the necessary papers to them.
- Action (inaction) of the head or founders of a legal entity or individual (IP), which led to the inability of the debtor to fully repay obligations to creditors and caused significant damage.
- Forced labor (up to five years maximum)
- Imprisonment (up to six years maximum) with payment of a fine of up to 80 thousand rubles or equal to the income of the offender for 6 months (upper limit) or without a fine.
There may also be accomplices in this crime. Thus, crimes related to bankruptcy represent a fairly limited range of illegal acts.
However, due to the significant consequences of their commission, they entail serious responsibility. In addition, during the bankruptcy procedure, elements of other crimes may be identified that are not related only to bankruptcy (they are also committed under other circumstances), but at the same time may entail punishment.
14.12-14.14 Code of Administrative Offenses).
Russian legislation establishes a strict procedure for recognizing the debtor's insolvency, violation of which is considered a crime and entails serious consequences. There are several types of illegal actions associated with bankruptcy.
Their description and the criminal liability provided for their commission are given in Art. 195-197 CC. Crimes related to insolvency proceedings represent a limited range of illegal acts.
They differ in objective and subjective characteristics, have significant consequences, and therefore entail serious penalties. The concept of insolvency Bankruptcy (insolvency) is the inability of the debtor, established by the court, to fully fulfill the creditor's demands for the obligations assumed or to pay the payments stipulated by the state.
Crimes during bankruptcy and criminal liability These acts are listed in Article 195 of the same name of the Criminal Code of Russia. These include: 1.
- Concealment (concealment) of property or any information about it, property obligations and rights, other information about property and related obligations and rights;
- transferring it to other persons for possession (temporary disposal of it);
- other alienation (compensated or gratuitous sale) or destruction of the property of the debtor;
- concealment, falsification, destruction of accounting or other accounting documentation reflecting the economic activities of the debtor (with the exception of documentation of financial organizations, criminal liability for falsification of which is provided for by another article of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), if these actions entailed major damage.
We suggest you read: How not to pay alimony to parents in a legal way
The purpose of bankruptcy from the point of view of the law is to protect the rights of creditors to the extent that it is in principle possible to pay their debts by selling the property remaining at the disposal of the company. Each bankruptcy is an individual case that is considered individually.
The insolvency administrator, appointed instead of the director, conducts research and analysis of activities and identifies the reasons that led to bankruptcy. If these reasons were objective and the manager could not foresee them in advance, the bankruptcy procedure is carried out in accordance with the provisions of the Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” No. 127. The consequence of bankruptcy in this case will be the complete write-off of debts and the exclusion of the company from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
Unprofessional actions of the director or orders of the founders could lead to bankruptcy.
Methods for investigating crimes related to bankruptcy To confirm true bankruptcy, the court appoints a temporary manager. He performs the functions of a director, examines and analyzes the work of the company, and identifies the reasons that led to insolvency.
Diagnosis of crimes in bankruptcy is based on:
- on methods of economic analysis;
- on inventories;
- during auditor checks.
At the same time, attempts by the debtor to conceal part of the property are revealed, starting from the period when payments on obligations ceased. Determine the amount of overdue debt.
Economic crimes bankruptcy
1.
195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation); director or founder (participant) of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur (Articles 196, 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). The subjective side is an intentional form of guilt.
I am going through a bankruptcy procedure, the restructuring stage, and now some man calls me, introduces himself as an investigator from the department for economic crimes, says that the microfinance organization has written a statement against me, and either a criminal case, or ask the microfinance organization to withdraw the application, they call me at work, there disseminate information.
Is this legal? What should I do? Lawyer Karavaitseva E.A., 56571 answers, 26881 reviews, on the site since 03/01/2012 1.1. Wrongful. In court you can recover compensation for moral damage. 2. Can a debtor, an individual, begin bankruptcy proceedings if he has been convicted of an economic crime or illegal banking activity?
Under what circumstances will he be denied bankruptcy? Lawyer Vlasova O.D., 2186 answers, 1462 reviews, on the site from 10/29/2017 2.1. Criminal prosecution is not a basis for refusing to declare bankruptcy, however, if the debt is caused by the imposition of penalties by a court verdict, you will be denied.
3. Will debts be written off in bankruptcy if there is a criminal penalty for an economic crime?
Lawyer Kolkovsky Yu.V., 100058 answers, 46662 reviews, on the site from 07/05/2015 3.1. Have a nice day. If you achieve bankruptcy through the courts, then all your debts will be written off, but this procedure is not quick and quite expensive Lawyer Charkina O.I., 69 answers, 35 reviews, on the site from 10/23/2017 3.2.
Good afternoon, In accordance with Art. 213.13 of the Federal Law, a plan for restructuring a citizen’s debts can be submitted in relation to the debt of a citizen that meets the following requirements: - the citizen has a source of income on the date of submission of the plan for restructuring his debts; - the citizen does not have an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for committing an intentional crime in the economic sphere and before the date of acceptance of the application for declaring the citizen bankrupt, the period during which the citizen is considered subject to
Consequences of bankruptcy
Bankruptcy of a legal entity is the financial insolvency of a commercial company in relation to its obligations to counterparties. The formal signs of bankruptcy are quite clearly defined in the current legislation: for example, Article 3 of Federal Law No. 127-FZ of October 26, 2002 “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” establishes that bankruptcy proceedings can be initiated in relation to a legal entity that has fallen behind on its debts. obligations.
Moreover, in fact, bankruptcy is a rather complex situation, from which both the enterprise itself, which has shown signs of financial insolvency, and its counterparties suffer. Thus, a business that has outstanding debt obligations and is the subject of a bankruptcy filing is likely to encounter difficulties in its day-to-day operations, even if its financial problems are temporary.
A damaged business reputation can make it difficult to attract credit funds, provide deferrals on current payments from counterparties, obtain guarantees and guarantees, and use other elements of commercial activity that are often necessary for successful business.
The negative consequences of a company's financial insolvency cannot but affect its counterparties. The bankruptcy procedure is quite lengthy, so its partners, suppliers and contractors in such a situation will have to wait quite a long time for the return of funds for outstanding financial obligations.
However, if the amount of such a debt obligation is significant and plays an important role in the business activities of such a counterparty, the delay in its payment, in turn, may adversely affect its own ability to conduct business and business reputation.
At the same time, one cannot ignore the fact that the bankruptcy procedure as a whole, as well as its individual elements, may be of interest to some persons interested in receiving financial and other benefits from its implementation.
For example, declaring a commercial company bankrupt on the basis of its inability to repay existing debt obligations, even if the required amount of funds is actually available, can save unscrupulous founders a considerable amount.
Another option for abuse in the field of financial insolvency could be the attraction of large amounts of credit funds with the subsequent recognition of the company that received them as bankrupt: in this case, these funds can be misused for the personal enrichment of individuals.
Criminal bankruptcy
Criminal insolvency is a specific type of fraud, which is quite hidden and disguised as a civil offense. In essence, the offender illegally takes possession of the creditors' property. The key point is to implement the intent over a long period of time, which can significantly minimize the risk of criminal prosecution. This is also facilitated by domestic legislation, which creates favorable circumstances for the implementation of illegal actions.
Thus, criminal bankruptcy is parasitic due to contradictions between law and law.
The variety of criminal schemes does not allow us to consider them all within the scope of this article.
In addition, the specific method of bringing an enterprise to insolvency depends on the object of bankruptcy . One common method is to create or acquire fictitious debts. A method associated with the removal of management or founders of a legal entity from managing the company can also be used.
Signs

Signs indicating criminal insolvency of a legal entity:
- Conclusion of fictitious agreements.
- Change in the composition of founders.
- Early fulfillment of obligations.
- Concluding transactions that are initially unprofitable.
- Creation of new enterprises to transfer part of the assets to them.
- Inflating the balance sheet, replacing liquid assets with illiquid ones.
- Seizure of accounting documentation.
- Concealing bank deposits, withdrawing money from accounts.
- Issuance of fictitious bills at a large discount.
- Other actions aimed at ruining the enterprise.
Enterprises undergo bankruptcy procedures strictly in accordance with legal requirements. Read what the LLC bankruptcy law says. A bankruptcy auction will help to quickly sell the debtor's property. Find out how the system works.
If you decide to open a paintball club, profits will not be long in coming. A sample business plan is here.
Responsibility
According to general rules, criminal liability is provided for criminal bankruptcy. However, this is not a guarantee that it will involve persons who are guilty of driving a commercial organization to insolvency.
It is extremely difficult to prove a violation of the law in court (see the subtitle “Dangerous Phenomenon”).
In this case, the responsibility for identifying signs of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy lies with the arbitration manager (Government Decree of December 27, 2004 N855). As a result of the inspection, the manager must leave a conclusion on the presence or absence of signs of insolvency. If the conclusion establishes the fact of causing damage on a large scale, then it must be sent to law enforcement agencies for a preliminary investigation (clause 15 of the Rules).
About crimes in the field of bankruptcy
In turn, the presence of a crime in the actions of persons participating in the implementation of the bankruptcy procedure entails criminal liability in accordance with the procedure provided for by current legislation.
We suggest you read: Bankruptcy of individuals with what amount
The main types of such violations, which constitute crimes related to bankruptcy, are recorded in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, registered in the code of laws of our country under number 63-FZ of June 13, 1996.
Here is the judicial practice on fictitious bankruptcy.
Concealment of bankruptcy
Concealing the true state of affairs from creditors who continue to invest funds in the business without realizing that it is unprofitable can lead to the fact that the invested funds will not save the situation, but will be irretrievably lost due to the incorrect policies of the company’s management or irrational organization of affairs. As a result, the commercial structure will be forced to declare itself bankrupt on its own or this will happen by order of the arbitration body of justice, after the end of quarterly non-payments, lenders begin to apply for funds.
Recognizing the company as unable to pay its debts and selling all its existing property, in this scenario, will not be able to help satisfy creditors, who will ultimately suffer significant losses only because the owner hid his economic insolvency from others.
The following video will tell about a case from judicial practice on concealing bankruptcy and other illegal actions:
Concept and types
Concealment of economic insolvency should be understood as concealment, untimely notification or transmission of deliberately false information about the financial condition of the company and its property in order to prevent the timely declaration of bankruptcy proceedings.
The motives for such behavior by an entrepreneur or owner of an organization may be to achieve the following goals:
- solving temporary economic difficulties without going through a bankruptcy procedure, accompanied by a comprehensive assessment of the enterprise and the intervention of third parties;
- bringing a commercial organization to a state of complete bankruptcy, when recovery is no longer possible and liquidation is inevitable;
- delaying liquidation procedures for the purpose of accumulating fictitious accounts payable with subsequent misappropriation of funds and avoidance of subsidiary liability.
The most common types of algorithms for concealing the actual state of an organization’s finances are the following:
- Declaration of data that does not correspond to the real state of affairs, achieved by providing:
- falsified information required to assess the financial well-being of a commercial structure;
- distorted responses to requests received from federal authorities performing the functions of control and law enforcement;
- false information serving to mislead credit institutions and other lenders.
- Distortion of documented results of economic activity, carried out through:
- production of constituent documentation and registration certificates that do not correspond to the real state of affairs;
- falsification of documents with the help of which the primary accounting of financial transactions and movement of funds is carried out;
- production of counterfeit documents indicating the provision or release of duties.
- Adjustment of accounting information and reporting documentation in order to distort information.
- Destruction, concealment or restriction of access to financial information about the organization's activities.
Corpus delicti
Registration of signs of a criminally punishable sequence of actions is possible only with a combination of several mandatory components, such as:
- Establishing the fact of providing information, the content of which does not correspond to the actual state of affairs and this is confirmed not only by the testimony of an individual or persons, but also by real audit data.
- The presence of a person responsible for the loss, distortion or other manipulation of the financial data of the organization, who has reached the age of sixteen and is subject to criminal prosecution.
- Diagnosis of the insolvent financial condition of an organization based on the state of repayment of accounts payable and insufficiency of liquid assets.
- Determining the occurrence of bankruptcy long before its declaration by a third-party auditor, not declared by the manager or owner of the business on a voluntary basis.
Read on to find out what legal norms to apply to if a latent stage of bankruptcy is identified.
Legal norms
Depending on the damage suffered by the creditors who went to court, the law provides for criminal or administrative liability for the management employees of a commercial structure or its owners. The critical mass delimiting liability for financial offenses is the amount of damage of 1.5 million rubles.
The following video will tell you more about the legal norms regarding illegal actions related to the bankruptcy of an enterprise:
Crimes related to bankruptcy
True bankruptcy
The first type is a situation where the commercial company in question does not actually have sufficient funds in its accounts to pay off its existing financial obligations.
Thus, this company is actually financially insolvent, that is, the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings against it looks legitimate. At the same time, during the implementation of this procedure, one or another of its participants may commit serious violations that constitute a crime under current legislation.
Crimes related to bankruptcies that fall into this category are recorded in Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, which deals with unlawful actions during the implementation of the procedure for declaring a commercial company financially insolvent.
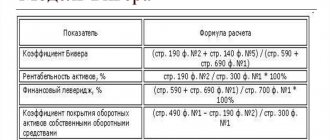
- concealment of any kind of information about the presence of any property at the debtor company that can be used to satisfy the legal claims of creditors. These unlawful actions constitute a crime falling under paragraph 1 of Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. For example, the destruction of a company’s financial statements may be recognized as an act consistent with the content of the specified section of this regulatory act. At the same time, however, it should be borne in mind that the action of a particular person can be qualified accordingly only if it entailed causing major damage to the interested parties. In turn, major damage, as established by paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, is a monetary amount exceeding 1.5 million rubles. In this case, a fine of up to 500 thousand rubles or equal to income for a period of up to 3 years, or more serious measures may be applied to the person guilty of concealing information: forced labor, arrest or imprisonment;
- extraordinary satisfaction of creditors' claims, violating the legal rights and interests of other creditors in the process of implementing the bankruptcy procedure. The specified corpus delicti is registered in paragraph 2 of Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the condition for the application of this section of this regulatory legal act is the infliction of major damage by the actions of the culprit. The monetary fine in this case can be an amount of up to 300 thousand rubles or correspond to income for a period of up to 2 years. Other punishment options for such an offense are forced labor for up to 1 year, arrest for up to 4 months and imprisonment for up to 1 year. In addition, these measures may be accompanied by a fine;
- any opposition to the work of the arbitration manager appointed and approved to implement the bankruptcy procedure by the arbitration court. The condition for qualifying an act as containing a crime, as provided for in paragraph 3 of Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, is also the presence of large damage resulting from such actions. In this situation, the culprit may be subject to a fine (up to 200 thousand rubles or equivalent income for a period of up to 1.5 years), forced labor (up to 3 years), arrest (up to six months) or imprisonment (up to 3 years).
We suggest you read: What is the order of payments in case of bankruptcy of an enterprise?
14.12-14.14 Code of Administrative Offenses).
Illegal actions during bankruptcy
When monitoring the bankruptcy process at an enterprise, the arbitration court pays special attention to the actions of the organization’s management. That is, strict control is carried out on the activities of managers in relation to the abuse of their powers and obtaining benefits during the liquidation of the enterprise. Such actions during bankruptcy are illegal and entail criminal or administrative liability.
Administrative liability is regulated by Art. 14.12-14.13 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, legal liability - Art. 195-196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Deliberate bankruptcy
Another group of offenses in the implementation of the procedure for declaring a company financially insolvent is the so-called deliberate bankruptcy. The elements of this crime are described in detail in Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation: this section of this legal act interprets deliberate bankruptcy as a set of deliberate actions taken by the manager or founder of a commercial company, the purpose of which was to achieve a state of bankruptcy by the organization, that is, the lack of sufficient funds for satisfying fair claims of creditors.
If such actions or their absence lead to the above consequences, the guilty person is subject to criminal liability. It should, however, be remembered that it occurs if such consequences can be qualified as major damage.
Criminal liability can be expressed in the form of a fine (up to 500 thousand rubles or equivalent to the income of the culprit for a period of up to 3 years), forced labor (up to 5 years) or imprisonment (up to 6 years).
The appointment of a measure such as forced labor or imprisonment by a judicial authority may be accompanied by the imposition of a fine. It should, however, be emphasized that the provisions of Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation do not imply the application of arrest to the accused.
Liability for intentional or fictitious bankruptcy
It is important to understand the risks of declaring yourself bankrupt or taking actions aimed at deliberate bankruptcy. Such actions can have consequences, including criminal liability, however, it all depends on the amount of damage received:
- If the act does not contain signs of a criminal offense.
In this case, if it does not lead to major damage, it is punishable in accordance with Article 14.12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Point 1, fictitious bankruptcy, point 2 – deliberate. Responsibility will be the same, from a thousand to three fines for citizens.
- If deliberate bankruptcy results in major damage.
This is punishable in accordance with Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, that is, a fine from two hundred to five hundred thousand or in the amount of the person’s income for a period of one to three years, forced labor for up to five years, imprisonment for up to six years with a fine of up to two hundred thousand or without its application ( may be replaced by a person's income for up to eighteen months).
- When fictitious bankruptcy leads to major damage.
Punishment is calculated under Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and can be expressed in the form of a fine from one hundred to three hundred thousand rubles (a person’s income from one to two years), forced labor for a term of up to five years, imprisonment for a term of up to six years with a fine of up to eighty thousand or without using it.
The fine can be expressed in terms of the income of the convicted person for up to six months.
In this case, the investigation and the court need to understand how to prove major damage (based on Article 170.2, major damage means an amount of two million two hundred and fifty thousand rubles).

Click to enlarge image
The damage that creditors will suffer as a result of declaring a person bankrupt is taken into account. For example, a citizen had to repay loans totaling one million rubles. In this case, he will be prosecuted only under the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
But if the amount of his debts, which he will no longer repay after the sale of his property at auction, amounts to the amount specified in Article 170.2, then the citizen has a chance to receive a criminal conviction.
Download to view and print:
• Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Intentional bankruptcy”
• Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Fictitious bankruptcy”
• Article 14.12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation “Fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy”
Read: Can you go to jail for non-payment of a loan?
Civil responsibility
Intentional bankruptcy can lead not only to criminal and administrative liability, but also to civil liability. The person who used such methods will receive an obligation to compensate creditors if he is proven guilty.
Thus, Article 311 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of revising decisions based on newly discovered circumstances. A court verdict or recognition of the fact of falsification can precisely act as a reason for revising a judicial act that has already entered into force.
Accordingly, bankruptcy can be cancelled, and the person will again receive obligations to repay the funds.
Creditors can recover not only previously accumulated debts that were canceled due to a person being declared bankrupt, but also losses incurred after that, if they are directly related to the fact of unintentional or fictitious bankruptcy.
We can also talk about lost profits if it can be proven.
Recovery of damages is carried out in civil law, that is, in compliance with the rules of the Arbitration Procedure Code and Civil Procedure Code, depending on the circumstances. The plaintiff will have to justify the amount of damages, as well as prove that they should be recovered at all and are justified.
Fictitious bankruptcy
Finally, the third group of offenses in the field of bankruptcy is associated with the implementation of fictitious bankruptcy, that is, the dissemination of information about the financial insolvency of a commercial company that does not correspond to reality.
Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides that if such actions cause damage to any individual or legal entity exceeding 1.5 million rubles in monetary terms, the perpetrator is subject to criminal prosecution.
This, in turn, implies that the judicial authority may apply one of the following measures to him: imposing a fine (up to 300 thousand rubles or equivalent to the income of the culprit for a period of up to 2 years), sending him to forced labor (lasting up to 5 years) or imprisonment (up to 6 years).
Concealment of property by the debtor
Advice from lawyers:
1. Bailiffs refused to initiate criminal proceedings 3 times. The arrest was lifted from the apartment. They left the arrest abroad. The debtor has a debt of RUB 3,621,684.39. Where did I turn? I am a collector, my daughter is already 20, and things are still there. The bailiffs write that checking the facts of concealment of unlawful concealment of income is not within the competence of the FSS and that property checks are carried out regularly. And recently the investigator sent me an answer that the debtor did not open the door. What to do with such cunning bailiffs?
1.1. Hello, all you have to do is write complaints to the prosecutor's office and higher authorities.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
1.2. You really need your daughter's father to have a criminal record. Aren't you afraid that this might interfere with her somewhere? Refusals to initiate criminal proceedings can be appealed to the prosecutor or to the court.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Consultation on your issue
8
Calls from landlines and mobiles are free throughout Russia
2. Does the bailiff, who came to seize property, have the right to search the debtor’s apartment for hiding valuables? Utility debt.
2.1. The bailiff does not have the authority to conduct a search.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
2.2. Of course not! I think you understand this yourself!
Did the answer help you?YesNo
2.3. Everything that he sees with his eyes is his, he makes a decision about the inventory and seizure of property. Open doors, hatches, etc. yourself. the bailiff has no legal right. You have the right to file a complaint against the actions of the bailiff to his boss or go to court (State Antimonopoly Service of the Russian Federation).
Did the answer help you?YesNo
3. Is it possible to prosecute an alimony debtor under Article 159 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation if it is possible to prove the concealment of income and property.
3.1. Irina Aleksandrovna, no, 159 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, this is fraud. And for the alimony debtor, this is 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Criminal Code of the Russian Federation Article 157. Non-payment of funds for the maintenance of children or disabled parents
1. Failure by a parent to pay, without good reason, in violation of a court decision or a notarized agreement, funds for the maintenance of minor children, as well as disabled children who have reached the age of eighteen, if this act is committed repeatedly, is punishable by correctional labor for up to one year, or forced labor for up to one year. the same term, or arrest for a term of up to three months, or imprisonment for a term of up to one year. 2. Failure by adult able-bodied children to pay without good reason, in violation of a court decision or a notarized agreement, funds for the maintenance of disabled parents, if this act is committed repeatedly, is punishable by correctional labor for up to one year, or forced labor for the same period, or arrest for for a term of up to three months, or imprisonment for a term of up to one year.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
4. Can a debtor-individual. a person who maliciously fails to comply with a court decision to repay a debt, enter into an agreement with an acquaintance and become a depositor in order to conceal his property?
4.1. Good afternoon. A person can do whatever he wants, but the conclusion of a storage agreement is not a reason why this property cannot be seized. If the bailiff determines the location and ownership of the property by the debtor, he can seize it.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
4.2. Svetlana, greetings! The consequences will be the following: 1. bailiffs will come and inventory the property. If you try to appeal their actions, the court will point out the imaginary nature of the contract and refuse to recognize the actions of the bailiffs as illegal. 2. A criminal case may be initiated for malicious failure to comply with a court decision, since the debtor is attempting to hide property.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
5. In order to bring criminal liability under Article 312 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for concealing property seized by bailiffs, should the debtor be warned of criminal liability for this? If yes, then please cite the NGO so as not to be unfounded.
5.1. Where did you get the idea that you should be warned? As you know, ignorance does not exempt you from responsibility.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
6. The debtor does not provide the bailiff with a car, cat. is prohibited. Do I have the right to write a statement to the police for failure to comply with a court decision, failure to comply with legal requirements of the court. bailiff about providing a car, about concealing property and evading payments (he pays 2000 in cash every month)? Under what article can a debtor be held liable?
6.1. - Hello, complain about the bailiff. It's just his job now. Best wishes.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
6.2. Responsibility for individuals persons for failure to comply with a court decision are not provided for. But the police are obliged to assist the bailiffs in finding property that is hidden.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
7. The court imposed a ban on registration actions on the debtor's car. The bailiff says that the debtor refuses to provide her with this car of his. Can the bailiff take any measures or force the debtor to produce property? Does the debtor face criminal penalties for concealing property and disobedience to the court? bailiff? How can I influence the bailiff?
7.1. A petition to search for the debtor's property... through the office... with a note of acceptance on the copy (for starters).
Did the answer help you?YesNo
7.2. Marina, you need to use your brain, or consult for money, have so many problems really piled on your poor head?
Did the answer help you?YesNo
8. The bailiff closed the proceedings under Article 46, Part 1, Clause 3. He said that there was no information about the property and place of work. In fact, the debtor is the director of the LLC. I have a car (owned for 8 months). Is it possible to hold bailiffs accountable? After all, this is a concealment of information. And what to do in this situation?
8.1. Write a complaint to the prosecutor's office.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
8.2. Hello. Appeal the actions of the bailiffs to the senior bailiff or to the court. In the application, indicate that the debtor has property, constant income from business activities, but the bailiff did not make the corresponding requests. But before that, I still recommend that you familiarize yourself with the materials of the enforcement proceedings in order to make sure which actions were carried out by the bailiff and which were not. Good luck!
Did the answer help you?YesNo
9. There will be a second court to foreclose on the debtor’s property held by third parties when the debtor’s ownership rights are recognized when he conceals the property. What else will the debtor's lawyers come up with, bypassing the laws and bribing judges? At the upcoming trial, I need to be on the safe side. There is more than one property, but everything is hidden and registered to direct relatives.
9.1. Look for evidence, collect information, you can answer more accurately if you know the circumstances.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
9.2. And you also “put a pig on them” to conclude an agreement with a representative, this is your right.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
9.3. To help you, you need to get involved in the process and study all the nuances of the case. It is impossible to help you simply with advice.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
10. How to invalidate a transaction and what evidence is needed in this case? During the period when enforcement proceedings were initiated against the debtor, he transferred all his property to his relatives in order to conceal it for the bailiffs to make an inventory.
10.1. Vladislav, you do not have such powers to challenge the transaction, only bailiffs can do this.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
11. A new, as yet unknown law on bankruptcy of an individual comes into force. There is a certain article about the illegality of the transaction. The question is, what if I am a debtor and I have property that will be transferred to other persons. There is a possibility that this property and this transaction will be considered illegal. Those. concealment of this property. And who, in accordance with this law, will be interested in declaring this transaction ILLEGAL? Thank you!
11.1. Your creditors!
Did the answer help you?YesNo
11.2. Of course, there is a possibility that this deal can be challenged in court. The interested party will be your claimants.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
12. The ex-husband is a debtor for alimony. As soon as enforcement proceedings were initiated, I transferred my car to my father under a purchase and sale agreement. Can I file a lawsuit to invalidate this transaction (the sale and purchase was concluded 1.5 years ago) and to deliberately conceal the property by the debtor? Has the statute of limitations passed?
12.1. Can I file a lawsuit to invalidate this transaction (the sale and purchase was concluded 1.5 years ago) and to deliberately conceal the property by the debtor? LIMITATION PERIOD – three years. You can file a lawsuit to recognize the transaction as IMAGINAL, GOOD LUCK TO YOU.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
13. Is it possible to hold a debtor criminally liable for waste of property for concealing property and a willful defaulter?
13.1. This is exactly why - no. Maybe for something else. Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. “Article 177. Malicious evasion of repayment of accounts payable. Malicious evasion by the head of an organization or a citizen from repaying accounts payable on a large scale or from paying for securities after the relevant judicial act has entered into legal force - is punishable by a fine in the amount of up to two hundred thousand rubles or in the amount of the wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to eighteen months, or by compulsory labor for a term of up to four hundred eighty hours, or by forced labor for a term of up to two years, or by arrest for a term of up to six months, or by imprisonment for a term of up to two years.”
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Consultation on your issue
8
Calls from landlines and mobiles are free throughout Russia
14. There is enforcement proceedings. The bailiff must recover N amount of money from the debtor. I am a debtor and I have nothing and no work either. There is a current account, but there is no money in it. And when, upon REQUEST, I compiled a list of property in writing, I did not indicate the current account, because... considered it unnecessary due to lack of funds. Is this a cover-up with malicious intent and what are the consequences?
14.1. Elena, if you take it literally, a current account is not property. Property – funds placed on the account. If they are not there, there is no property.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
15. Is the bankruptcy creditor obliged to notify the bankruptcy trustee and the meeting of creditors about the assets, property, and debtor known to him; in the event of concealment of information about the debtor’s property, does this creditor fall under Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation,
15.1. Hello Rafael! There is no bankruptcy creditor if the assets and property are not with him, but the debtor is obliged.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
16. The court refuses to hold the debtor accountable for evading the execution of a court decision on the basis of Article 177 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. The court reasons that the debtor was not warned by the bailiff about liability for evading the execution of a court decision or concealing property. Is this legal?
16.1. If the debtor was not warned about the existence of a decision to collect accounts payable that has entered into legal force, he should not be held liable. You need to read the court verdict, after which you can evaluate it. I think that you did not understand the legal intricacies of the situation.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
16.2. Roman, only after reading the case materials can one determine the legality of the court’s decision.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
17. Article 9 of the Bankruptcy Law obliges the debtor manager to timely file an application for insolvency. According to which article? Can a management company prosecute a manager who has not applied to the arbitration court for unlawful action in bankruptcy? But is there only concealment of property and documents?
17.1. Hello, Alexander. Art. 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for the responsibility of the manager for actions related to the concealment of property and documents. You need to competently draw up a statement to law enforcement agencies, and then accompany his movement. Sincerely, lawyer A. Timofeev.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Illegal bankruptcy, composition and types of this crime
Let's consider what crimes can occur during bankruptcy proceedings, and what is the criminal liability for their commission. The content of the article
- Introduction to the topic
- Crimes in bankruptcy and criminal liability
- Deliberate bankruptcy
- Fictitious bankruptcy
Introduction to the topic Criminal law provides for liability for 5 types of unlawful actions related to bankruptcy proceedings. At the same time, under bankruptcy, according to Federal Law dated October 26.
2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, refers to the inability of the debtor, established in court, to fully satisfy the monetary demands of creditors or transfer obligatory payments to the budget system and extra-budgetary funds.
Dangerous phenomenon

Enterprise failure is a vital phenomenon for a market economy. Bankruptcy is inherent in all economically prosperous states, as well as in countries experiencing a crisis. The difference lies only in the scale of the event, which has objective or subjective causes. However, the actual bankruptcy of a commercial organization or the technical insolvency of a legal entity is fundamentally different from criminal activity in this area.
Criminal bankruptcy is a combination of several elements of crime that are associated with the insolvency of an enterprise.
The main danger is that criminal acts are difficult to detect. As a result, it is almost impossible to apply adequate countermeasures to the offense. The most complex element of the crime is its objective side.
In this case it is necessary:
- Correctly select legally significant signs of a crime.
- Select the appropriate construction of the crime.
- Clearly state the identified signs.
Further, if we consider the insolvency of credit institutions, then such a concept as “Project Bankruptcy” has appeared. This is when the bank undertakes obligations to finance the construction of a facility. Most of the assets of the credit institution are transferred to this project, after which the financed business goes bankrupt. As a result, the bank begins to experience a liquidity crisis, and its arrears on personal obligations increase.
Problems with equity lead to the bankruptcy of a credit institution.
As an example, you can take the Granit battery . Therefore, project bankruptcies should be considered criminal if, when issuing a loan, the bank violates the standard for the maximum amount of risk per borrower and falsifies reporting documentation (Instruction of the Central Bank dated December 3, 2012 N 139-I). However, the main criminal factor in this case is the direct participation in the construction of the facility by the owners of the credit institution.
As already mentioned, it is extremely difficult to determine the moment of intentionality of a project bankruptcy. The issuance of loan funds usually occurs through front organizations. Most often, the key factor is the lack of collateral. These circumstances, regardless of the crisis, can already serve as grounds for bank bankruptcy. In this case, if the borrower has property, for example, a construction project or a factory, then the debt can be repaid by selling it by court decision. However, if the loan was issued to a technical company whose function was to pump money, then it will most likely be impossible to return the money.
It is difficult to get money back from banks that have closed. Read about bank failures. The simplified bankruptcy procedure is not applicable to everyone. Read more in the article.
Conditions of occurrence
The persistent relevance of the criminal insolvency of commercial organizations lies in the difficulty of proving the intentionality of the act, i.e. intent.
In addition, one of the main problems is the inconsistency of the actions of specialized experts when conducting financial and economic examination.
In other words, if economists prepare a financial analysis, and lawyers later try to document it, then it is very difficult to find a common denominator. The situation is similar with law enforcement agencies. Investigators transfer the collected material to economists, who must analyze the documents. Such an examination is carried out in accordance with the regulations of the Central Bank.
The key criteria are:
- financial condition of the borrower;
- debt service;
- any information about the debtor.
However, if the bank is involved in a project bankruptcy, then in this case the documents may show excellent loan servicing. For this purpose, additional technical companies are usually used, through which loan funds are distributed and collected. Most often, it is almost impossible to find such companies at their registered address. In this case, the main capital is transferred to a leading technical company, which subsequently regularly pays interest with the money of the credit institution.
This is due to the fact that it does not have economic activities, and, therefore, does not have its own sources of financing.
As already mentioned, the task of economists is to conduct a financial examination of documents. Therefore, they are not authorized to analyze those circumstances that are subject to legal assessment. As a result, inconsistency of actions excludes the possibility of adequately assessing the borrower on the Central Bank scale.
The subsequent output of the expert displays the following data:
- the financial condition of the borrower is poor;
- Debt service is good.
Kinds

The type of insolvency discussed includes:
- intentional bankruptcy;
- fictitious insolvency;
- illegal actions during bankruptcy.
Deliberate insolvency implies the commission by the director or owner of a legal entity of actions that entail the inability of a commercial organization to satisfy the demands of creditors (Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Fictitious bankruptcy means a deliberately false public announcement by the executive body or the owner of an enterprise about the insolvency of a legal entity.
The main factor in this case is causing damage on a large scale (Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Unlawful actions in bankruptcy must be understood as concealment of property (property rights) or information about it, including concealment of accounting documents reflecting the economic activities of an enterprise (Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
The main elements of criminal bankruptcy include:
- Subject of the crime.
- Circumstances of bankruptcy.
- The identity of the offender.
- Ways to conceal the insolvency of a commercial organization.
- Circumstances that contributed to the commission of the crime.
However, as already mentioned, the most difficult element of the crime is its objective side. It should be noted that these criminal procedural norms have their own defects. For example, unlawful actions in bankruptcy do not reveal the essence of the crime, but only describe a list of private actions that are illustrative in nature. Whereas, the essence of the offense comes down to reducing the bankruptcy estate. In this case, it is logical to consider the actions specified in the article as evidence in the commission of a crime.
The rule on intentional bankruptcy demonstrates inconsistency with the civil law definition of insolvency, i.e. “Failure to satisfy the demands of creditors.”
In addition, there is a logical vulnerability in the essence of this article. An increase in insolvency implies its existence, and, therefore, excludes the debtor’s guilt. After all, business activities cannot be carried out without financial obligations.
As for fictitious bankruptcy, in this case the goal of the interested party is rather not to mislead creditors, but to obtain a deferment of payments or non-payment of debt. However, to achieve this goal, a method such as misinformation of lenders is used. In addition, the norm of the Criminal Code does not contain instructions in what form a false announcement must be made. Because one form of notification indicates fraud on the part of the debtor (Article 159 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), and the other boils down to fictitious insolvency. At the same time, the main element of the crime is the consequences.
Watch a video about criminal bankruptcy
Legislation
The procedure for establishing and terminating the activities of commercial enterprises is established by the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies” and the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”. As for credit institutions, they are guided by the Federal Law “On Banks and Banking Activities”. Registration of legal entities occurs on the basis of the Federal Law “On State Registration...”. The bankruptcy procedure for commercial organizations is carried out within the framework of the Federal Law “On Insolvency...”.
Criminal liability for unlawful actions in the field of economic activity is carried out in accordance with the rules of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.