Receivables maturity date
When analyzing financial statements, to assess financial stability in the short term, an indicator such as the maturity of receivables is used.
Definition. Receivables repayment period - (Accounts receivable * Duration of one period) / Average annual sales on credit;
The receivables maturity period is the average period of time during which a company, having sold its products, expects the receipt of money. Determines the average receivables turnover time in days, taking into account changes in sales revenue.
Formula icon (acronym): DSO
Synonyms: Receivables turnover period, receivables turnover in days, average payment receipt period, average collection period, Days sales outstanding, RTD, Receivable Turnover in Days, receivables turnover period.
Formula for calculating the maturity of receivables:
, Where
DSO - receivables repayment period, days; DAP—duration of one period, days; AR — accounts receivable (Account receivable), rubles; NS — revenue (net) from all types of sales (Net Sales, Average annual sales on credit), rubles;
Purpose. If the average actual maturity of accounts receivable exceeds the established one, this may also affect the degree of liquidity of the company.
The most important element of the analysis of accounts receivable is the assessment of its turnover.
The trend in this indicator is often used to determine the validity of a discount for early payments. The higher the turnover rate, the less money is invested in accounts receivable. The number of receivables turnover is calculated using the formula:
DSOob = NS / AR;
Recommended values. Depends on the industry. According to Western sources, for an average company the value of this indicator is 45 days (or 8 revolutions per year).
Example: The duration of one period is 365 days. Accounts receivable 58.21 million.
Accounts receivable turnover (formula)
Accounts receivable turnover indicates how long it takes to repay customer debt for goods delivered.
This indicator, among others, characterizes the financial stability of the company. Why is the accounts receivable turnover ratio calculated?
The receivables turnover period is defined as the ratio of receivables to revenue
How to determine the repayment period for receivables without errors?
How to analyze accounts receivable turnover?
Results
Why is the accounts receivable turnover ratio calculated?
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is used to conduct a financial analysis of the company's sustainability in a competitive market environment. The calculated accounts receivable turnover ratio will show how effectively the company collects debts for goods supplied.
A decrease in the coefficient may indicate that:
- The company increased the share of insolvent customers.
- The company decided to pursue a more lenient policy with customers in order to gain a larger market share by providing longer payment deferrals to its customers. Accordingly, the lower the specified ratio, the higher the company's need for working capital, which is necessary to increase sales volumes.
To calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio, a simple formula can be used that looks like this:
Kob = Op / DZs g,
Where:
Kob - debtor debt turnover ratio;
Op - sales volume at the end of the year (revenue from sales);
DZsg - average annual debt of debtors.
To determine the average annual DZ, the following formula is used:
DZsg = (DZng + DZkg) / 2,
Where:
DZng - debt as of the beginning of the year;
DZkg - debt as of the end of the year.
You can learn about the procedure for keeping records of receivables from our article “Keeping records of receivables and payables.”
The receivables turnover period is defined as the ratio of receivables to revenue
By calculating how quickly receivables will be repaid in days, you can determine the average period required for the company to collect debts from buyers. To calculate it, the receivables turnover formula is used, which looks like this:
Psb = DZsg / Op × D n,
Where:
PSB - debt collection period;
Days—number of days in the billing period. If the calculation is made for a year, then Day will be equal to 365.
As a result, the receivables turnover period is determined as the ratio of the amount of average annual “receivables” to the volume of revenue. If the repayment period of receivables needs to be calculated in daily terms, then their number in the calculation period is added to the denominator.
How to determine the turnover period of accounts receivable without errors?
In order to calculate accounts receivable turnover with the smallest error, you should:
- abandon the practice of using the value of revenue cleared of indirect taxes (excise taxes, VAT), since receivables, as a rule, contain these indirect taxes;
- Please note that sales revenue is calculated when products are shipped, while payment for them is made later.
For more information about how sales revenue is reflected in accounting, see our article “How is revenue reflected in the balance sheet?”
How to analyze accounts receivable turnover?
Accounts receivable turnover (value in days) shows the average length of deferred payment that the company offers to its customer customers.
The lower the receivables turnover value is, the more efficiently the company’s capital works, since funds are released faster for new investments. If borrowed funds are used for turnover, then reducing the period of use of these funds makes them cheaper.
Results
Without calculating accounts receivable turnover, the company will not be able to build its own credit policy for working with customers. The decision to grant a deferred payment and its duration should be made taking into account all information about the financial condition of the company and its strategic plans.
Having analyzed its own resources/capabilities and compared them with its goals, the company determines the maximum and minimum limits of possible deferment of payment by customers. This value will subsequently be used when concluding transactions with them. This can significantly reduce the repayment period of accounts receivable.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Source: https://nalog-nalog.ru/analiz_hozyajstvennoj_deyatelnosti_ahd/oborachivaemost_debitorskoj_zadolzhennosti_formula/
Repayment of debit debt and determination of its period
rubles at the beginning of the year, and at the end 69.21 million rubles. Revenue (net) from all types of sales is 395.12 and 428.47 million rubles, respectively. Determine the change in the receivables maturity ratio for the year.
The value of the receivables maturity ratio at the beginning of the year: DSOstart = 365 * (58.21 / 395.12) = 53.8 days.
The value of the receivables maturity ratio at the end of the year: DSOcon = 365 * (69.21 / 428.47) = 58.96 days.
Change in value: DSO = DSOend / DSOstart = 1.0959 or increased by +9.59%.
Answer. The receivables maturity ratio increased over the year by 9.59%.
All business entities are faced with the concept of accounts receivable (AR). It represents the amount of money that an individual entrepreneur or enterprise has the right to receive from individuals and/or legal entities for obligations arising in the course of business activities. Legally, debt is expressed in property claims against debtors, in accounting it is recorded by entries and reflected in accounts, and “on paper” it is represented by contracts and other documents.
Accounts receivable are an integral part of the work of a modern enterprise. For it to be financially stable, the debt to the company must exceed accounts payable. However, the accumulation of obligations under the contract and exceeding the period for their fulfillment negatively affects the well-being of the organization. For this reason, it is necessary to monitor the solvency of debtors, analyze and monitor the situation and take timely measures to recover the amounts due.
Economics is easy!
Problem solving and books on economics.
In the article “Liquidity Indicators” we solve the problem.
1. Accounts receivable maturity (DSO) and turnover. 2. Accounts payable statute of limitations (APP). 3. Inventory Turnover Time (DIT) .
4. Own funds ratio (OFR).
Accounts receivable maturity date (DSO). The company's accounts receivable amount to 380,000 rubles. Revenue from all types of sales is 2,000,000 rubles. We will assume the duration of repayment of receivables to be 1 year and the number of turnovers per year. DAP = 365. AR = 380,000. NS = 2,000,000 DSO = 365 * 380,000 / 2,000,000 = 69.35 days.
Essence, structure, causes of remote sensing
Accounts receivable are included in the amount of the organization's working capital and are determined as of a specific date (for example, according to the date of drawing up the balance sheet). Deposits are considered as a means to pay off accounts payable, part of goods sold but not paid for, or as a share in the company’s current assets (they can be financed from own or borrowed funds). Settlements on receivables are carried out in generally accepted ways: they pay in money or bills, mutually offset the debt, assign claims to it, forgive or transfer.
DZ occurs under different circumstances:
- the products have been shipped and ownership has been transferred to the counterparty, services/work have been performed by the company, but the moment of payment stipulated in the contract has not arrived;
- an advance payment has been made to suppliers, performers or contractors, but they have not yet fulfilled their part of the obligations;
- the employee received accountable money (for example, for a business trip), but the time for reporting the debt has not yet come;
- the company has overpaid taxes, penalties, and so on.
The above cases are examples of normal receivables. If the documented deadlines for settlement of the debt are exceeded, then it is called overdue and, in turn, may be doubtful or hopeless. To identify the reasons that led to the emergence of “complex” receivables, as well as to prevent undesirable situations, a regular analysis of the debt is carried out and compared with accounts payable.
Calculation and analysis of indicators related to the timing of debt repayments
The analysis is carried out for each of the debtors separately, taking into account the timing and accounting data (AC). Debt is distributed in accordance with balance sheet items - among customers, bills received, advance funds issued, subsidiaries and other organizations. Analysis is necessary to determine the total size of receivables, compare them with creditors, find out why delays occur and what their dynamics are.
To effectively manage debts, a company needs complete information about the repayment of obligations for each debtor, data on unpaid invoices, and exceeding the agreed terms for them. Information on accounts payable is also required (average amounts and periods of delinquency for all counterparties). Data on bad and doubtful obligations of creditors is calculated on the basis of standards established by the company. For the analysis, you will also need ratios that are calculated with a certain regularity in order to monitor receivables and control the situation.

Accounts receivable turnover ratio
Depending on the market situation, DSO varies from 30 days to 75 or more. When determining the effectiveness of remote control management, analysts compare real values with the standards established by the company and compare them with competitors’ data.
The formula for calculating DSO is as follows: the average annual DZ is multiplied by 360 days and the resulting number is divided by the company’s revenue. You can calculate the period in another way - divide 360 days by the turnover rate of the remote control (see below). If the DSO ratio decreases over time, this means that the company’s receivables are diverted for less time, and vice versa - the relationship is direct. Whether this is good or bad, analysts decide in each specific case, taking into account the quality of the data, the use of loans and other factors.
Average repayment period of receivables and other indicators
When analyzing a loan, it is necessary to know the average period of its payment. It characterizes how long the company waits between the delivery/sale of goods and receipt of funds. The parameter determines the average debt turnover period. Its formula is the duration of the period multiplied by the receivables, the resulting amount divided by the proceeds from the sale in net terms.
Among other coefficients when analyzing debt, the following are used:
- debt turnover indicator - the ratio of revenue to the average amount of debt;
- share of receivables in working capital - its percentage in the total amount;
- the percentage of doubtful debts in the total amount of receivables - it characterizes how liquid the company is (can cover its obligations with its own resources);
- ratios for accounts payable - turnover and payment periods, growth rates, and so on.
Accounts receivable turnover: formula
One of the most important calculated indicators of the financial stability of an enterprise is the accounts receivable turnover (AR), which reflects the rate at which the debt of counterparties-debtors is converted into cash. We will find out how remote control influences the development of a company and in what ways it is managed.
The concept of accounts receivable
All companies take into account remote assets, since it is impossible to do without this asset. It arises due to the mutual interest of the company offering its services/products and the consumer of these goods - enterprises and individuals.
The agreements concluded between them often become mutually beneficial: the manufacturer finds markets by supplying goods by agreement without advance payment, with subsequent installment payments, and the buyer is given the right to use the purchased product without payment for a certain time.
This is how a remote payment arises, the size of which is determined by the monetary equivalent of future receipts. In the balance sheet, this asset is reflected on line 1230.
In addition, advances to supplier enterprises for subsequently purchased goods are also included in the purchase order. Transactions with deferred payments are always associated with serious risks, and therefore are very carefully controlled.
Accounts receivable turnover
Since DZ diverts funds from the company’s turnover, the economist cannot help but worry about the speed of its conversion into money.
This indicator is called accounts receivable turnover and allows you to determine the number of turnovers of the occurrence of debt and its repayment in the period under study, as well as to calculate the length of the period of time required to return funds for sold products. It is calculated in days and times.
Accounts receivable turnover serves as an indicator of the effectiveness of working with counterparties in matters of collecting the resulting debt. Let's consider the algorithm for calculating the turnover of remote parts in times. It establishes the number of times debt arises and is repaid by receipt of payments from debtors for the analyzed period.
The calculations use the accounts receivable turnover ratio. It is found by dividing the amount of revenue (income) by the size of the average income using the formula:
- KobDZ = V/DZ avg/ 100, where V is revenue, and DZ avg is the average DZ, more precisely the average debt balance, the value of which is calculated according to information from the company’s financial statements using the formula:
- DZav = (DZnach + DZkon)/2, i.e. the sum of the balance of DZ at the beginning and end of the time period under study is divided in two.
The initial data for the calculation are the balance sheet and the Profit and Loss Statement: information on the amount of income is on page 2110 of the Report, and information on the availability of debt is on page 1230 of the balance sheet.
So, the accounts receivable turnover ratio shows the number of accounts receivables generated and payment received in the amount of the average accounts receivable for the year.
Normative value
There are no clear standards established for the accounts receivable turnover ratio.
Despite this, analysts focus on the optimal value of the coefficient, which characterizes the normal level of liquidity of the enterprise, equal to 1.
When the coefficient is above 1, one can judge the fulfillment of obligations by debtors, and if it increases, one can confidently assert that the rate of repayment of debts by debtors is increasing.
Accounts receivable turnover in days: formula
In addition, accounts receivable turnover is calculated in days and indicates the number of days required to return accounts receivable. It is calculated by dividing the number of days in the analyzed period by the asset turnover ratio in times:
- OD = Dp/KobDZ, where Dp is the duration of the study period in days.
The calculation of receivables turnover will be incomplete if the receivables turnover period is not established, i.e. the amount of time required to pay off the debt.
The receivables turnover period is calculated using the formula:
- Podz = 365 / Kodz. The number of days in the formula must correspond to their number in the period under study, for example, 365 days for a year, 91 for a quarter, etc.
Accounts receivable turnover analysis
Accounts receivable turnover is an indicator that reveals the degree of efficiency in the use of production resources, and its fluctuations are a kind of indicator of the state of affairs at the enterprise: are they prosperous or is it time to take measures to improve the condition of the company and collect debts.
The decreasing turnover period of accounts receivable leads to an increase in KobDZ, which indicates the repayment of accounts receivable by consumers and competent control of the economic situation in the company.
A slight decrease in the KobDZ indicates an insufficiency of working capital and should stimulate the enterprise to intensify efforts to collect the DZ. A significant decrease in the indicator is a signal of negative manifestations, for example, such as a decline in sales volumes, sales problems, etc.
It encourages the company to identify reserves of working capital, strengthen activities to collect debt, and take measures to accelerate its turnover.
Debt deadlines violated: actions and collection procedure
Debt that arises during the standard operating cycle of the organization (one year or a period specified separately) and is repaid no later than 12 months from the balance sheet date is considered current, short-term, and for a longer period - long-term. If the debt to the company is not repaid at the right time, it turns from normal into doubtful. It is identified during inventory, which is mandatory for all companies - it is carried out once every 3 months or more often.
The standard three-year statute of limitations applies to DD. If it is exceeded and the funds are not received, the debts go from doubtful to hopeless. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation also includes such debts as obligations that cannot be fulfilled due to the liquidation of companies or for other reasons specified in the relevant state act. It is unrealistic to collect receivables in the event of bankruptcy of counterparties, an arbitration decision to terminate the activities or restructuring of the debtor's bank, and in a number of other situations.
What happens to personal data after the statute of limitations expires?
If the debts have expired, they are necessarily written off based on an order from the company’s management. To write off the financial results, an inventory of the debt is carried out and the bad amounts are repaid from the reserve for doubtful debts. To prevent this, the company must take timely measures to prevent the emergence of dangerous debts and begin working with creditors on time.
It is necessary to negotiate, launch claims activities, and if unsuccessful, apply to the courts to recover the debt. Each of the procedures is full of legal and other nuances, therefore, to successfully obtain funds for debts, professional legal and organizational support is needed. It will be provided by the Center for Effective Collection. Experts specializing in debt recovery will provide advice and help you receive the funds owed within the legal framework and in full.
The value and economic meaning of the dz coefficient
Any turnover indicators (ratios) illustrate the rate of turnover of assets or liabilities: how efficiently and actively the company conducts business.
Accounts receivable reflect the monetary obligations of third party counterparties to our company. This is the money that is owed to us (for services rendered, work performed, goods shipped).
Indirectly, accounts receivable can be called losses of the enterprise. The service has been provided, but there is no money yet - we cannot put it into circulation. In addition, there is a risk of liquidation or bankruptcy of the debtor. Therefore, the creditor company necessarily evaluates the financial stability and liquidity of the counterparty.
The accounts receivable turnover ratio reflects the speed of return of funds for goods or services and characterizes the effectiveness of interaction between the company and counterparties. The higher the indicator, the faster the company pays its customers.
What is the coefficient for? To find ways to increase the profitability of the enterprise.
Forecasting through turnover analysis
Regular analysis of accounts receivable turnover helps predict the repayment of obligations by customers. When calculating the amount of receipts from debtors, the general formula for debt turnover is used:
DZ coefficient = Sales volume for a given period / Average DZ for a given period.
Drawing up a forecast of cash receipts from customers involves calculating the turnover ratio for the previous period. Then, based on the obtained value of the indicator, you can calculate the balance of accounts receivable, that is, determine what portion of sales will be unpaid by the end of the future period. Forecasting cash flows based on the turnover ratio is a simplified method and its results do not have a high degree of accuracy.
Calculation of accounts receivable ratio
To calculate the indicator, you need a balance sheet (Form 1) and a statement of financial results (Form 2).
The classic formula looks like this:
Kdz = sales revenue / average annual accounts receivable.
To find the denominator, we take the sum of the indicator at the beginning and end of the analyzed period and divide by 2.
We will calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio based on financial statements. Balance formula:
Kdz = line 2110 / (line 1230np + line 1230kp) * 0.5
Data for the numerator is taken from Form 2, for the denominator - from Form 1.
We use Excel to calculate the capabilities.
In order for business activity ratios to be calculated automatically, the balance sheet and financial statements must be maintained in Excel.
An example of a balance sheet with the line required for calculations:
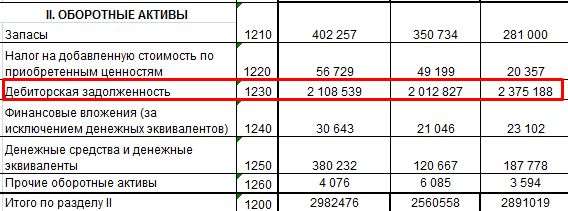
An example of a company's financial performance report (the required line is highlighted):
Now let’s calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio - substitute references to the cells of the corresponding reports into the formula:
You can analyze not only for the year, but also for the month and quarter.
The number of days during which receivables are converted into cash is called the receivables turnover period. From an economic point of view, the importance of this indicator is obvious: this is the average number of days in the analyzed period of time during which money from customers arrives in the company’s current account.
The accounts receivable turnover ratio in days is calculated using the formula:
Tdz = 365(360) / Kdz.
Let's find the turnover period using Excel:
Let's display it in dynamics on the graph:
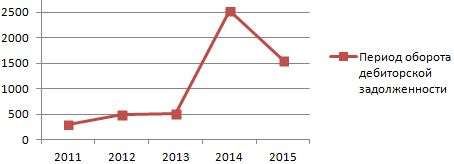
Having analyzed the calculations and the schedule, we conclude: accounts receivable are not repaid on time.
calculation of accounts receivable ratio in Excel
The enterprise incurs considerable losses, because... counterparties cannot or do not want to repay debts. Or the company sells goods on credit, which is why the turnover ratio is so low. Or it has an incorrect credit policy.
a) Sales revenue; Average annual accounts receivable balances;
b) Average annual balances of accounts receivable; Revenue from
implementation;
c) 360; Accounts receivable turnover ratio.
d) 180; Accounts receivable turnover ratio
12. An indicator is considered significant if it:
a) non-disclosure may affect the economic decisions of interested users made on the basis of the reporting information;
b) failure to submit will mislead potential users of the reporting;
c) non-disclosure will lead to misstatement of financial statements;
d) failure to submit may affect effective management decisions.
13. Information on changes in the financial and economic activities of the organization is presented:
a) in the notes to the financial statements;
b) in the explanatory note to the balance sheet and financial results statement;
c) in appendices to financial statements;
d) in the financial report.
14. Analysis of the specific manifestation of technical progress at the enterprise under study is an analysis of:
a) foreign economic activity of the enterprise;
b) organizational and technical level;
c) risks of business activity;
d) level of organization of production and management.
15. The volume of product sales that will allow the enterprise to cover all costs and reach a zero profit level is:
a) financial leverage;
b) optimal production level;
c) margin of financial strength;
d) break-even point.
16. Information essential for making a decision, i.e. it contains the data that should be taken into account when preparing information:
a) relevant;
b) irrelevant;
c) optimal;
d) commercial.
Option 2
1. Financial analysis is:
a) external analysis, based on financial accounting, serving external users of information about the enterprise, who act as independent subjects of economic analysis based on data, as a rule, public financial reporting;
b) analysis of the enterprise’s financial investments;
c) analysis of financial ratios;
d) analysis of financial indicators and financial condition of the organization, carried out for all interested users of information.
2. In deterministic factor analysis, the connection between factors and the effective indicator is:
a) probabilistic nature;
b) functional nature;
c) temporary nature;
d) random nature.
3. The influence of individual factors on the analyzed indicator is not determined using the method:
a) chain substitutions;
b) relative differences;
c) absolute differences;
d) comparison of indicators.
4.
Receivables turnover formula
Turnover is in first place among indicators of the commercial efficiency of an enterprise. There are several types of it, one of them is accounts receivable turnover. According to reporting standards in English, this indicator looks like Receivable Turnover.
Within the framework of the enterprise’s activities, this parameter can be classified as “Business activity”. The essence of the calculation is to determine the speed of use of certain assets of the company.
In practice, the accounts receivable turnover formula allows you to determine how effective the company's commercial work is and how pronounced its business activity is.
Receivables turnover formula: detailed definition
Accounts receivable (RA) is a set of monetary obligations that individuals and legal entities have in relation to the analyzed company.
For example, a service was provided to translate a contract from one language into another, but money for its provision has not yet been received. This amount of money is recorded in the general section of accounts receivable, which, by the way, entails indirect losses in the company’s profit.
This can be explained by the fact that the actual amount for the services provided is not yet available, so it cannot be put into circulation.
Traditionally, the amount of debt an enterprise can receive after a certain time. But, besides this, there is also money that cannot be returned. This situation may arise due to the liquidation or bankruptcy of a person who has a debt to us.
Because of these considerations, an entity acting as a temporary lender is exposed to the credit risk that funds may not be repaid.
In order to minimize it, it is important to carry out a detailed assessment of the counterparty’s solvency before granting a loan.
How to calculate accounts receivable
The economic essence of inventory turnover
Receivable turnover is represented by a coefficient, which in English is designated as RTR, which means “Receivable turnover Ratio”.
By calculating this parameter, it is possible to give a full description of how effective the interaction is between the company in question and its debtors. The parameter reflects the rate at which an organization's goods and services are converted into money and become assets.
In general, in dynamics, this factor can give an idea of in which direction the debt is changing, and what should be done to prevent losses.
As for remote control management, its key role is to increase the turnover ratio. This can be achieved through the use of two main methods:
- increase in sales revenue;
- decrease in the PD indicator over a certain period of time.
In order to obtain a rational effect, it is worth assessing the financial stability and liquidity of the company at the stage of issuing loans. From a practical point of view, it is worth considering 3 areas of credit policy. It can be conservative, moderate, aggressive:
- In the first case, there is a desire of the enterprise to ensure control of all its loans to minimize risks on loan obligations.
- In the second situation, we are talking about the organization taking on medium-level risk factors.
- If we are talking about an aggressive policy, the company takes on large credit risks.
Thus, it can be noted that turnover includes the factor of the speed with which credit obligations are repaid by counterparties.
That is, it characterizes how quickly the company receives payment for sold goods or services.
By correctly calculating the parameter, you can measure the company’s performance with clients in terms of debt collection, and evaluate the overall policy regarding sales of goods on credit.
Scope of application of the turnover ratio
This value is relevant in situations where there is a need to determine directions to increase the profitability of the company. Key people using this option include employees such as:
- gene. director of the company;
- commercial specialist;
- sales department management;
- manager for sales of products and goods;
- service responsible for the safety of the commercial process;
- legal part.
Types of accounts receivable
Formula for calculating the indicator
The formula for the accounts receivable turnover ratio has the following external representation.
KODZ = VP / SDZ.
The VP parameter in the formula means sales revenue, and SDZ indicates the amount of accounts receivable. It is worth remembering the fact that the denominator contains the average amount.
This suggests that when performing settlement actions, it is necessary to take the receivables at the beginning of a certain period of time, add them to the debt at the end of the period, and divide the result by 2.
According to the balance sheet and reporting data, we can distinguish the following formula by which this value is calculated.
KODZ = 2110 / (1230 NP + 1230 KP) * 0.5
NP is the code value of the line, suggesting the beginning of the period, and KP is the end of the period. This interval can be a month, a quarter, or a year. If we consider the conduct of settlement transactions on the basis of the old form of the balance sheet, which was in force until 2011, then the formula looked like this:
KODZ = page 10 / (page 230 + page 240) * 0.5.
Both formulas have similarities with each other, only the location of the data required for the calculation has changed. Within the framework of this equality, all the values are clear; all that remains is to perform a few actions with them and get the ready value of the calculated coefficient. It is a dimensionless quantity, although percentages are sometimes used to calculate it.
Distribution turnover period
Together with the parameter under consideration, another key indicator is used, called the turnover period. Its value reflects the number of days that are needed for the receivable to be converted into monetary value. The formula for accounts receivable turnover in days looks like this:
PODZ = 360 / KODZ.
360 within this formula, this is the number of days in a year; sometimes the number 365 can be used.
The economic essence of this parameter is to determine the average number of days during which funds from the company’s counterparties will arrive in the current account.
This is how the receivables turnover period is calculated. The fundamental units of measurement are days.
How to achieve accounts receivable turnover
Is there a norm?
There is no specific level for this indicator. But the greater its value, the higher the speed of money turnover between partner companies. If suddenly there is a decrease in the value under consideration, we can talk about the fact that the partners have delays and late payments.
In order to effectively assess the turnover of this debt, it is necessary to calculate its value not only for the enterprise, but also for the industry, and then compare the indicators with the leader in this area.
This approach will allow you to create some guidelines and constantly improve the results of commercial work.
It is important to know! Effective commercial work will not always be accompanied by a high turnover rate. The fact is that if we are talking about the credit sale of a product or service, the loan balance will have a high value, and the coefficient itself will be low.
Ways to increase the value of KODS
Accounts receivable turnover, the formula for calculating the balance sheet was discussed earlier, despite the absence of any norms and boundaries, can be increased. There are several ways to achieve this result:
- An increase in prices for goods, which will lead to an increase in revenue.
- Limitation of time limits for counterparties to pay for commodity items through the conclusion of contracts.
- Increasing sales volumes by finding new buyers and selling more products to existing counterparties.
- Improving advertising policy to attract new paying customers and partners.
- Refusal to provide credit, working with clients strictly on an advance payment basis.
All these measures are aimed at ensuring that the value of the coefficient increases noticeably, and the turnover ratio of household items increases. If you provide a competent approach to their implementation, you can achieve a positive result not only within this indicator, but also the activity as a whole.
Summarizing
Average turnover acts as the most important financial criterion. It is this that allows us to determine the effectiveness of the company’s work with contractors and draw certain conclusions regarding partnership relationships.
Most management employees of the enterprise use this parameter to improve commercial activities as a whole and to increase the value of the indicator. Practice shows that the ratio has a direct and close relationship with the financial stability of the company, as well as its liquidity.
This can be explained by the fact that with high rates, money for goods is received by the enterprise quite quickly and quickly goes into circulation.
BEST LOANS OF THIS MONTH
Source: https://fintolk.ru/likbez/formula-oborachivaemosti-debitorskoj-zadolzhennosti.html