Actions of the creditor
The judicial act on bringing to subsidiary liability (collection of losses / debt on a loan or guarantee / unjust enrichment, etc.) has entered into legal force. Then there are 2 possible scenarios:
- the creditor will go to the bailiffs;
- the creditor will file a bankruptcy petition for the debtor as an individual.
Very often you can hear from debtors the opinion that the creditor is acting unlawfully by immediately filing for bankruptcy. Like, “it’s much more profitable for me for a creditor to take my property through a bailiff than for it to depreciate to the penny at a bankruptcy auction.”
The desires of debtors are understandable, but who cares about these desires? According to the law, the claimant has an unlimited opportunity to independently choose the method of protecting his rights. And if he chose the option of bankruptcy, then that is his right. There is no prohibition on such actions in the law.
Therefore, an attempt to force the creditor to choose a different path - collection through a bailiff - is doomed to failure.
But let's return. So, what are we preparing for?
Option 1. The creditor initiates enforcement proceedings.
The writ of execution is transferred to the bailiff service. The bailiff initiates proceedings and sends out inquiries about the availability of property from the debtor. Everything that is found is placed under arrest: from now on, you cannot do anything with your shares in the LLC, real estate, bank accounts, etc.
If the bailiff is smart, he will send a request to the registry office to find your spouse. All the money in the wife’s accounts, and the real estate and cars registered in her name, are by default assumed to be common (jointly acquired), which means that, at a minimum, they include your 50%.
Proving that in fact it was the wife’s personal property because it was received by inheritance / as a gift / under a marriage contract is now a headache for the wife. If she cannot convince the bailiffs that she is right, she will have to go to court.
We have seen with our own eyes how such stories end, you can read about our experience in the article “How we lost the court to recover damages for 210 million rubles.”
The key point of the activity of bailiffs is that they work with assets available at the time of initiation of enforcement proceedings. If by this date the debtor has neither personal property nor an official marriage, then the most that can be expected from the bailiff is an attempt to challenge the withdrawal of assets according to the norms of Civil Law.
In theory, this is possible - we analyze judicial practice and find claims filed by bailiffs under Article 10 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation “Abuse of Law”.
But these are isolated cases. In practice, all the bailiffs I know, as soon as the question of challenging transactions for “ten” arises, they roll their eyes with the silent question “Why do I need this?”
By the way, the creditor himself has the right to appeal the debtor’s actions to alienate assets with abuse of right. In parallel with enforcement proceedings. But filing a claim and winning it are two very different things.
We will send you an example of judicial practice - leave your e-mail in the form above.
Total:
- the bailiff works with what the debtor currently has
- if the debtor is married, then property registered in the name of his spouse will also be at risk
- The bailiff can challenge transactions for the withdrawal of the debtor’s assets according to the norms of Civil Law, but does not often use this. And if he does, he wins only in the most obvious cases.
- In general, the bailiff is not the most serious opponent due to the lack of proper legislative support, experience and motivation.
Option 2. The creditor makes the debtor bankrupt.
The creditor files an application for bankruptcy of an individual to the Arbitration Court. If the amount of debt is more than 500 thousand rubles, then one of the bankruptcy procedures is introduced (debt restructuring or sale of property) and an arbitration manager is appointed (in the bankruptcy of an individual he is called a financial manager, but changing the name does not change the essence).
The financial manager has powers similar to the bailiff: he requests information about the debtor’s property and marital status, checks completed transactions and the availability of bank accounts, etc.
Likewise, he will show interest in the property of the official spouse, if there is one at the time of bankruptcy. And if the wife is in the process of divorcing our debtor, then on his behalf she will take part in the divorce process and try to get the most out of it in favor of her customers. You can read how this happens in the article “Division of marital property during bankruptcy.”
But there are also significant differences between bankruptcy and enforcement proceedings: an arbitration manager can (and should) work not only under civil law, but also under bankruptcy law. And in the Federal Law “On Bankruptcy” there is Chapter III.1 - challenging the debtor’s transactions made on the eve of bankruptcy. And according to these standards, asset withdrawal transactions fail much more often than according to the notorious “top ten”. It is logical - Chapter III.1 was precisely invented for such cases.
By the way, in bankruptcy the debtor has an excellent chance of losing his only home. But we will not repeat ourselves; we have already covered this topic in the article “How to protect the debtor’s only home.”
Total:
- in bankruptcy, the financial manager can use all the same tools that the bailiff has, and a bunch of new mechanisms from bankruptcy legislation,
- the arbitration manager will look for property alienated by the debtor because
- transactions to withdraw the debtor’s assets are contested much more easily on bankruptcy grounds than under the Civil Code,
- A financial manager is a professional, motivated to achieve results. He knows where to dig and where to look for what. You don't need to kick it to do its job. At a minimum, because the AU has a higher responsibility: if he misses some transactions, losses can be pinned on him.
By the way, if the debtor dies, the debts themselves do not stop and are not written off anywhere. You can also work on them - exactly as we wrote in the article “What to do if the debtor dies.”
In general, the main thing you need to understand is that the bankruptcy of an individual is much more dangerous for the debtor (from the point of view of parting with his personal property) than the initiation of enforcement proceedings. And a competent lender will go exactly this way.
This means that we must prepare for this scenario.
How to find the property of a debtor of a legal entity
Of course, you can present a writ of execution to the bailiff, but there is a high probability of wasting time on various bureaucratic procedures.
In the event that you do not know the debtor’s current accounts, then the claimant, in accordance with clause 8 of Art. 69 of the Law (hereinafter referred to as the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings”), you have the right to request the tax authorities. It is necessary to write a request to the tax authority, attaching a copy of the writ of execution. In accordance with paragraph 10 of Art. 69 of the Law, tax authorities are required to respond within 7 days from the date of receipt of the request.
The claimant may request the following information from the tax authorities (clause 9 of Article 69 of the Law): - on the name and location of banks and other credit organizations in which the debtor’s accounts are opened; - about current account numbers.
At the same time, if the debtor has several current accounts, a question arises.
- income received from ownership of shares, securities;
- income received from the use of means of individualization;
- income received from the use of intellectual property results, etc.
Such requests can be sent by a bailiff when an initial check of the debtor’s property status has been carried out and there is initial information about the debtor and information about the debtor’s identity.
During these activities, requests may be sent to the following government agencies.
Internal Affairs Bodies
Information center of internal affairs bodies.
Deadline for challenging transactions
Competent preparation for personal bankruptcy, first of all, consists of the debtor checking his transactions for contestability. To do this, you need to understand for what period and how certain transactions are disputed.
1) Challenging the debtor’s transaction according to the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
There are many grounds for challenging transactions under civil law, but the most popular of them is abuse of law (Article 10 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
When challenging a transaction under this article, it is necessary to prove that the debtor alienated the property for the purpose of evading payment of the debt, and not for the purpose of obtaining a financial (economic) result.
We discussed how this works in practice here and will talk about it in more detail below. Now let’s look at the limitation periods so that you understand the period during which this problem can arise:
There are two key points here:
- Firstly, the statute of limitations under civil law is counted forward from the date of the transaction.
- Secondly, the parties to a transaction can challenge it only within 3 years from the date of completion. But since creditors and the financial manager are not in any way a party to the transaction and cannot know about its terms (and sometimes even about its existence), for these guys three years begin to flow from the moment they received information about the transaction. But to prevent this process from becoming endless in time, the legislator introduced a limitation - no more than 10 years from the date of the transaction.
Total: we can assume that within 10 years from the date of completion of any transaction, creditors can try to challenge it according to the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, a transaction is understood as a contract of sale or gift, as well as the contribution of property to the authorized capital, registration of a mortgage (pledge), a marriage contract or an alimony agreement. It's all about transactions.
2) Challenging the transaction under bankruptcy standards (under the Federal Law on Laws).
There are also several grounds here, but most often they go through challenging a transaction made with the aim of causing harm to creditors. On this basis, it is necessary to prove that the transaction was made:
- during the period when the individual already met the criteria of insolvency;
- the transaction caused damage (done on non-market terms);
- the party to the transaction knew about the debtor’s situation (was affiliated or interested in the result).
We discussed in detail how this works in practice in the article “Everything about challenging the debtor’s transactions in bankruptcy proceedings,” and now we’ll just focus on the statute of limitations, which debtors usually have big problems understanding.
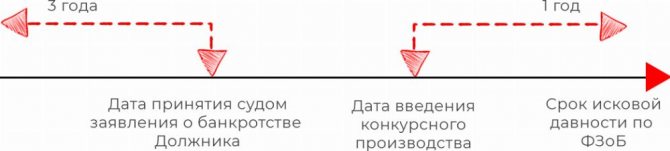
Here are the following nuances:
- Firstly, the law clearly defines the period during which a transaction subject to challenge must be completed - this is a maximum of 3 years before the bankruptcy petition is accepted (or after its acceptance). That is, the countdown date is the moment the Arbitration Court accepted the creditor’s application for the debtor’s bankruptcy - from this moment we count back three years and mark everything that fell within this period in red: transactions in the risk zone. But if the transaction falls out for at least one day over a three-year period, bankruptcy rules can no longer be applied to it (but you can go through the Civil Code).
- Secondly, there is a separate deadline for filing an application to invalidate a transaction. It lasts for 1 year and, in general, accounts forward from the moment of the introduction of bankruptcy proceedings (sale of property). If the arbitration manager files a claim even 1 day later, the debtor has a good chance of winning the court case for missing the deadline.
Here are some obvious conclusions:
- It is more interesting for the creditor to file for bankruptcy as early as possible.
- If this is done, then the debtor can delay the process of introducing bankruptcy even indefinitely - this will not help him much (at least on bankruptcy grounds).
- When it comes to defending their transactions in court, the debtor needs to check both dates, so that later it will not be very painful for a stupidly lost trial.
Grounds for seizure of property by bailiffs
Seizure of real estate by bailiffs occurs only if the requirements of the law are met, as well as in the presence of a limited list of circumstances. This is due to the fact that arrest implies a restriction of a citizen’s property rights, which are guaranteed to him by the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, in practice, the FSS service tries to use other methods to achieve its goals, and only when the employee is convinced that it is impossible to act in any other way, the institution of seizure of the debtor’s property is applied.
Legal restrictions can be imposed on material assets only if each of these conditions is present:
- the minimum amount of debt must be 3 thousand rubles;
- the presence of a writ of execution or an agreement on the basis of which the debtor must transfer funds (provide services) to the creditor (recipient of funds);
- the bailiff can independently decide to seize property if there are sufficient grounds for this;
- The procedure can be initiated by the recipient of the money (plaintiff) by submitting a handwritten application;
- compliance with the intended purpose of such a procedure.
Property may be seized only to satisfy the following objectives:
- sale of material assets in order to compensate for the amount of accumulated debt on loans, alimony and other monetary obligations;
- execution of a court decision to confiscate the property of the offender.
How to dispute
To prepare and carry out reliable transactions, you need to know not only the period of their contestability, but also the general rules and principles by which the court recognizes them as invalid.
We at Igumnov Group have never gravitated towards chewing on theory, so we will talk about methods of destroying and protecting transactions below directly using specific examples. We think this will be clearer than quoting laws and plenums here, which you are unlikely to be able to apply in a real situation (otherwise, what have you forgotten here?).
Next, we move directly to the strategy and tactics of protecting personal assets.
Defense strategy
All protection of personal property comes down to two sequential tasks.
First. Find an asset custodian.
This can be any legal entity or individual that you either trust as yourself or can control. The main requirement for the Asset Custodian is that he himself should not be at risk. And this includes everyone who is actively running a business.
Finding an asset custodian is always the responsibility of the client; we do not do this. An exception is if we are talking about creating offshore/trust structures and the client is ready to pay several tens of thousands of dollars annually for their maintenance.
Second. Transfer your property to the Custodian.
There are a million options for re-registration of property. And all of them can be laid out on a line, where at point 1 there will be the most reliable and impeccable deal that meets the highest requirements of creditors, and at point 2 there will be a dummy deal that will burst with a slight pressure.
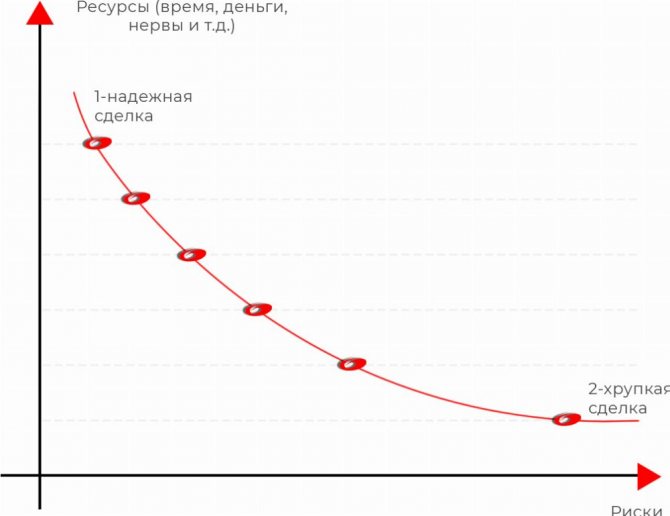
What determines the reliability of a transaction?
Looking at the graph, it’s easy to guess the answer - depending on the availability of resources to complete it. Here and below, by resources I will mean a combination of 3 factors:
- Availability of funds or the ability to obtain them for the required period.
- The amount of time until a judicial act on collection from an individual debtor enters into legal force.
- Willingness to waste your nerves and/or depart from the usual order of things.
Time/money are two key issues. Or trustees turn when there is no longer time to use a reliable tool. Or when there is no longer money to implement it. Considering that transactions can be challenged both 10 years and 3 years before bankruptcy - depending on the basis - it becomes clear that time is a very scarce resource. I'll show you with an example how it works:
Point No. 1 on the chart is a property purchase and sale transaction. This deal is 100% undeniable if 3 conditions are met simultaneously:
- The property is transferred to a non-affiliated person whom you see for the first and last time.
- The transaction is carried out at the market price (not at the cadastral price, not at the residual price, or at any other price - namely, at the market price!)
- The money for the transaction was received in full by bank transfer.
Here are the resources you will need to complete such a transaction:
- Time: the property should not be under arrest or interim measures, i.e. the deal is done in advance. And it is very desirable that the debtor does not have overdue obligations and lawsuits to collect them.
- Money: for running / paying taxes / renting a new home, etc.
- Nerves/personal comfort: you need to live somewhere, get discharged somewhere, register your children somewhere and solve a bunch of other organizational issues, etc.
If the client is ready for such expenses, then the deal will be ideal. If there are no resources to undertake the feat, you will have to move down the curve: compensating mechanisms will be developed that will reduce the level of costs. The negative consequence would be a shift to slightly riskier policies.
An example of how this works can be found in the article “Can a purchase and sale agreement be challenged?”
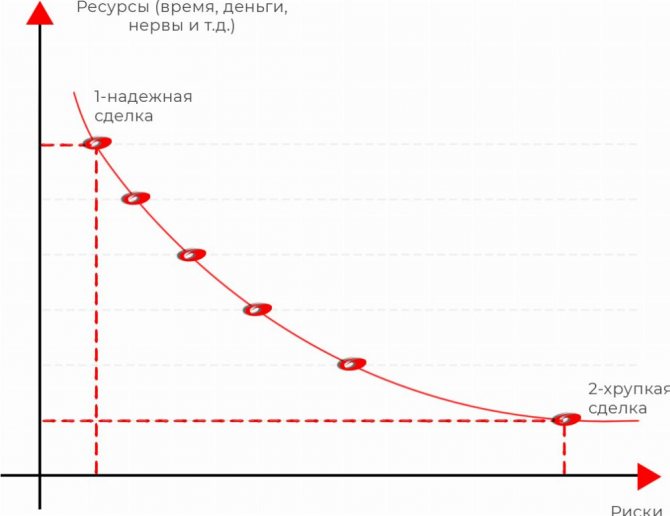
Point 2 is the most fragile deal option. In practice, this is a gift transaction: it is done when there are no resources: neither time (here, they will arrest you), nor money, and therefore is easily disputed for at least 3 years:
- The default gift is made in favor of an affiliated person (or do you seriously expect that the court will believe that you could have donated property to a stranger off the street?)
- At its core, this is a gratuitous transaction, which means it was made on non-market conditions, which means it deliberately causes damage to creditors.
- The law requires, of course, to prove a third circumstance - that the transaction was made when the individual had signs of insolvency. In fact, the courts turn a blind eye to this or take formal signs from the category: “the debt has not yet existed, but the debtor, having the proper qualifications and competence, could have foreseen its occurrence.”
All other options - no matter how you want them - will be on the curve between points 1 and 2.
Those that are more energy-consuming will be more reliable, others will be riskier. But in fact, both of them have the right to life.
For example, in our practice there was a case when we were able to defend transactions for donating apartments to children. There is nothing special to boast about, since all the courts were won only thanks to the creditor - he did not hire professional bankruptcy lawyers and preferred to gain personal experience in debt collection. As a result, he merged all the courts and gave up his last chances to reach the debtor’s property. And if there were no donation transactions, the apartments would have gone off the market long ago. You can read more about gift transactions as a tool for protecting personal assets in the article “How to challenge a gift agreement.”
How to find an individual’s property abroad
Let's take a closer look at how to find the property of a debtor - an individual.
Searching for the borrower's property: what can bailiffs do?
Let's consider the main ways to check the property status of a debtor by a bailiff:
- Checking bank accounts. To obtain such data, the bailiff can simply send a request to the bank, in response to which he will receive all the information available there about this client (if he opened an account there).
- Studying the income of the defaulter is another component of the search. It is clear that if they are high enough, then he most likely has a corresponding amount of material assets. It is not difficult to obtain such information when it comes to official work. But if he works unofficially, then this task will be more difficult.
Defense tactics
And finally, we will analyze specific transactions for the alienation of assets regarding their contestability, pros and cons.
The list of transactions below is not final, but contains the most commonly used methods of protecting property within the framework of Russian legislation. We will add new options as we are able and willing, but the best way to find out about them before your opponents is to order the development of a plan for structuring personal assets.
As part of this work, we analyze the current situation, possible risks, available resources and prescribe a step-by-step action plan. Will you move on it yourself or contract it out to us? This is the second question. The main thing is that you have it.
And now we invite Vasya to the studio and learn from his example.
Donation agreement
Complexity: 1/5
Price:
- For notarization - 0.5% of the contract amount or cadastral value, but not more than 20,000 rubles
- 2000 rubles - state duty in Rosreestr
With whom is it concluded: a gift agreement is a case when family ties play to one’s advantage. At the very least, the need to donate real estate can be explained by the desire to provide housing for children, parents, grandchildren or other family members. It will be more difficult for the court to believe in the purity of intentions to donate valuable property to a stranger Petya.
How to do it: The gift agreement is drawn up in writing. If a share in real estate is given, notarization will be required. The state duty is paid for registering the transaction in Rosreestr. Ready.
So, the gift has been given, the deal has been finalized, Rosreestr is aware. And also, creditors are aware that they are not at all delighted with such generosity. Especially given the fact that the mansion was donated during a period of unpaid debts.
Opinion: In our opinion, this is one of the lousiest ways to protect assets. A gift transaction is a gratuitous transaction. Such unprecedented generosity will be appreciated by the recipient, but not by the donor’s creditors.
If you need an example, leave your e-mail and we will send you the case law within an hour:
Moreover, an unsuccessful donation transaction could backfire if Vasya donates his only home. Thus, the real estate property will lose executive immunity. As a result, Vasya will lose both his property and the roof over his head.
There is a chance of survival only if the transaction was completed beyond 3 years to challenge it and provided that at the time of conclusion Vasya had absolutely no financial problems or debts.
Read more about the gift transaction here.
Alimony agreement
Complexity: 3/5
Cost: state fee for notarization - 1000 rubles
With whom is it concluded: with the parent or guardian of the child, or family members who are legally entitled to payments. But more often the option with children is used.
How it’s done: Vasya has children who are entitled to alimony. These could be children from a first marriage or in the current one.
Vasya remembered that he had never really bothered with child support, and so he decided to fulfill his parental duty. So, alimony can be paid monthly to a special account, or you can do better - calculate the alimony that is due to children under 18 years of age and pay this entire amount at once. Or give property commensurate to the payments to pay child support. For example, the same mansion. There is a tidy sum, and the children are provided with housing - everyone will be happy.
If there are no children, you can think about relatives who are entitled to payments. But here it is more complicated, because relatives must fall under certain criteria by law. Also, the payment period for them is not defined, which may also raise questions. In general, this is a case where you need to exploit children or your retired parents, especially if the law allows it.
Opinion: From the point of view of protecting assets between close people, this is one of the most reliable methods, provided that it is properly justified and executed, of course. Judge for yourself:
- it is necessary to conclude with family members, i.e. there is no need to go into someone else’s garden and look for strange people;
- Alimony can be both cash and property;
- If alimony has not yet been assigned, you can enter the register of creditors with a demand for payment. Or even file for bankruptcy of the debtor. At the same time, you will be in the first league of creditors.
But don’t rush to write everything off for your children; there is a downside. Despite the universal love for loved ones, it will not be possible to give them all your property. The courts have practice in reducing the amount of alimony based on the ratio of income level to the amount of payments, as well as the average cost of living per child in a specified region or country.
If you need an example, leave your e-mail in the form below.
Also, if Vasya officially has an income of 20,000 rubles, and he assigned alimony in the amount of 200,000 rubles or completely relinquished the mansion, the question arises: where does the money come from?
Read more about the alimony agreement here.
How to find the property of an individual by tax identification number
By law, the bank is obliged to transfer the amount of debt under the writ of execution immediately, which must be reported to the creditor or bailiff within three days from the date of fulfillment of the relevant requirements.
Thus, you will need to prepare two documents: a request to the tax office about the debtor’s current accounts and funds, and a request to the bank to write off funds from the debtor’s current account in your favor. After completing all the activities, all you have to do is wait for the collected funds to be credited to your account.
Legal provides full support in accompanying the procedures for satisfying the requirements for the writ of execution.
Marriage contract
Complexity: 3/5
Cost: notarization of the marriage contract - 500 rubles
Who is it with: spouse
How it’s done: Vasya takes his beloved Katya by the hand and signs a marriage contract (BD) with her, according to which all property acquired during the marriage will go to Katyusha. And then he files for bankruptcy. And this is a failure.
Even the Family Code takes into account that there must be an equal division of property between spouses. 50/50 is excellent, it works both with and without a database. But then there is no point in using the database.
60% to the spouse, 40% to the debtor - no longer worth it.
70% to 30% and above - the marriage contract will definitely be challenged.
Opinion: For the database to actually start working, it needs to be concluded and divorced.
The fact is that the statute of limitations for challenging the database begins to be calculated only from the moment of official divorce - after all, it is at this moment that the actual division of property occurs and one of the spouses may realize that his rights have been infringed.
If you need an example, leave your e-mail in the form below.
At the same time, it would be good to conclude a BD not one day before filing a divorce application. Then it can take into account both the actual assets and those that will appear in the future. And when this property appears, get a divorce safely.
If the division of property is also organized with a show in the form of a trial, it’s absolutely beautiful. When Vasya ends up in bankruptcy, there will be +1 argument in favor of the fact that the division of property took place according to the law and this was certified by the court. But this is already serious aerobatics, which requires temporary resources.
Read more about the prenuptial agreement here.
Property division agreement
Difficulty: 3 out of 5
Price:
- state duty for notarization - 0.5% of the transaction amount, but not less than 300 rubles and not more than 20,000 rubles;
- registration of the agreement in Rosreestr - 2000 rubles.
Who is it with: spouse
How it’s done: Vasya dearly loves Katya and flatly refuses to divorce her. But the mansion needs to be saved. Vasya transfers the mansion to Katya, then registers the deal with Rosreestr. But the trouble is, he has no other liquid property. At all.
And as we remember, the separation agreement falls under distribution on exactly the same grounds as the marriage contract. But unlike the database, it has a peculiarity - the agreement comes into force from the moment of its registration in Rosreestr. And this can be done in marriage, while continuing to live your usual life.
If you need an example, leave your e-mail and we will send you the case law:
There is one thing - if it is possible to include in the database both existing property and that which will appear in the future, then the agreement indicates only the property that actually exists on the day of its conclusion.
Opinion: The method is good if it respects the principle of equivalence during division: by analogy with alimony and BD, it will be difficult for the court to believe that due to the influx of feelings, Vasya gave all the property to his wife, even his beloved.
Read more about the agreement here.
Production cooperative
Complexity: 5/5
Price:
- state duty for legal registration. persons - 4000 rubles
- legal services for document preparation - from 0 to infinity.
- annual expenses for maintaining the organization
What you will need: Vasya and at least 4 more people. There may be family, friends or strangers. But it’s better with friends - it’s calmer.
How it’s done: Vasya finds a circle of like-minded people, at least 4 more people. These five form a production cooperative, to which everyone must contribute - some with property, some with labor - the so-called shares.
Moreover, the core of this idea is an indivisible fund into which personal property can be contributed. The strength of this fund is that it cannot be levied against the participant’s personal debts, be they credit debts or subsidies. At the same time, if the PC itself has its own debts, then the property from the indivisible fund will have to say goodbye.
Opinion: Yes, the indivisible fund cannot be levied against the debts of our Vasily, but do not forget that creditors can challenge the very transaction of transferring the property of an individual to this very fund. Therefore, the key resource for its competent implementation is a reserve of time and high-quality elaboration of small details.
In addition, it is advisable for a production cooperative to conduct at least some activity. Otherwise, questions may arise for him.
Well, here’s the cherry: having contributed property to an indivisible fund, you cannot take it away from there whenever you want. Only in case of liquidation of the PC.
Read more about the production cooperative here.
The debtor has no property
Good evening, Nina Igorevna, if he is registered with the Employment Center, then you can try to deduct him from unemployment benefits, that is, the Bailiffs must deduct him, but if not, then nothing, either he receives some kind of benefit or payments from the state. Doroshenko Elena 8908329964
Elena, the bailiffs can do this without you. Article 46. Return of the writ of execution to the claimant after the initiation of enforcement proceedings 1. The writ of execution, according to which the collection was not carried out or was made partially, is returned to the claimant: 4) if the debtor does not have property that can be foreclosed on, and all those accepted by the bailiff measures allowed by law to find his property were unsuccessful; But Spanish production, as you noticed, does not stop, isp. the sheet is returned to the claimant.
01 Aug 2020 stopurist 185
Share this post
- Related Posts
- RSA database official website diagnostic card check
- Apartment renovation: how much noise can you legally make?
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation article continuous work experience
- Article number of voluntary dismissal 2020
Contract of sale
Complexity: 4/5
Preparation cost:
- fees for notarization of the contract - 0.5% of the value of the property being sold under the contract, but not less than 300 rubles. and no more than 20,000 rubles
- State duty of Rosreestr for registration of a real estate transaction - 2000 rubles
With whom it is concluded: with anyone, but ideally a non-affiliated buyer is needed
How it’s done: Vasya decides to sell his mansion. By “sell” we mean concluding a contract, registering the mansion in the name of the buyer and arranging the circulation of money in nature. The deal is made with the brother. The mansion's market value is estimated at 30 million, and is sold for 10. The money is transferred in cash.
These are the top mistakes when concluding a policy. Moreover, in addition to the affiliation of persons, the fact that Vasya’s brother works as a mechanic at a factory with a salary of 40 thousand per month will play a role. Where did he get 10 lyams for a mansion, despite the fact that he still lives and is registered with his mother?
If you need an example, leave your e-mail and we will send you court practice on the use of PrEP:
Opinion: This is one of the most popular ways to protect assets. And also costly, because you have to spend real money. At the same time, the policy can be challenged on a number of grounds, and each of them needs to be examined under a magnifying glass. In short, it is important to remember the following rules:
- if the transaction is with an affiliate, it is important to prove the buyer’s solvency and the existence of a real transfer of money;
- If the property was sold at a reduced value, it will be important to provide evidence that the price was justified. For example, the roof of the mansion was leaking, there was no plumbing, and the gas pipeline had not yet been installed;
- if there was no real transfer of money...oh, it’s better not to do that, but if you do, you need to bother so that it is on paper with a further explanation of where the money came from and the buyer and where it went from the seller. For example, the money came in cash, and that’s how much went to the children, that’s how much to live on, but that’s how much good Vasya paid to the creditors.
Read more about the purchase and sale transaction here.
Pledge agreement
Complexity: 3/5
Preparation cost:
- a bunch of different government duties and rates depending on the type of property, transaction and with whom the contract is concluded. See the table in the article on the topic.
What you will need: Vasya, collateral and lender
How it’s done: Vasya invites his friend Petya to give him money as collateral for the mansion. Considering that we are talking about real estate, a visit to Rosreestr will be required to register the transaction. So, Petya gives money, Vasya gives a mansion. As expected, Vasya stops paying and the deposit goes to Petya. But if everything was so simple, they would live on pledges alone.
If Vasya goes bankrupt, his creditor will need to be included in the register in order to retain the priority right to the pledge. If it does not turn on, you will have to say goodbye to the collateral in favor of other creditors.
Moreover, if the loan amount and interest are lower than the value of the collateral, then after selling the property, the money will go first to a friendly lender, and then will be distributed to other people in need. The defense will be so-so
Opinion: With the help of collateral, you can not only protect property, but also directly participate in bankruptcy. But there is also a downside.
A lopsided pledge with the wrong creditor, property and a dubious transaction amount is a good chance for the pledge agreement to be declared invalid, followed by removal from the register of creditors and loss of the pledged item.
If you need an example, leave your e-mail and we will send you a case law on the application of a pledge agreement:
Read more about collateral transactions here.
What to do if bailiffs describe property that does not belong to the debtor
But in practice, it happens that the following picture is observed: the bailiff service comes to you and takes away your “hard earned”, and not the debtor at all. It becomes important to figure out how to prove to the bailiffs that the property is yours and not the debtor’s.
Next, the items specified in the inventory are assessed, and only after this the right to arrest arises. The appraisal process takes place in the presence of the debtor and ends with his consent; if it is absent, the owner of the property has the right to invite independent appraisers. The legality of the FSSP’s actions is prescribed in the legislation:
We recommend reading: How to Pay Utilities Without Penalties
Bankruptcy of individuals faces
Complexity: 4/5
Price:
- legal costs for bankruptcy proceedings - from 0 to infinity
- costs for a “friendly” lender - depending on the chosen instrument
- costs of an asset protection transaction - see paragraph above
With whom is it concluded: the bankruptcy procedure is initiated by the debtor himself or through friendly creditors
How it’s done: Vasya understands that creditors are already on the doorstep and there is no time to save the mansion with collateral, much less with a production cooperative. There is only one thing left - personal bankruptcy. But there can be problems with it too. If he filed for bankruptcy at a time when the subsidy is still shining, the task will be to complete the procedure as quickly as possible. If the debt is already hanging, the only question will be the volume of losses.
In all of these cases, having a friendly lender will solve the problem. If you have one with him, you can organize your bankruptcy and protect your property.
Opinion: personal bankruptcy is the last opportunity to save property, or at least part of it. But do not forget that the claims of “friendly” creditors can also be disputed and not included in the register of claims.
If you need an example, leave your e-mail and we will send you the case law:
Thus, with active resistance from creditors, the procedure will take a couple of years, at least, and will require qualified forensic specialists. Therefore, if someone tells you that they will organize bankruptcy for you with a fixed fee of 15,000 rubles per month and everything will be top-notch - be sure to sign up, the main thing is not to forget to say
mantra: “a sucker is not a mammoth, a sucker will not die out.”
Read more about this tool here.
How to seize the debtor's property
If the defendant has a notice in hand and considers the punishment to be unfair, then the help of an experienced lawyer is needed. A lawyer will be able to come up with many ways to mitigate this situation. For example, he will be able, if there is an insignificant evidence base, to prove that the things subject to seizure were transferred for the use of other persons.
SSP officers can seize property and property only in the presence of enforcement proceedings. The main condition for carrying out such actions is the decision to initiate proceedings based on a decision of the court, the Federal Tax Service, the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate and other government agencies with authority. Such a document is considered binding for the debtor.






