There is no legal act on how to study a citizen’s solvency. Since October 2020, citizens have had the opportunity to become debt-free. An individual may declare insolvency. But nothing is said about how the financial condition of an individual should be analyzed during bankruptcy.
The bankruptcy procedure for legal entities has been clarified. Government Decree No. 367 of June 25, 2003 is in force. Arbitration managers use financial statements data in their analysis. This is part of one of the stages of bankruptcy of an individual.
How to analyze the financial condition of an individual during bankruptcy?
Information from the debtor's financial statements is taken into account.
Five sources of information that are taken into account when analyzing solvency:
- 2-NDFL certificates;
- agreements concluded with banks and other counterparties;
- responses to requests received from the territorial department of Rosreestr, State Traffic Inspectorate;
- lists of creditors;
- information from court materials.
Official data obtained from government organizations are taken into account.
4 goals that the financial analysis of an individual has in bankruptcy:
- Decide whether the debtor will be able to repay the debts.
- Justify whether it makes sense to start bankruptcy proceedings.
- Find out whether the individual’s funds are sufficient to pay legal costs and pay for the services of a financial manager.
- Clarify the reasons for bankruptcy to find out whether it is fictitious.
Articles No. 67 and 70 of the Bankruptcy Law define the purposes of the analysis.
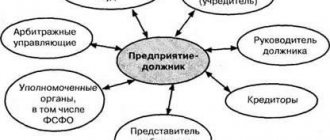
Enterprise bankruptcy procedure
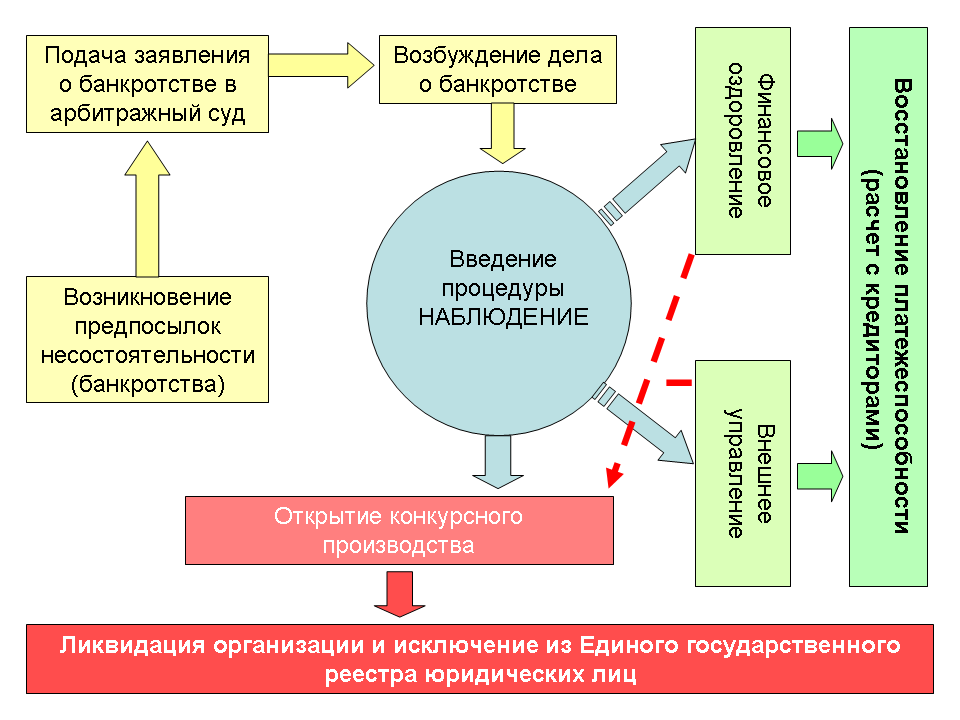
Scheme of the bankruptcy procedure for an enterprise
The procedure begins with a bankruptcy petition.
Applications are accepted both directly from companies and from lenders in order to return their investments. After the application is accepted for consideration by the arbitration court, the veracity of the information and the appropriateness of the application are analyzed. Then, following the law, the court appoints the main procedure out of four possible ones - observation. According to the rules, the period for completing this procedure is no more than seven months.
The main task of the observation procedure is the safety of material assets. This is necessary for an objective consideration of the financial situation of a legal entity and for an honest settlement of debts to creditors. For the sake of objectivity, temporary management is established for the duration of the observation procedure.
The purpose of analyzing the financial component is to determine whether it is possible to restore the company's solvency. Another main function of the procedure is the formation and systematization of creditors’ requests. From the moment the temporary management comes into force, the creditor sends the temporary management to the arbitration court, in this way the total amount of the company's debt is established.
Decisions on creditors' claims are made by the court separately, as are applications from creditors. In this way, the validity is determined and a court verdict is made on the advisability of including it in the register of claims.
Meeting of creditors
The first stage of the observation procedure. At the meeting, creditors consider the possibility of further actions (whether financial recovery or external administration is possible, or immediately proceed to bankruptcy proceedings) and whether it will be possible to reach a peace agreement between creditors and the insolvent organization. The meeting also installs a new leader who will manage subsequent processes.
Financial recovery
Firstly, during this procedure, the organization continues to function despite some restrictions. For example, he cannot independently decide on reorganization issues or enter into transactions without the knowledge of the committee. Secondly, the court sets deadlines for repayment of all debts and the duration of this procedure. The duration of the procedure cannot exceed more than two years; if during this time there are unresolved issues, then the meeting of creditors applies to the court to change the procedure.
External control
In this case, all the old management will be removed from management and a new one will be appointed. An important feature is that from the moment the new management is introduced, a moratorium is established on all debts of the organization that were before it. This gives additional time to settle your financial situation. The duration of this procedure is from 18 months to six months, during which time a plan is drawn up according to which the new management will operate.
Bankruptcy proceedings
The last procedure is introduced if the above measures do not help. From the moment bankruptcy proceedings begin, the company is officially considered bankrupt. The purpose of the procedure is to liquidate the organization and cover all its debts at the expense of its own inventory.
The execution period is six months. During this period, an inventory of property and monetary valuation is carried out. Due to this, all claims of creditors and investors are covered.
Once they are satisfied, the arbitration court issues a verdict to complete the bankruptcy proceedings stage. A corresponding document is created for the registration authorities, they, in turn, deregister in the unified state register and mark the liquidation of the legal entity.
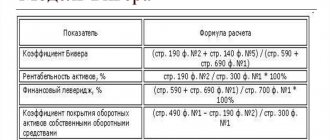
Formula for calculations
Kpt = Liabilities as of the current date/average income for the month.
CPT shows whether a citizen’s income allows him to repay the debt.
Example of calculations. Debt of Petrov A.S. on the loan is 1,029,141 rubles 55 kopecks. Salary of Petrov A.S. is 15,000 rubles. Let's determine how long it will take A.S. Petrov to pay off his debts.
Kpt=1,029,141.55/15,000=68.6.
It will take sixty-eight months for Petrov A.S. paid off the bank. The time period exceeds five years. Calculations are made on the condition that the income of Petrov A.S. will not decrease.
Methods
Order of the Federal Office for Insolvency (Bankruptcy) under the State Property Committee of Russia No. 31 -r approved the principles (provisions) for assessing the real situation of the debtor organization, as well as the principles for considering and confirming the unstable reporting structure of a legal entity.
The analysis is based on determining current liquidity and coverage ratio.
The balance sheet is usually recognized as unsatisfactory, and the company is on the verge of bankruptcy, if any of the two indicators is close to a certain value:
- the current liquidity ratio at the end of the reporting period is less than 2;
- coefficient of provision with own working capital – below 0.1;
In case of poor financial condition, the coefficient of loss of solvency is additionally considered. This is necessary to establish the realistic time it will take to restore the organization's sustainability.
What are external factors?
These are circumstances that do not depend on the citizen and bankruptcy of the individual occurs.
8 external factors influencing the debtor’s solvency:
- Economic condition in the region where the citizen lives.
- Cost of the minimum food basket.
- Average income of the population.
- Level of price growth.
- Number of unemployed.
- Profit that companies receive.
- Amount of taxes. Taxes on transport, property, income, and land are taken into account. It calculates how much citizens should contribute to the budget.
- State of the labor market. It takes into account how much demand the citizen’s profession has. Opportunities to earn funds to pay off the loan are assessed.
When a financial analysis of an individual in bankruptcy sample is compiled, all of the listed factors are taken into account. As a result, the financial manager makes a conclusion about whether there is a chance of repaying the debt. All property owned by a citizen is taken into account. It takes into account when the property was purchased and its condition.
Bankruptcy assessment
There are three generally accepted ways to assess bankruptcy:
- Using methods of formalized and informal criteria. In this method, factors are taken into consideration that will directly affect the financial condition (debt to creditors, liquidity level, outstanding receivables) and circumstances that actually reflect deterioration (credit refusals, loss of clients, dismissal of key specialists).
- Forecasting with methodological explanations for identifying signs of insolvency. This method is designed to early identify bankruptcy trends using the Beaver ratio and divide bankruptcy into different stages.
- Construction of multifunctional mathematical models , function - insolvency indicator, variables - the value of the intra-financial state. There are many models, for example, Altman, Lis, Taffler.
Example of property value calculations
The financial manager compiled a list of A.S. Petrov’s property.
| No. | Property name | Price in rubles including wear and tear |
| 1 | LCD TV Samsung UE32J4000AU | 18 000 |
2 | Coffee makerDelonghi EC 680 M/R/BK DEDICA | 13 000 |
| 3 | Vacuum cleaner Karcher DS 6.000 | 16 500 |
| 4 | Living room wall TriYa Jazz TD-211.01 Cuthilt, Texit | 13 100 |
| 5 | Total property value | 60 600 |
The Federal Cadastral Chamber provided a response to the request that there is no real estate owned by A.S. Petrov.
The State Traffic Inspectorate reported that there is no vehicle registered to the citizen.
Conclusions, which include a sample financial analysis of an individual in bankruptcy:
- Will the citizen be able to pay off creditors?
- Is there enough property to pay for the services of a financial manager and pay legal costs?

Find out the cost of writing such a paper!
Reply within 5 minutes! Without intermediaries!
Content
- Introduction
- Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations for assessing financial condition
- 1.1. Contents, goals, objectives of financial analysis
- 1.2. The concept of enterprise bankruptcy
- 1.3. Methods for diagnosing financial condition
- Chapter 2. Assessment of the financial condition of Panorama LLC
- 2.1. General characteristics of the enterprise's activities
- 2.2. Analysis of financial indicators of Panorama LLC
- 2.3. Assessment of the probability of bankruptcy of Panorama LLC
- Chapter 3. Development of measures for the financial recovery of Panorama LLC
- 3.1. Financial recovery plan for Panorama LLC
- 3.2. Economic justification for measures to strengthen the financial condition of Panorama LLC
- Conclusion
- List of sources used
INTRODUCTION
The relevance of the chosen topic is that at present, in market conditions, the main factor in the stable state of an organization is its financial stability as an indicator characterizing the financial condition of the organization. A bankrupt enterprise undergoing bankruptcy proceedings, regardless of the complexity of the situation, is obliged to pay taxes and other obligatory payments. Thus, in addition to previous debts that arose before being declared bankrupt, the organization continues to have new debts on mandatory payments even after the opening of bankruptcy proceedings. Moreover, the tax authorities believe that they have the right to satisfy demands for these payments out of turn.
Practice shows that sustainable organizations are more focused on adapting their activities to difficult market conditions. The financial policy of such organizations is aimed at identifying and optimally using their competitive advantages in the market. The low financial stability of a large part of Russian organizations is associated not so much with a shortage of financial resources, but with the inability to manage these funds. To ensure the effective functioning of any organization, competent management of its activities is necessary, which is largely determined by the ability to analyze it.
With the help of analysis, trends in the development of the organization are studied, factors changing the results of its activities are examined and assessed, plans and decisions are formed and justified, their implementation is monitored, the results of the organization's activities are assessed, an economic strategy for the development of the organization is developed, ways and reserves for increasing the efficiency of activities are determined. The basis of any assessment of the effectiveness of organizations is formed by various criteria with a certain system of indicators. Criteria express a specific goal that must be fulfilled during the business process.
The main principle of analysis at an enterprise is the principle of economy, efficiency and effectiveness of the process, i.e. carrying out the analysis in such a way that it provides a complete and comprehensive study with a minimum of costs for its implementation. This is achieved by using the latest analysis techniques, computer technologies, methods of collecting and storing information.
Despite the differences in methods, almost the entire range of methodological approaches to assessing the financial condition of an organization includes the calculation of a system of financial indicators in the following areas: indicators of liquidity and solvency, indicators of financial stability, indicators of business activity, indicators of profitability (profitability). Issues of optimizing a set of indicators that most objectively reflect trends in the financial condition of an organization are resolved by each author independently.
In practice, each enterprise is also independent in choosing a system of indicators. Defining the concept and boundaries of financial sustainability of organizations is one of the most important economic and practical problems in modern conditions. Insufficient financial stability can lead to the organization's insolvency and bankruptcy. The financial position of organizations determines the prospects for its development, its characteristics, and determines the competitiveness of the organization. In a market economy, organizations are faced with the task of independent planning, control, evaluation and analysis of their activities.
The main goal of almost all organizations has become survival in market conditions and obtaining maximum profit from their activities. This is influenced by many factors, both external and internal, since increasing the economic efficiency of the organization’s activities becomes its primary task. If an enterprise is stable and sufficiently solvent, then this gives it certain advantages in the face of other organizations of the same niche (for example, in the person of creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.).
The degree of stability of an organization shows its independence from sudden changes in market conditions and gives a greater chance of not being on the verge of bankruptcy. Various problems and difficulties arise in the financial condition of organizations, which can be combined into two main manifestations: low liquidity (cash shortage) and insufficient return on capital invested in the enterprise (low profitability).
The theoretical basis of the work was the works of Russian scientists devoted to the study of problems of financial stability of organizations, various organizational and legal forms, Belyaev A.A., Korotkova E.M., Rodionova V.M., Stoyanova E.S., Fedotova M.A. ., Sheremeta A.D. and others. A significant contribution to the solution of the problems under consideration was made by foreign scientists J. Keynes, J. Neumann, J. Hicks, I. Fisher.
The purpose of the dissertation research is to develop measures based on the results of financial analysis to bring the organization Panorama LLC out of a financial crisis.
Research objectives:
- consider the theoretical basis for diagnosing the bankruptcy of an organization;
- conduct an analysis of the financial condition of Panorama LLC;
- develop a project of measures aimed at stabilizing the financial condition of the organization and bringing it out of the crisis.
The object of the study was the organization Panorama LLC.
The subject of the study is the methodology for diagnosing the bankruptcy of an organization.
The methodological basis of the study was regulatory documents, educational materials, periodicals and electronic sources on the topic under study. The study used such general scientific research methods as: techniques of a systematic approach and analysis, which made it possible to ensure the reliability of the financial analysis and the validity of the conclusions.
The theoretical basis of the study was the work of domestic and foreign scientists on financial analysis and financial management.
The sources of specific information for the study are: the financial statements of the enterprise, Form No. 1 - “Balance Sheet” and Form No. 2 “Report on Financial Results”.
The main ideas and recommendations in the dissertation are formed taking into account the possibilities of their practical implementation and based on analysis.
Scope and structure of the dissertation. The dissertation consists of an introduction, three chapters, a conclusion, appendices and a bibliographic list of sources.
The introduction substantiates the relevance of the dissertation research topic, defines the object and subject of the research, reveals the purpose and objectives, as well as practical significance.
In the first chapter, “Theoretical foundations for assessing the financial condition and bankruptcy of enterprises,” the following were studied: the content, goals, and tasks of analyzing the financial condition; the main stages and methods of analyzing financial condition were considered, and the economic essence was revealed and methods for assessing bankruptcy (insolvency) were identified.
In the second chapter, “Assessment of the financial condition of an enterprise using the example of Panorama LLC,” the general characteristics of the enterprise are studied, an analysis of the financial stability of the enterprise is carried out, and basic indicators are analyzed.
In the third chapter, measures are developed to bring the enterprise out of crisis.
In conclusion, the results of the study are summarized, conclusions and proposals of a scientific and practical nature are formulated.
When writing the work, literature was used, including civil legislation, bankruptcy legislation, as well as methodological materials on analysis and articles by practicing lawyers and economists considering the problems of bankruptcy and crisis management.
Chapter 1. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK FOR ASSESSING FINANCIAL STATUS
1.1. Contents, goals, objectives of financial analysis
One of the important conditions for competent management of an enterprise’s financial resources is an analysis of its financial condition. The content and main goal of such an analysis is to assess the financial condition and identify opportunities for increasing the efficiency of the business entity.
The financial condition of an enterprise is a set of indicators that reflect its ability to pay off its debt obligations. Financial activity is the process of formation, movement and ensuring the safety of the property of an enterprise, control over its use.
The financial condition of an economic entity can be characterized by a number of indicators that reflect the process of formation and use of its financial resources. We can say that the assessment of the financial condition of an enterprise reflects the final financial result of its activities. Any investment decision is based on this assessment. According to A.D. Sheremeta: “Assessing the financial condition of an enterprise is an ambiguous operation. At the same time, many users need a reliable and objective assessment of the financial condition of an enterprise” [21, p. 54].
All this determines the importance of conducting a financial analysis of an enterprise. Financial analysis is an indispensable element of both financial management and its economic relationships with partners, the financial and credit system and the state.
The assessment of the financial condition is carried out in order to: increase the effectiveness of the current management of the enterprise; valuation of securities when buying and selling shares of an enterprise on the stock market; establishing the value of the enterprise in the event of its purchase and sale in whole or in part; enterprise restructuring; developing an enterprise development plan; assessing the creditworthiness of the enterprise and the value of collateral in case of lending; determining the value of assets for insurance in anticipation of losses; making informed management decisions; implementation of an investment project at the enterprise.
The main goal of financial analysis is to obtain the most informative parameters that can give an objective and accurate assessment of the financial condition of the enterprise, its financial performance, changes in the structure of assets and liabilities, accounts receivable and payable. In addition, the management of the enterprise may be interested in both the current financial condition and its forecast for the near or more distant future, i.e. expected parameters of financial condition.
Based on the goal, when analyzing the financial condition, you need to solve the following problems:
- based on an analysis of the relationships between various indicators, it is necessary to assess the implementation of the plan for the influx of financial resources and the effectiveness of their use in terms of improving the financial condition;
- building models that help assess and diagnose financial condition, as well as conduct factor analysis;
- forecasting possible financial results, based on the current conditions of economic activity and the developed model for assessing and diagnosing the financial condition;
- development of specific measures aimed at strengthening financial condition [10, p. 33].
The basis for assessing financial condition, as well as financial management in general, is the analysis of financial statements. The purpose of analyzing current financial statements is to determine the real financial condition of the organization as of the assessment date. Since the book value of assets, as a rule, differs from their market valuation, the accounting data is adjusted to determine the market value of the assets.
According to the recommendation of O. V. Efimova: “when analyzing the financial statements of an organization, it is imperative to normalize them, i.e. make adjustments for various extraordinary and one-time items of both the balance sheet and the statement of financial results and their use, which were not of a regular nature in the past activities of the organization and are unlikely to recur in the future" [19, p. 54].
Based on the work of scientists, we will consider their vision of the financial condition of the enterprise and approaches to its assessment.
According to A.D. Sheremet and R.S. Saifulin: “The financial condition of an enterprise is characterized by the composition and allocation of funds, the structure of their sources, the rate of capital turnover, the ability of the enterprise to repay its obligations on time and in full, as well as other factors.” There are seven levels of indicators for the purpose of assessing the financial condition of an enterprise” [41, p. 77].
G.V. Savitskaya believes that: “The general assessment of the financial condition of an enterprise is based on a whole system of indicators characterizing the structure of the sources of capital formation and its placement, the balance between the assets of the enterprise and their placement, the balance between the assets of the enterprise and the sources of their formation, efficiency and intensity use of capital, solvency and creditworthiness of the enterprise” [11, p.62].
V.V.Kovalev Fr. Offers nine levels of indicators for analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise [21, p. 34].
When assessing the financial condition for the short term, indicators are given to assess the satisfactoriness of the balance sheet structure (current liquidity, provision of own funds and the ability to restore (loss) solvency.
M.I. Bakanov considers the main indicators of the financial condition of the enterprise (total capital, assets, liabilities, and so on) and gives the procedure for determining them, and also makes an analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise based on ratios [10, p. 21].
N.P. Lyubushin understands financial condition as “the ability of an organization to finance its activities. Financial condition is characterized by the availability of financial resources necessary for normal functioning, their appropriate placement and effective use, financial relationships with other legal entities and individuals, payment and creditworthiness, financial stability.” This is the most complete definition. He proposes a methodology for analyzing financial statements, in which he identifies seven main areas: horizontal (temporal), vertical (structural), trend analysis, analysis of relative indicators (ratio), comparative (intra-business, inter-business), factor analysis and analysis based on stochastic models [ 26, p.28].
Currently, many methods have been developed for analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise, covered in the economic literature by various authors. But still, the results of the analysis of popular methods cannot always be used to make further management decisions. It is necessary to consider the features of various methodological approaches and evaluate their applicability to the analysis of the financial condition of an operating enterprise. Methodology for analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise, proposed by Sheremet A.D. and Saifulin R.S., taken as a basis.
Methodology of Sheremet A.D. and Saifulina R.S. proposes to calculate such financial ratios as the profitability coefficient, the coefficient of management efficiency and market stability [42, p. 25].
It should be noted that the main goal of this methodology when analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise is to ensure and improve the efficiency of management and assessment of financial stability.
Next, we will consider the methodology for analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise, proposed by L. T. Gilyarovskaya [11, p. 39].
When analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise using this methodology, the following stages are distinguished:
- the following financial ratios are calculated: liquidity, solvency, profitability, coverage of obligations with own funds;
- the values of the financial ratios of the analyzed enterprise are compared with the average values for the industry: an assessment is made of the degree of liquidity, solvency, profitability, and security of obligations;
- The dynamics of the above coefficients are analyzed and the long-term trend is determined.
- Percentage analysis of statements for several years is carried out (vertical and horizontal analysis of the balance sheet by item is combined).
- an index analysis of reporting for several years is carried out (based on the calculation of basic and chain indices for the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet).
Considering the various approaches of scientists to the procedure for analyzing and assessing the financial condition of an enterprise, it can be noted that the authors propose to first carry out an express analysis of the financial activities of the enterprise. But, despite the wide variety of approaches to the procedure for conducting analysis, in the works of most scientists there is a mandatory presence of the main six levels of indicators: a general assessment of the dynamics and structure of balance sheet items; liquidity; solvency; financial stability; profitability; business activity.
The main characteristics of the financial and economic activities of an enterprise in a market economy are solvency and financial stability. The enterprise will have advantages over competitors in attracting investment resources, when obtaining loans, when choosing suppliers and recruiting qualified personnel, if it is financially stable and solvent.
The work will use the methodology proposed by Sheremet A.D. and Saifulin R.S. At the same time, the indicators that will be used in the practical part of the work at each stage of the analysis will not be limited to the authors’ data, but will use a comprehensive range of methodological tools for assessing financial condition, which we will consider in the next paragraph.
1.2. The concept of enterprise bankruptcy
Business is a type of activity that in most cases is associated with crisis risks. The company may find itself in debt and not have the resources to pay creditors. But in this case, Russian legislation has established a procedure within which the company and its partners can still try to find a common understanding of the problem and develop solutions to the current situation.
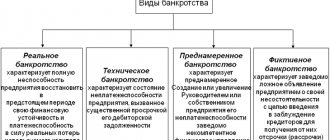
So, today we will talk about bankruptcy. Despite the unflattering name, it is this procedure that can help a company overcome a crisis. Therefore, the assessment of bankruptcy in the Russian business community is not always negative. Moreover, in the foreseeable future, individuals will also be able to take advantage of the opportunities that the official recognition of a debtor as insolvent opens up (the corresponding law has been signed).
How can bankruptcy really help solve the problems of business and citizens? Definition According to a definition widespread among Russian lawyers, bankruptcy is the inability of an individual or legal entity with a debt to fulfill obligations to the creditor in full [17, p. 28].
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation has a number of additional criteria that predetermine whether a subject of civil legal relations receives the appropriate status. For example, the key authority that must recognize bankruptcy is the court. There are, of course, unofficial options for defining the term in question.
The concept of bankruptcy can be interpreted by many lawyers and entrepreneurs much more broadly than when compared with court decisions provided for by law. This term can be understood, for example, as a synonym for inefficiency in doing business. That is, the company, perhaps, does not owe anything to anyone, and the company’s own reserves are used to pay off current expenses.
However, current results and those seen in the near future may give an outside observer, investor, or competitor a reason to call the company bankrupt. But such an opinion of market players will not have official significance.
What kind of obligations may constitute the subject of a non-dischargeable debt in a scenario in which the concept of bankruptcy is associated with a corresponding court decision? In general, this is a sum of money transferred by the creditor to the debtor on the terms of a civil transaction or other grounds provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Also included in the obligations is the payment of taxes, fees, and contributions to state funds established for certain categories of citizens and legal entities in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation [18, p. 26].
Russian lawyers, when defining them, often turn to the wording of special legislation. In particular, a number of legal acts in force in the Russian Federation state that it is lawful to talk about bankruptcy, first of all, upon discovery of the fact that the subject of legal relations is not able to fulfill the payment obligations assigned to it for three months or more.
We noted above that, according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the status of the subject in question is established by the court. The fact is that previously the relevant authority could not accept an application from creditors for the debtor to be recognized as an insolvent payer. Of course, we are talking here about the key official sign of bankruptcy. The debtor may be de facto insolvent, however, he can receive legal bankruptcy status only after the case is considered by the court.
There are also indirect signs of bankruptcy, which, as a rule, do not have official significance, however, they suggest that an enterprise or individual with debt obligations is highly likely to receive the appropriate status. Their exact nature will depend on the type of company.
If this is, for example, a large enterprise, then signs indicating problems with debt servicing may include mass layoffs of employees and a decrease in the company’s market share. Diagnosis of bankruptcy Russian lawyers identify a number of tools that can be used by both competent government bodies and interested private structures in order to identify the probable bankruptcy of an enterprise [15, p. 23].
Let's name them.
Firstly, this is financial monitoring. Due to the fact that the figures reflecting the monetary aspect of a business are often secret, this tool is usually used by government agencies due to the permitted access to the relevant confidential information.
Secondly, this can be an analysis of reporting - mainly accounting. The study of information about current fixed assets, payment transactions and other activities reflecting the activities of the company is carried out.
Thirdly, the number of activities through which the possible bankruptcy of an organization can be identified includes external audits, as well as research into their results. It should be noted, however, that in practice, regulatory authorities and other interested subjects of legal relations most often can gain access to the necessary information reflecting the activities of a company in terms of financial stability, provided that their intentions are coordinated with the object of study.
If the company's management wants to avoid a possible bankruptcy case, then it is possible that access to the desired information for third parties or certain departments will be closed.
How much will litigation cost?
Bankruptcy is not a free procedure. The manager works for money. Clause 3, Article 20.6 of the Law “On Insolvency” established the amount of remuneration in the amount of 25 thousand rubles. And declaring an individual bankrupt will also cost money.
Costs for consideration of the case in court:
- The duty is six thousand rubles. The amount is established by subparagraph 5 of paragraph 1 of Article 333.21 of the Tax Code.
- Payment for postage.
- Publication of information about insolvency.
- Additional payments to the manager.
What does false failure mean?
This is a deception of creditors. A citizen can repay the loan, but does not want to. Trying to get the court to establish the fact of insolvency. Deception can be costly for the debtor.
Important! We do not recommend starting insolvency proceedings if you have the means to repay the loan. You will have to answer according to the law for deception.
Responsibility for defrauding creditors:
Administrative. Clause 1 of Article 14.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses established a fine of one thousand to three thousand rubles. A citizen will get off with a fine if the amount of damage does not exceed one million five hundred thousand rubles.
Criminal. Article 197 of the Criminal Code establishes penalties for breaking the law.
- a fine of one hundred to three hundred thousand rubles;
- deprivation of liberty;
- forced labor.
The judge determines the punishment for the offender.