What is a company's net debt (Net Debt)
Home page ➞ Stock market info ➞ A little knowledge about the stock market ➞ What is a company's net debt (Net Debt)
Net Debt is used in more detailed (objective) multipliers - EV (Enterprise Value), Net Debt/EBITDA, etc.
Short- and long-term debt burden is taken into account in the company's balance sheet, but is not always included in the multiplier formula. For example, market capitalization does not take it into account, which is not entirely objective. Whatever the value of the company, if its profits are used to pay off debts, then its real value is several times lower.
What is a company's net debt (Net Debt)
Net Debt represents all the company's debt to internal and external creditors, adjusted for cash and investments. Net Debt differs from total debt (another financial indicator for analyzing a company's valuation) in that it reflects the actual picture. The amount of debt a company has alone is not an indicator of its debt burden, since the company may have the resources to pay it off. Therefore, total debt is adjusted to liquid assets (cash and short-term investments), which can be instantly used to pay off debt.
To explain it in very simple terms, let’s say... Petya owes Vasya 100 rubles, but Petya has a stash in his pocket for a rainy day in the amount of 70 rubles. As a result, Petya’s net debt is 30 rubles, since Petya can use his nest egg to pay off the debt.
Formula for calculating the multiplier on the balance sheet of foreign companies:
Net Debt = Total Debt – Cash&Cash Equivalents
Due to differences in accounting standards, the formula for calculating net debt of Russian companies is more complex:
Net Debt = short-term loans and borrowings + long-term loans and borrowings - cash and cash equivalents = Debt - Cash
By equivalent we mean not only cash and currency, but all short-term, highly liquid investments that can be quickly converted into cash and used to pay off debt.
Paradoxically, a negative net debt value is considered a negative indicator. Lack of debt (the excess of cash and liquid assets over debt) indicates that the company is not using money efficiently. The use of borrowed funds allows for production growth (the effect of financial leverage). Therefore, a negative net debt value means:
- for the lender - a positive signal, since the absence of a debt burden and the availability of liquidity mean minimal risks of non-payment;
- for the owner (manager) of the company - a positive signal. There are no debts or the possibility of their repayment - there is no risk of bankruptcy. A high value of net debt (compared to equity) is a threat to financial stability and the need for urgent corrective measures;
- for the investor - a negative signal. Free liquidity means missed opportunities to increase profitability, ineffective management and disposal of money;
There are no standard values for net debt. They differ depending on the industry, so the net debt indicator is compared with similar indicators of companies in the same industry.
Practical Net Debt Calculation
As an example, let's take the financial statements of MMK at the end of 2016. To calculate the company’s total debt, open page 2 of the statements and add “Long-term loans and borrowings” with “Short-term loans and borrowings, as well as the current part of long-term ones.” I got 30207 million rubles (10797+19410)
Next, we calculate the “stash” that the company has. To do this, we add up “cash and cash equivalents” and bank deposits, which I found on page 48 (in section 18). I got 18683 million rubles (16135+303+2245)
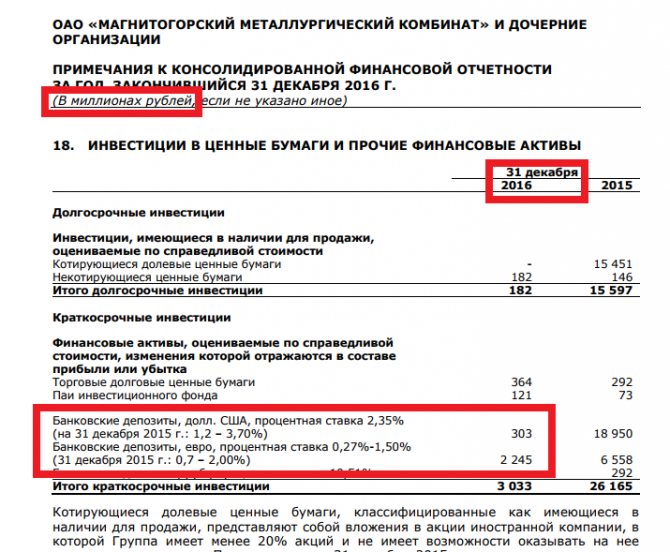
Now we subtract the nest egg from the total debt and get 11,524 million rubles (30,207-18,683). The MMK company kindly calculated its net debt for us, but it is in dollars... to compare our calculations with the company’s calculations, let’s convert the net debt in rubles to dollars. It turns out 11524/60 turns out to be 192.07 million dollars (I took the exchange rate approximately, although the reporting should show the exact rate)
What the company calculated for us can be found in the “Press Release“. We open the third page of the press release and see 192 million US dollars. Our calculations are correct.

If you don’t want to calculate your net debt (Net Debt) yourself and have it calculated for you, you can use the paid service “Conomy” or search at smart-lab.ru/q/shares_fundamental
Conclusion . Net Debt is one of the objective financial indicators for both the lender and the investor. True, even such a simple ratio is not so easy to calculate due to complex reporting and the lack of a unified approach to accounting standards. And calculate it on your own or trust official statistics - it’s up to you!
Net debt is the financial reliability of the enterprise
This question worries many company leaders. Each organization must be assessed for financial stability, which is a prerequisite for the development of the enterprise. Financial stability is usually understood as a financial indicator, i.e. availability of funds to carry out activities and issue loans.
One such factor that helps analyze sustainability is net debt, which has financial autonomy.
What is net debt
There are two types of debt - net and gross.
Debt of the first type is considered to be funds that the company did not repay on time. Gross debt must be calculated through a formula that includes two indicators - short-term and long-term.
For what indicators is net debt used?
The formula for calculating net debt must be compiled correctly to give an objective assessment of the company and its ability to perform calculations. The following groups of entrepreneurs and investors are asking to calculate net debt:
- If you want to invest money in a company, but in order to protect yourself from risks, it is important to assess their size and the possibility of activation during specific situations. Therefore, the investor asks financiers to assess the condition of the enterprise in order to know whether to buy or sell shares. If the net debt is very high, the company is considered unstable and the investor will not invest money.
- Heads of companies for whom this is a management element. This is necessary to develop the company in the right direction. When financial analysis shows that the company is on the verge of bankruptcy, then it is better to close the company. But this situation can often be avoided, since competent directors or managers conduct analysis on time, which helps to calculate the level of debt.
Banks and individuals who provide money for the development of an enterprise at the request of a specific businessman. They can allocate finance, but there is always a risk of not getting it back, so before granting a loan, an assessment of the company’s ability to repay the loan is carried out.
Features of calculating net debt
In order to perform such calculations and assess the financial condition of the company, you need to take into account many nuances. First of all, this concerns the availability of a package of receivables, which include such types of agreements as:
- Loans received from lenders and investors.
- Papers about the sale and purchase of real estate or property. Only objects are taken into account, which are then exchanged for specific financial resources.
- Financial checks and papers demonstrating settlements for various transactions. Documents confirming certain indicators.
Other nuances include the fact that long-term and medium-term indicators need to be compared with the average values for a specific area. If a firm's debt levels are higher than what is generally accepted in the industry, then there is cause for concern.
This is due to the fact that companies will be a source of concern for directors, investors, and creditors. They will refuse to provide loans or invest money, since the data obtained will indicate that management does not know how to develop a flexible plan for maneuvering in the market.
The value of net debt and ebitda for the company
Who might need to calculate the indicator? Net debt is one of the important financial indicators. It may be required by the following groups of people:
- Investors. Investing in a company is a rather risky undertaking associated with a number of risks. Therefore, before investing his funds, the investor conducts a thorough check of the financial condition of the organization. Calculating the indicator in question will help resolve the issue of the advisability of buying or selling shares. If the result obtained is high, the investor may decide that it is not worth investing because the company is unstable;
- Creditors. Lenders are those persons who provide the company with funds for use with the condition of their return. This is also a big risk, and therefore, before transferring funds, a person must check the solvency of the company.
Favorite indicator of banks, or once again about financial stability
Increasing the investment attractiveness of an organization is achieved by assessing its financial stability. The results obtained are used, among other things, to obtain bank loans, through which the enterprise expands. Net debt and EBITDA are analytical indicators obtained during this analysis.
Formula for calculating net debt on balance sheet
Almost all business managers are concerned about the formula for calculating net debt on the balance sheet. This is due to the fact that every company must undergo a financial stability assessment. Only in this case can you be sure of its stable development.
The concept of financial stability means the availability of financial resources to independently pay off one’s debt obligations. It is thanks to the net debt indicator that an enterprise can be analyzed.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right or call +7 8
It's fast and free!
What is net debt?
There are only 2 types of debt:
- Clean.
- Gross.
Net debt refers to the amount of financial resources that were not spent on paying off your debt obligations on time . Gross debt is calculated using a formula that includes, among other things, long-term and short-term debt.

Needless to say, the calculation of net debt on the balance sheet should be carried out correctly and as accurately as possible? This is necessary in order to provide the most objective assessment of the company’s ability to service its debts. often necessary to calculate net debt ( Net Debt ) for the following groups of investors and entrepreneurs:
- In order to evaluate and at the same time protect yourself from risks when investing in an enterprise, it is very important to consider all possible indicators of the company, including assessing the condition of the enterprise. This is required to understand what to do with stocks.
- For banking and credit organizations , this indicator is also required in order to assess the company’s ability to repay it before granting a loan.
- Thanks to financial analysis, the head of the enterprise will be able to soberly assess the condition and determine the future direction of the company (read in this article how to sell an LLC with debts).
Net debt: principles of calculation and analysis
Net debt is one of the financial metrics for analyzing a company's liquidity, which shows its ability to service its obligations. The article contains a formula for calculating net debt on a balance sheet, a standard value, as well as an example of calculation and analysis of the indicator.
Net debt shows the company's ability to pay off all debt at the time of analysis. To do this, it is necessary to compare the size of long-term and short-term borrowings with the highly liquid assets available to the analyzed company. Net debt is important to managers and investors because it allows them to compare available cash with the amount of debt.
The indicator reflects the company’s ability to attract additional borrowed funds to develop the business or solve current problems, refinance existing problem debts without attracting expensive financing from the owners. For creditors - how
Financial debt calculation formula
Good afternoon dear friends. I am happy to meet you again on the lines of another article. Today the material will be somewhat different from what I usually write, it will be somewhat more research-based and maybe somewhere philosophical, at least that’s how I see it. I admit that perhaps someone will consider it empty and lean, so I think it’s right to immediately make an announcement that we will talk about financial indicators and their application. In this regard, readers who are not interested in this area will be able to save their time, and those who are interested will be able to move on to the discussion. A clash of views on the market gives birth to a market; a clash of views outside the market often gives rise to unconstructive elements of communication among interlocutors. I deeply value every reader and gratefully respond to any reasonable feedback.
Today we will discuss approaches to determining net debt. On the one hand, there is nothing special to discuss here: there is a generally accepted practice that is well-established among companies, and you will often find the size of this indicator ready-made in a press release or company presentation. Despite the fact that the indicator is not standardized according to IFRS, discrepancies here are not very common.
Net debt = Short-term financial borrowings + Long-term financial borrowings - Cash and equivalents - Short-term financial investments
Long-term and short-term financial loans are quite easy to find, usually this is the line “Credits and borrowings” in the balance sheet, but “Financial lease obligations” are often added here, sometimes some other obligations (usually in this case they do not have a large amount and will not globally affect conclusions after calculation).
Short-term financial investments are sometimes included in DS and equivalents, so sometimes this line is missing. The logic of Net Debt itself is quite simple: we take on those debts that not only have an impact on cash flow, but are subject to additional interest, and in addition, we have priority liability to these borrowers. We reduce this amount by the amount of the most liquid funds: cash directly and those that we can quickly convert into cash to pay off debt. However, questions may arise in determining liquidity; consider the example of Tatneft.
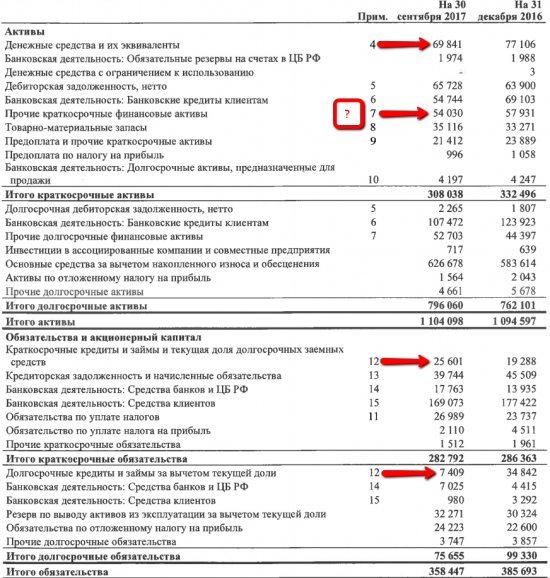
We see that Tatneft, when taking into account only financial debts (in previous articles we have already discussed that DS deposited into accounts are also included in liabilities), our net debt is negative. However, in Appendix 7 we can go a little deeper into the current assets that the company has.
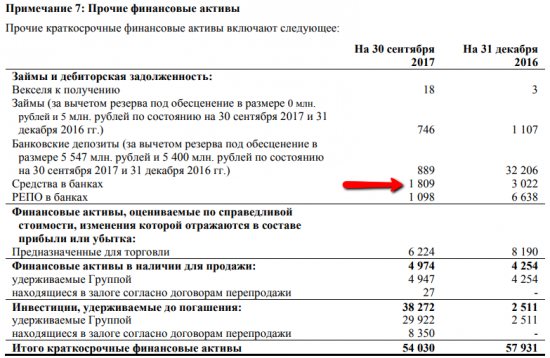
Of the presented 54 billion rubles. other assets (many of which we cannot easily classify into liquid and illiquid), liquid funds in banks occupy 1.8 billion, which is lost both in this amount and against the background of DS and equivalents in the amount of 70 billion rubles.
By this I want to show that any non-standardized indicator is open to discussion and can be modified. It is important not only how you calculate it, it is important to adhere to the same calculation logic for all companies. The point is not so much what figure you get, the point is how you compare companies with each other and what conclusions you draw.
Taking this further, I want to draw your attention to an alternative way to calculate net debt.
Net debt = Total liabilities - DS and equivalents
Some well-known investors on the Internet pay attention to this method of calculation. Companies themselves almost never think this way (only once have I seen such a calculation in IFRS reporting), so you won’t find this figure in the presentation.
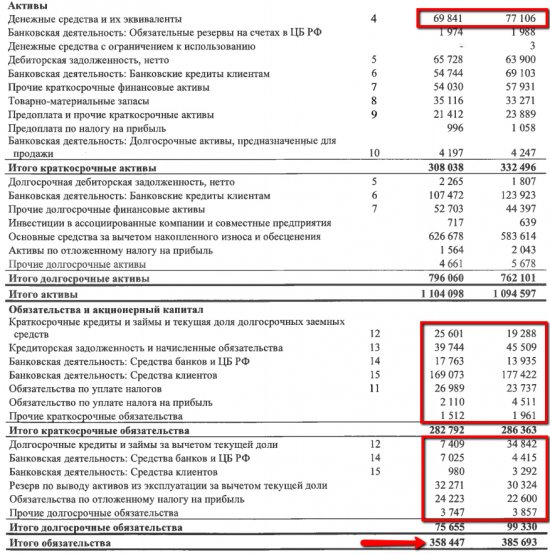
Then for Tatneft it would be necessary to deduct cash and equivalents from the total amount of debt. In this case, we would not receive negative net debt and would take into account absolutely all types of debt: - financial debt - commodity debt - debt on funds placed in the company - tax debt - pension obligations and other debts to employees.
Profitability and creditworthiness
For any enterprise, an important task is to maintain financial integrity, which may depend on the functioning of the industry, its economic policies, market position and many other aspects. The degree of safety of investing money in a company is also important.
A significant indicator in economics is the size of the gross product, its market value, industry analysis, and sensitivity to changes in activity.
An important task of management in market conditions is to manage the reliability of the enterprise, independence from external factors, rational use of assets, and their financing.
The profitability of a company is characterized by the availability of funds that allow it to maintain its activities for a specific time, as well as with loans received.
The financial reliability of any company is determined by various indicators.
The company's management independently determines which characteristics and indicators are suitable for this company and which are not.
Why is the net debt of an enterprise calculated?
Net debt makes it possible to assess the real stability of an enterprise, assess its solvency and sustainability. Unlike gross debt - existing debts to financial institutions, net debt is calculated by adding several indicators and plays an important role in further cooperation with partners.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call. It's fast and free!
What is net debt
Net debt is the financial stability of an enterprise; the main function of the indicator is an objective assessment of the capabilities of an object; in order to study the potential of an enterprise, it is necessary to have a clear idea of how much real debt it has.
In ordinary words, it is the difference between total debt and cash on account and short-term investments. Its presence implies the company’s ability, if necessary, to repay all debts simultaneously using liquid assets.
This indicator may have a negative value if the company's cash exceeds its total debt. Important: this is why for investors the size of net debt plays a major role when investing in various projects.
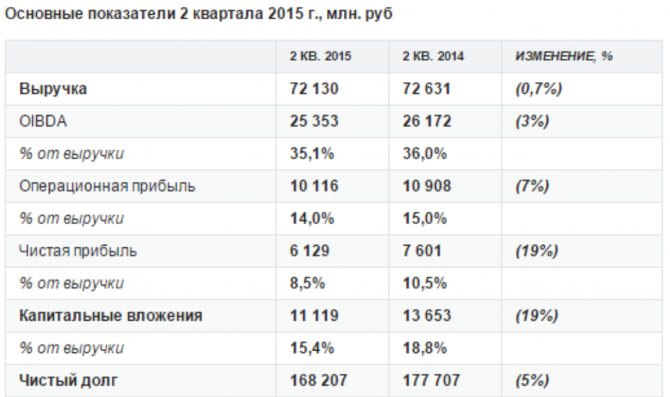
An example of calculating net debt.
For whom is it important?
Formulas for calculating net debt are used by those categories of investors who are interested in investing funds or expanding the scale of an enterprise, but understanding the real risk, want to receive reliable information:
- Entrepreneurs who want to invest in a particular project ask financiers to calculate an indicator to be able to objectively assess the liquidity of the enterprise in order to accurately know whether to buy or sell shares of a given company. If the figure turns out to be too high, investment is out of the question.
- Lenders who are approached by businessmen to obtain a loan in order to be sure of their repayment.
- Owners and managers of organizations who take the right orientation in business development, based on the indicators obtained from calculations. Carrying out timely calculations protects enterprises from collapse and collapse.
These groups of people are the main ones who require timely analytical work.
Calculation formula
To calculate net debt, a certain formula is used:
BH = KO + DO – DSE
Its decoding is as follows:
- ND – net debt;
- KO - short-term obligations for a period of up to a year;
- DO – long-term obligations, the fulfillment period of which is more than a year;
- DSE – cash and cash equivalents: currency, shares, finished products, accounts receivable.
What is the meaning of EBITDA, watch in this video:
When using this formula, it is necessary to take into account all the features, in particular all available accounts receivable documentation, including:
- Loans from lenders;
- Real estate sales papers;
- Checks, receipts, bills of exchange as evidence of the completion of financial transactions.
It is necessary to compare the obtained indicators with the average values in this segment.
What does net debt show?
At the same time, credit institutions will be willing to invest in this enterprise, because the fact of return due to the insignificant financial burden is high. For an investor in this case, the situation is the opposite - the company’s potential has not been revealed due to insignificant capital investment, which means it will be of little interest in the investment market.
Also important is the percentage of the ratio of net debt to personal funds, which are different for different industries. For the manager, this indicator, after analysis, should not exceed the norm for this industry, otherwise the company will become a matter of concern.
Three Pillars of Clean Debt
The government's federal debt has exceeded its assets
After a year in which Russia lived without net debt, federal debt again exceeded government assets by early July. The money in his accounts is shrinking and his debt is growing, but this does not threaten fiscal stability

Photo: Pavel Golovkin / AP
The federal government’s debt, against the background of the pandemic crisis, falling oil prices and the purchase of Sberbank with funds from the National Welfare Fund (NWF), again exceeded its liquid reserves, follows from the monthly statistics of the Ministry of Finance and the Bank of Russia, which was studied by RBC. A positive difference between assets and debt, as RBC wrote, has been observed since last summer. Analysts noted its uniqueness for emerging markets.
The change does not pose a threat to fiscal stability, but is a symbolic consequence of the current crisis, which combines low oil prices, a record decline in domestic oil production, the coronavirus and a sharp increase in budget spending to support Russian families and businesses.
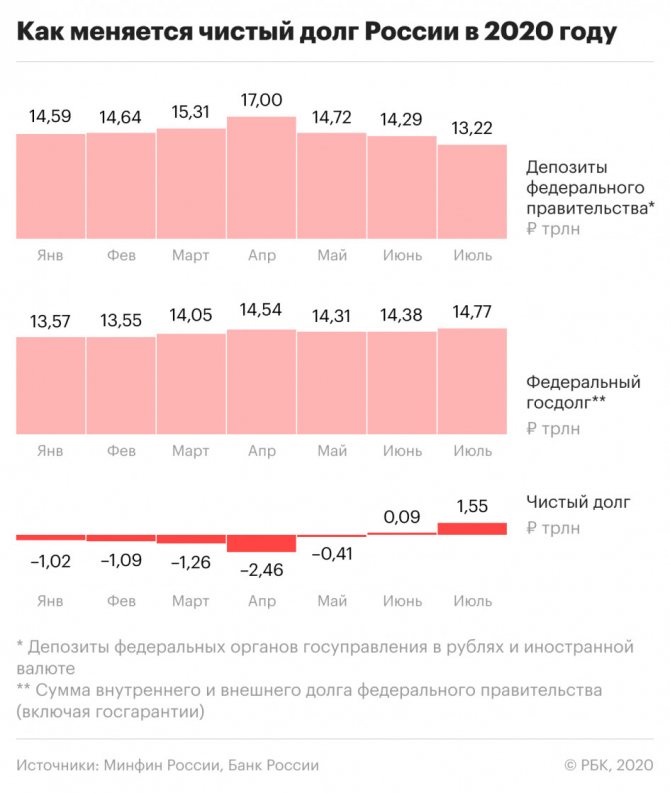
How much money has left government accounts?
- On April 1, which can be considered the conditional starting point of the coronavirus crisis in Russia, ruble and foreign currency deposits of federal government bodies placed with the Central Bank and commercial banks reached a record 17 trillion rubles, follows from the Central Bank Banking System Review (.xlsx). These are mainly the foreign exchange reserves of the Ministry of Finance, which have been transferred or will later be transferred to the National Welfare Fund (NWF).
- As of the same date, the federal government debt (domestic plus external, including government guarantees; external converted into rubles at the dollar exchange rate as of April 1) amounted to 14.5 trillion rubles. (see infographic). Thus, the government's financial assets exceeded its debt by almost 2.5 trillion rubles.
- However, on June 1, public debt and reserves almost equaled (at around 14.3–14.4 trillion rubles), and on July 1 (the most current data), public debt already exceeded government deposits by 1.55 trillion rubles, statistics from the Central Bank and the Ministry of Finance show .
In the second quarter, government deposits systematically decreased (by 3.8 trillion rubles per quarter), and government debt gradually increased. Domestic debt increased by 834 billion rubles in April-June, and external debt even decreased, since the Ministry of Finance has not entered foreign capital markets since 2020 due to sanctions and only repays Eurobonds.
Economy
The Ministry of Finance proposed to reduce expenses for Crimea

Why Russia has a net debt again
The trend is due to the imbalance of the federal budget this year: the Ministry of Finance is forced to compensate for the shortfall in oil and gas revenues, as well as to increase expenses beyond the limits determined by the budget rule. Additional expenses in 2020 in the amount of more than 3 trillion rubles. it is expected to be financed by increasing domestic government borrowing and using ruble balances in accounts.
“There is an increase in the debt burden as part of anti-crisis support, and the second fact is an increase in the federal budget deficit and, as a consequence, a decrease in the balance of available funds placed in the banking system,” said Sergei Konygin, chief economist of Gazprombank.
A significant part of the reduction in deposits was due to a deal for the government to purchase a controlling stake in Sberbank from the Central Bank, which was concluded even before the pandemic. The press service of the Ministry of Finance told RBC that it became the main factor in the reduction of deposits in foreign currency. In April, these deposits decreased by 1.9 trillion rubles. (the purchase of Sberbank cost the government 2.1 trillion rubles). During this transaction, the NWF's liquid assets (currency in accounts with the Bank of Russia) were exchanged for Sberbank shares, which remained in the NWF's portfolio.
Half of the NWF money paid for Sberbank almost immediately returned to the federal budget: the Central Bank transferred 1.1 trillion rubles to the Ministry of Finance, which will partially finance this year’s anti-crisis expenses.
The Ministry of Finance did not disclose other factors that influenced the reduction in liquid reserves. But the ministry's foreign currency deposits are also falling due to monthly sales of dollars, euros and pounds under the fiscal rule. In April-June, the Ministry of Finance sold foreign currency in the equivalent of 475 billion rubles. (including July - 600 billion rubles). The proceeds are used to compensate for lost oil and gas budget revenues to maintain expenses. In July, the average price of Russian Urals oil exceeded the budgeted base price of $42.4 per barrel for the first time since March, but the Russian government is still short of oil and gas revenues relative to the base level. This is due to a record reduction in oil production in the country due to the OPEC+ deal, RBC reported.
Business
Bloomberg and WSJ learned about OPEC+ preparations for revising the oil deal

Ruble deposits of the federal government in June decreased by 765 billion rubles, according to Central Bank data. The funds were used to finance the budget deficit, which amounted to 682 billion rubles in June. In total, the Ministry of Finance plans to use up to 1 trillion rubles this year. ruble balances from last year. “Changes in such obligations [to federal government bodies—that is, government deposits] during the year are primarily due to the irregularity of budget execution in terms of income and expenses,” the Ministry of Finance says.
How the situation with debts and assets may develop
In total, in 2020 the budget deficit could reach 5 trillion rubles. (about 5% of GDP), the Ministry of Finance estimated in July. Of these, about 4 trillion rubles. will be financed through net domestic borrowings (placement of government securities minus repayments). The Fitch rating agency predicts that the federal public debt will increase at the end of 2020 to 15.8% of GDP from less than 13% of GDP at the end of 2019. Federal government deposits (currency deposits in the National Welfare Fund and ruble budget accounts) will amount to 13–14% of GDP in 2020, according to the Fitch report. It follows from it that by the end of 2020 the difference between public debt and government assets will reach 1.9–2.9 trillion rubles. (currently about 1.5 trillion rubles).
Society
Experts named the category of Russians most affected by the coronavirus crisis

Beyond 2020, the gap between government debt and deposits is likely to slow growth and stabilize by 2022. In the base scenario, the Bank of Russia predicts that in 2022 the average price of a barrel of Urals will be $45 (at the level of the neutral price in the budget), and multilateral restrictions on oil production will cease to apply - in this case, sales of foreign currency by the Ministry of Finance from its deposits will cease. Federal debt will stabilize at 17.2% of GDP by 2022, Fitch experts believe. Starting next year, the Ministry of Finance proposes to reduce budget expenditures relative to 2020, that is, the need for debt financing will decrease.
EBITDA - what is it and what is its standard?
EBITDA is the profit received by the organization without deducting related expenses, which include:
- Interest on obligations;
- Depreciation;
- Taxes.
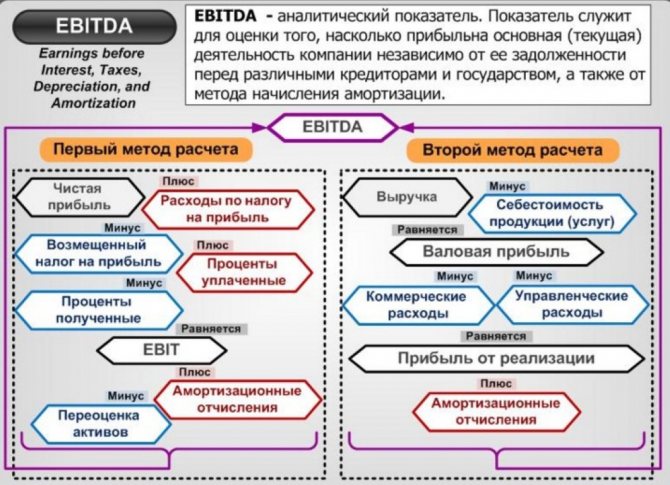
Why is EBITDA used?
This indicator provides a rough assessment of cash flow, without taking into account current expenses, focusing on the efficiency of business activities. It is a tool for investors to compare performance with other similar industries, want to make an injection and expect returns from these transactions.
If the EBITDA indicator tends to decrease, we can talk about the instability of the company and the question arises, about its insolvency if the situation is further ignored.
With negative EBITDA, we can talk about the enterprise being unprofitable at the operational level, which will inevitably lead it to bankruptcy.
Important: when assessing the situation, they take into account the correct repayment of accounts receivable by customers, otherwise financial non-repayment leads to a decrease in the solvency of the organization, but this in no way affects the ratio of accounts payable to EBITDA.
Net debt to EBITDA ratio
This ratio indicates the difference between an organization's debts and its net cash flow. Makes it possible to calculate how much time it will take with existing income to settle accounts with creditors.
Important: EBITDA is one of the most important indicators for investors in determining the sustainability of a company. If the value is too high, then repayment of loans will lead the organization to a deplorable state or may not take place at all.
This video will tell you how EBITDA is calculated:
If low, it indicates missed opportunities to build the organization's capacity. Important: the ratio, as an indicator, unlike the debt load ratio, may have a negative sign.
When calculating the ratio coefficient, it is necessary to take into account the indicators of other similar enterprises, since each industry has its own taxation indicators and differs in terms of lending, and therefore deviations to a lesser or greater extent are allowed.
Current ratio
Definition The current (total) liquidity ratio is a measure of the organization's solvency, the ability to repay the organization's current (up to a year) obligations. Lenders widely use this ratio in assessing the current financial position of an organization and the danger of issuing short-term loans to it. In Western practice, the ratio is also known as the working capital ratio. Calculation (formula) The current ratio is calculated as the ratio of current assets to short-term liabilities: Current ratio = Current assets / Short-term liabilities The numerator of the formula is taken from the balance sheet asset, the denominator - from the liability. Normal value The higher the current ratio, the higher the liquidity of the company's assets. A coefficient value of 2 or more is considered normal. However, in world practice it is allowed to reduce this indicator for some industries to 1.5. A low value of the ratio (below 1) indicates probable difficulties in the organization's repayment of its current obligations. However, to complete the picture, you need to look at the cash flow from the operating activities of the organization - often a low ratio is justified by a strong cash flow (for example, in fast food chains, retail trade). A current ratio that is too high is also undesirable, since it may reflect insufficiently efficient use of current assets or short-term financing. In any case, lenders prefer to see a higher ratio as a sign of a company's sound position.
What does net debt show?
Important: when receiving a negative value, the enterprise is considered unstable, since there is practically no debt, which means that there is no business expansion and long-term development of production capabilities, which is ensured by lending.
At the same time, credit institutions will be willing to invest in this enterprise, because the fact of return due to the insignificant financial burden is high. For an investor in this case, the situation is the opposite - the company’s potential has not been revealed due to insignificant capital investment, which means it will be of little interest in the investment market.
Also important is the percentage of the ratio of net debt to personal funds, which are different for different industries. For the manager, this indicator, after analysis, should not exceed the norm for this industry, otherwise the company will become a matter of concern.
EBITDA is the profit received by the organization without deducting related expenses, which include:
- Interest on obligations;
- Depreciation;
- Taxes.
Why is EBITDA used?
This indicator provides a rough assessment of cash flow, without taking into account current expenses, focusing on the efficiency of business activities. It is a tool for investors to compare performance with other similar industries, want to make an injection and expect returns from these transactions.
What is a company's net debt (Net Debt)
Net Debt represents all the company's debt to internal and external creditors, adjusted for cash and investments. Net Debt differs from total debt (another financial indicator for analyzing a company's valuation) in that it reflects the actual picture.
The amount of debt a company has alone is not an indicator of its debt burden, since the company may have the resources to pay it off. Therefore, total debt is adjusted to liquid assets (cash and short-term investments), which can be instantly used to pay off debt.
To explain it in very simple terms, let’s say... Petya owes Vasya 100 rubles, but Petya has a stash in his pocket for a rainy day in the amount of 70 rubles. As a result, Petya’s net debt is 30 rubles, since Petya can use his nest egg to pay off the debt.









