Issues of assessing the liquidation value of an object
Liquidation value is the price for which an object can be sold on the market within a limited time frame. This type of value is always less than the market value.
The condition for the appearance of liquidation value is the presence of extraordinary circumstances that affect the change in the normal market situation.
One of the most common areas for assessing liquidation value is the assessment of an enterprise if it becomes necessary to go bankrupt.
Factors affecting salvage value
- Exposure period. There is a direct relationship between the liquidation cost and the sale period - the lower it is, the lower the cost. The duration of exposure depends on many factors: type of property, initial sales price, level of demand, etc.
- General economic situation on the market.
- The degree of attractiveness of the object for the market. The attractiveness of an object is determined by its individual characteristics and depends on the demand for a specific type of object.
- Subjective factors.
The assessment of liquidation value is carried out in the following cases:
- if the company is under threat of bankruptcy;
- if the assessment of the enterprise’s business indicates that the value of the company upon liquidation will be higher than if the organization continues to operate;
Methods for estimating liquidation value
1. Direct method. This method involves the use of a comparative approach.
Methods used:
- sales comparison - direct comparison with analogues;
- The method of correlation and regression analysis is a quantitative method for determining the dependence of the liquidation value of objects on various factors.
Concept and formula for calculating liquidation value
Sometimes, due to current circumstances, there is a need for an urgent sale of the property. In this case, you should not rely on the average market price - special conditions of liquidation significantly reduce the value of the object being sold. Today we will talk about what liquidation value is and how it is calculated.
It's fast and free!
This is the amount that the seller has to agree to, since due to the limited time of the transaction, it is not possible to familiarize all potential buyers with the property being sold.
The price for reorganizing an enterprise can be determined from any property owned by the enterprise. To do this, use the balance sheet of the enterprise for the last reporting period. Each section of assets and liabilities is examined in detail, defining assets in use, receivables and payables, as well as the amount of liabilities that must be repaid with proceeds after sale.
The property of the enterprise includes:
- Fixed assets. These are real estate, equipment, cars and other property, more expensive than 10,000 rubles, with a useful life of more than 1 year.
- Securities, bills. By owning them, the company makes a profit, but their sale can also bring significant income. This could be shares of another company or bonds.
- Intangible assets. These are objects that have no physical form. These include licenses, patents, copyrights, intellectual property, etc.
- Products for production.
- Finished goods in warehouses.
- Materials in the pantry.
Determining the liquidation price of all these balance sheet items is necessary in various cases, but in any of them, we are talking about a forward transaction within a limited period of time, in order to generate income.
In what cases does liquidation value arise?
The use of this concept is necessary in a number of cases:
- Liquidation of the organization.
- Sale of collateral property.
- Emergency sale of all properties.
Liquidation of an organization is divided into two types:
- Planned - when an enterprise ceases its activities by decision of its founders. This happens if a decision is made to reorganize or restructure a company, for example. At the same time, a plan for the sale of property is drawn up, the amount of profit received is determined, depending on the wear and tear of the asset, its relevance and other factors. The sale of property is proceeding as planned.
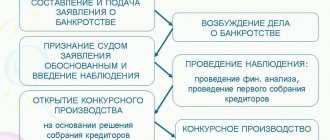
- Compulsory - we are talking about the bankruptcy of a legal entity. In this case, all property is assessed and the so-called bankruptcy estate is determined. Then it is sold through auctions in the shortest possible time.
When selling collateral, using the concept of the liquidation price of the property is necessary to determine the lower limit of the loan or credit amount. By determining this type of cost, the lender can clearly understand what the minimum amount will be able to receive upon the sale of such an object, in the event of the borrower’s failure to repay the loan.
If such a situation occurs, the property will be sold to pay off obligations on loans and borrowings.
If it is necessary to urgently sell all existing property, time is usually very limited. In this case, two types of implementation are also distinguished.
It, as in the first case, can be voluntary or forced:
- Voluntary sale of objects occurs in the case of the sale of the entire enterprise. After this, it continues its activities further.
- During a forced sale, the seized property is sold during legal proceedings, in case of non-payment of taxes by the enterprise or other violations of the law. The transaction is being carried out in an accelerated manner, due to the need to urgently repay the resulting debt, since its amount is increasing every day by the amount of penalties and fines.
But no matter which option is used, in any case, the time for the transaction is very limited. Failure to repay loans leads to an increase in debt due to the addition of fines and late fees to the principal amount of the debt. Therefore, the time within which the borrower can receive money for his property plays a decisive role.
Legislative incidents
In modern legislation there is no unambiguous definition of liquidation value and clear cases of its application.
Thus, in Law No. 119-FZ of July 21, 1997, regulating the rules of concepts in enforcement proceedings, it is necessary to calculate the price of property at the market price, which must be sold at auction within 60 days.
And if its sale occurs through trading, that is, in a compressed time frame, which is typical of non-market methods of sales. All this does not fit the definition of market value described in Law No. 135-FZ of July 29, 1998, which establishes rights and obligations in the valuation field. In such a situation, appraisers in their activities should use not the market price, but the price of the property that is seized.
Factors affecting salvage value
If it is necessary to calculate the liquidation value of a legal entity’s property, this is not always easy to do, since its size is influenced by many factors:
- Time. As a rule, in such cases, the time frame for selling real estate is very tight. And in a short period of time, finding a buyer who will agree to a deal at an acceptable price is not so easy. Therefore, we have to reduce the cost of the object. The dependence is very simple - the less time for sale, the lower the proceeds from the sale of property.
- Demand. Depending on the demand at a given time for a particular type of property, the maximum price at which it can be sold depends. If the demand is high, then the sale will be carried out as soon as possible, and the seller will receive the maximum benefit.
- Attractiveness. The more interested the buyer is in acquiring the enterprise, the more profitable the deal. Here, a lot depends on the condition of fixed assets, their wear and tear, and the staffing level of the enterprise as a whole.
- Field of activity. Much depends on what kind of activity the legal entity is engaged in, and how competitive and economically profitable it is. If a company occupies a certain niche in the market segment and the product or service it sells is in demand, the revenue for its assets increases significantly.
- Force Majeure. It is necessary to take into account other, independent circumstances, which, if they arise, can have a significant impact on the amount of proceeds from the transaction.
Methods for estimating liquidation value
We’ve sorted out the definition a little, now it’s worth considering how to evaluate property and what methods exist for this. There are two main assessment methods: direct and indirect. The direct calculation method is based on comparison with an analogue, and can be carried out visually or using statistical analysis.
But this method is uninformative under Russian legislation, since it is prohibited to disclose information about transactions during forced sales, as well as the amount received during their execution.
It includes three steps:
- Determination of the market price of the object.
- Calculation of the discount arising due to the urgency of the transaction.
- Direct calculation of the liquidation price.
In this case, it is most difficult to calculate the discount percentage for urgency, since this requires a detailed analysis of the market and a comparison of factors that influence the proceeds from the sale of property.
And to calculate the value of an object upon liquidation, the difference between the proceeds from its sale and the costs associated with its implementation is calculated. But at the same time, it is better to seek help from qualified appraisers, since they have extensive experience and information, to give a more accurate assessment of the proceeds from the transaction.
Liquidation assessment, what difficulties may arise
Sometimes, when an enterprise collapses, it is quite difficult to determine how much its assets are worth. What problems might you encounter?
The main difficulty in real estate transactions, when eliminating the legal entity, is the limited time for sale. Registration of a transaction and transfer of ownership is not a simple or quick process. And in order to meet the deadlines, and for this we have to resort to reducing prices.
Another difficulty is that the circle of potential buyers is significantly narrowed, and not all of them can familiarize themselves with the terms of the transaction; this, again, is due to the transience of the transaction. Also, in an unstable economic situation, it may be necessary to reduce the amount received for real estate due to a decrease in the solvency of buyers.
Estimation of liquidation value in crisis conditions
An unstable economic situation affects all aspects of people's lives and enterprise activities. It also significantly influences the determination of the value of assets during the reorganization of the organization. One of the signs of instability in the economy is the release of jobs. All industries and areas of business suffer at the same time, losing profits, and some cannot withstand this situation at all.

But there are also positive aspects to this situation. Real estate is becoming cheaper and you can start purchasing it or invest money in it. This requires a detailed market analysis to determine the real value of the objects. At a time when the economy is stable, all real estate is sold at market value, but in times of crisis we have to adapt to the situation on the market.
This is where the liquidation value is used, that is, it is the market price, taking into account a discount on various factors that influence it downwards. As the crisis progresses, all these factors become more relevant due to instability in the economic and financial sphere.
The difference between liquidation value and market value
Before understanding the differences between these types of prices, it is necessary to define market price.
Market value is the amount of money that can be obtained for an object on the market, in conditions of open competition, when each of the parties to the transaction acts consciously, taking into account all available information about the object, and the price of the object is not influenced by extraneous, extraordinary factors.
At the same time, there is enough time for sales so that a sufficient number of potential buyers can familiarize themselves with the terms of the transaction. All information about the subject of the transaction is as accessible as possible, and each party can easily use it. In this case, the transaction amount suits both parties; for the buyer it is the minimum of those offered, and for the seller, on the contrary, it is the maximum.
The absence of influencing extraordinary factors means that both the seller and the buyer act in their own interests, without exerting pressure. Therefore, the entire operation takes place as planned, without haste and in a sufficiently long time.
This is the main difference between these types of prices. In essence, the liquidation cost is equal to the market cost, but taking into account the factors influencing it downwards. And the main factor is the time frame within which the sale must be completed. That is, the liquidation tariff differs from the market tariff in that it is not influenced by third-party factors, and its size is set in accordance with the current state of the market.
How is the transition from market price to liquidation price carried out?
These two concepts of value exist in parallel with each other, and the liquidation price directly depends on the market price. When using the indirect method of real estate valuation, these types of prices are compared for the final price calculation. In this case, a discount is calculated for the urgency of the transaction.
It can reach up to 50% of the market value of the property. The size of the discount depends not only on time limits, it is also influenced by market demand, the state of the economy and the financial condition of the enterprise. It is important to conduct a detailed analysis of all indicators in order to obtain the most tailored cost for a specific type of property.
Thus, the transition is carried out when assessing the property of a legal entity by an indirect method, taking into account various factors.
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
What factors does it depend on?
The amount of this assessment depends on the following factors:
- the period during which implementation is planned;
- size (area, length, number of storeys, etc.);
- condition of the object - finished building or unfinished, presence of good finishing, equipment, etc.;
- market attractiveness, taking into account the location;
- seller's mood;
- general buoyancy of the real estate market.
Each of these factors makes its own adjustment to the final result, and in an unfavorable situation, it may happen that none of the factors contributes to increasing the value of the estimated amount.
For example, you can take the simplest option – an apartment. It is no secret that small-sized housing is in high demand, and it can be sold in the shortest possible time.
And if such a popular property, without a good expensive renovation, is also located in the most sought-after area, then the liquidation assessment may even exceed the price of a 4-room apartment in the same area.
Since it may not be possible to quickly find a buyer, all that remains is to lower the liquidation value, and this is precisely dictated by the seller’s mood.
Often circumstances force the owner to compress the period to such an extent that the liquidation valuation may be below a reasonable limit - this happens in bankruptcy, as well as when selling collateral.
There is a division of liquidation value into the following types:
- orderly (when the sale period allows the property to be sold at reasonable prices);
- forced (when release to the market and sale are carried out in the shortest possible time - in case of bankruptcy, for example);
- with the cessation of the existence of the owner’s assets (in this case, the objects as such are not purchased, but are dismantled, that is, dismantled, in order to use the place for the construction of other real estate).
Legislatively, the process of determining the liquidation valuation is regulated by such state acts:
- Federal Law dated July 29, 1998 N 135-FZ “On assessment…” as amended in 2019;
- Art. 54 Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Enforcement Proceedings” No. 119 – Federal Law of July 21, 1997;
- Art. 82 Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 119-FZ dated July 21, 1997;
- Art. 130, 132 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
There is such a direction in business when real estate that is sold for next to nothing, urgently, is bought up by businessmen, and then sold when a profitable option is found.
Liquidation value of real estate: what is it?
This cost means the price of housing at which it will be sold in a short time, on time, less than the usual exhibition period, other similar objects, without additional conditions. The exposure period is the period of time that begins from the date when the property is presented to the valuation market until the final date of the transaction.
Many institutions need liquidation value values, such as:
- Banks that provide mortgage lending for the purchase of an apartment, since it will be pledged for the entire period of payment for the mortgage;
- Any real estate buyer who is interested in purchasing it;
- Federal and municipal authorities, when destroying real estate that is in emergency condition;
- In court, during confiscation of housing for debts.
Residual, initial and salvage value
Salvage value is sometimes confused with other varieties. For example, with the initial or residual. Let's look at these terms in more detail. The initial value is the value with which the asset is taken into account in the balance sheet of the enterprise. This value usually includes all costs that the owner incurred to acquire or manufacture the property.
Residual value is the value determined by the difference between the original cost of the property and the accumulated depreciation rate. That is, this value shows how much the product costs after use. In fact, the residual value is the price of a used asset that is sold under normal (not crisis) conditions.
The price of the property upon liquidation is neither the residual nor the original. In terms of value, it is usually close to the residual value, but, as a rule, it falls lower due to the shortened sales period. Knowledge of all types of value is necessary for thoughtful business management and calculation of the sale of assets if necessary.
Liquidation value of real estate in valuation: what is it?
There are many definitions, the essence of them all boils down to the following in relation to real estate: the liquidation value of real estate in the assessment is the market value that can be obtained in the shortest possible time for the sale of the object.
Such steps are taken in relation to real estate in the following cases:
- to receive at least some revenue from unpromising “long-term construction”, when the building is just being destroyed, and its purpose, layout and other characteristics have lost their relevance during many years of inactivity;
- the business attached to the building has ceased to be profitable, and it is more logical to sell it than to aggravate the situation by continuing unprofitable activities;
- before putting up for auction an object owned by the state;
- in enforcement proceedings with bankrupt enterprises;
- if there is a need for an urgent sale of real estate for private reasons, etc.
If the structure is dilapidated or no one is interested in it as a building, then the liquidation value may include the price of building materials, equipment, structures that are formed during dismantling, and land .
There is a direct relationship between the urgency of implementation and the final figure of the liquidation value. The faster you need to sell, the lower the liquidation valuation of the property.
Usually they shop around for a long time, look for options before selling an object, and try to embellish it in order to increase the impression of its appearance in order to receive more revenue. In the case of a liquidation assessment, no marketing steps are taken to avoid investing funds, since the goal is different - to sell the property as quickly as possible.

What is salvage value?
Liquidation value is the monetary indicator of the valuation object, reduced by the amount of costs associated with its sale (for example, commissions, advertising costs, storage, delivery, etc.). In practice, the need to define it arises if the corresponding object needs to be implemented as soon as possible.
As a rule, the calculation of liquidation value is carried out if a commercial company leaves the market through bankruptcy or pays off debts with existing assets in the form of certain infrastructure facilities.
An enterprise can also decide to sell assets at liquidation value if, for example, it involves selling a business or optimizing its production model to meet new market requirements. Then the presence of outdated, from a technological point of view, enterprise funds may cause a shortfall in profit in an amount exceeding that which would characterize the sale of assets at standard prices. Therefore, the liquidation value of fixed assets can be reduced to a minimum - only so that the company will sooner have the opportunity to modernize production facilities, and then begin to generate more revenue due to the release of more technologically advanced groups of goods to the market.
A prompt sale of a company’s assets may be in demand if the business owner decides to engage in work in a fundamentally different segment, and he urgently needs cash. Selling company-owned assets at a reduced price may be preferable to taking out a loan, since interest payments on it may be significantly greater than the difference between the liquidation and standard price of the assets.
As a rule, the considered indicator is significantly lower than current market prices for the corresponding objects. But provided that the company’s management works effectively, the liquidation value of the asset can be generally comparable to the standard one. Moreover, if the object being sold is characterized by high price volatility, then it can, theoretically, be sold more profitably (at the peak of market value) than if the sale was carried out at regular prices, but during a period of declining prices.

It may be noted that the liquidation value of an object in some cases is not calculated in a short time. For example, if a multi-stage and, as a rule, lengthy bankruptcy procedure for a large enterprise is carried out. In this case, the price of the object being sold may not differ so significantly from the market price.
How does liquid value differ from market value?
The market value of real estate is determined based on marketing. The cost of housing is calculated without taking into account the time limit that will be required to sell it, and depends entirely on the actual price on the market. The market price is the real value of the property that currently exists in the housing market.
The liquidation value of housing has a certain amount of real estate, for which it can be easily and fairly quickly sold.
There are visible differences between the two types of cost:
- The liquidation price of the property is much lower than the market price and has a time limit.
- The market price of real estate will be influenced by the condition of the residential building and the proximity of infrastructure.
The liquidation value of the apartment is
Thus, in a number of transactions the liquidation value of housing is used. How does it differ from the market one? In what situations does it need to be determined?
“Market value is the most likely price at which a property can be sold in the near future,” says Inna Ignatkina, director of the department (GC “MIC”). – The market value depends on a number of factors (transport accessibility, type of house, square footage, etc.). Only a professional appraiser or an experienced realtor can most accurately determine the market value of a property.”
Often, home sellers who are poorly versed in the real estate market set prices for the properties they sell that differ significantly from the market average. Of course, everyone wants to sell their apartment at a higher price. However, the opposite also happens. Thus, an owner who wants to reduce the exposure time of the property being sold can set a price below the market price. In this case, we are already talking about the liquidation value of the property. “In other words, the liquidation value is the cost of housing that the seller will have to agree with if he needs to quickly sell the property he owns,” says MIC-Real Estate.
It is noteworthy that when issuing a mortgage loan, most credit institutions take into account not only the market value, but also the liquidation value of the home. This is done mainly so that in the event of a borrower's default, the collateral property can be sold without delay. If the bank puts residential space on the market at a price close to the market price, this will delay the process of selling the property.
It will be difficult for a person who does not understand the situation on the real estate market very well to independently determine both the market and liquidation value of the housing he owns. “Almost every real estate website today has an online calculator, which, by analyzing the data entered by the user, determines the cost of the apartment,” says Inna Ignatkina. – However, you need to understand that such programs do not take into account a number of pricing factors and nuances, and therefore the real price cannot be calculated in this way. It is not without reason that experienced appraisers and realtors always try to go to the property and inspect it in person in order to take into account all the features of the property, from transport accessibility to the quality of repairs in the apartment. Therefore, in preparation for a serious transaction, it is recommended to turn to professionals.”
If a client asks to estimate the value of a property for a quick sale, this is not a request for market value, but for liquidation value” (when the product cannot be publicly sold for the required time).
Liquidation Value refers to market-type estimated values for which the existence of a separate market is possible, since its calculation is associated with the use of market information reflecting the characteristics of the market to which the valuation object belongs.
Procedures for calculating market-type values are based on the market’s understanding of the value of the object being valued and take into account the typical motivations of its typical subjects.
This is the value in exchange - objective, calculated (or assigned) under the influence of supply and demand factors formed in the corresponding open and competitive market, based on the purchase of goods by the average, abstract (typical) buyer.
Although liquidation value also refers to market-type values, it represents a valuation base that is different from the market value, since its determination violates two important features present in determining market value as a type.
The liquidation value is determined if the property must be alienated in a period less than the usual period of exposure of similar objects, and represents the net amount of money that the owner of the property can receive upon its forced (forced) sale.
Determining liquidation value differs from determining market value in that it violates two conditions:
1) the sale is forced; 2) the period of exposure on the open market is shorter than typical for a certain market segment (the object is sold in a shorter time and, therefore, somewhat cheaper).
Unfortunately, in all known sources, including FSO-2, the case when only the first condition of the above is violated in determining the market value, that is, the sale is forced, but the period of exposure of the object is comparable to the typical one and is not strictly limited. In this case, value values can be obtained that are numerically close to market values (as a rule, higher values), but nevertheless, the value must be identified in this case as liquidation value due to the forced sale.
In the methodological literature, a distinction is often made between ordered and forced liquidation. Orderly liquidation (determined by Orderly Liquidation Value) is carried out for a period of time sufficient to obtain the maximum price. Orderly liquidation involves the development of a calendar schedule for the liquidation of assets. Forced Liquidation Value means the sale of assets as quickly as possible, and naturally, it involves obtaining less value. In case of involuntary (forced) liquidation, there is usually a decision of the court, arbitration, or bankruptcy commission. There is a rapid sale of assets, the exposure period is reduced, sometimes very significantly, and can be 1-3 months.
But here there seems to be a violation of logic: if this liquidation pair differs in the urgency (the second sign) of the liquidation procedure, then why is this not reflected in the names? The first name - ordered - only means the presence of a strict liquidation schedule, and not at all its leisurely nature. The second name generally speaks of compulsion (the first sign), as if orderly liquidation were not such? This terminological absurdity can be removed if, when comparing on a time basis, we use the concepts: liquidation within an acceptable time frame (comparable to typical ones in determining market value) and accelerated (forced) liquidation.
There is a fundamental difference between the liquidation value of a business and the liquidation value of real estate from its property complex. The calculation formula first contains the company's obligations, etc. Besides. The range of liquidation costs for an enterprise is much wider. Western practice shows that the liquidation value of a company as a whole is less than the amount of proceeds from the sale of its assets. The total costs of liquidating a business include:
— administrative costs for maintaining the operation of the enterprise until its liquidation is completed; - severance pay and payments: - expenses for advertising, legal and accounting services, organizing sales, commissions, transportation of assets being sold, etc.
When determining the liquidation value of real estate, liquidation costs are taken into account (advertising costs, legal and accounting services, organization of sales, commissions to sales agents, etc.).
The proceeds from the sale of assets, net of associated costs, are then discounted to the valuation date at an increased discount rate that reflects the liquidity of the assets and takes into account the risk associated with the liquidation procedure (as a forced sale).
The liquidation value of a property can be calculated on the basis of an already determined market value by introducing an empirical or otherwise determined discount. Its size can range from 0 to 100% depending on the level of liquidity of the type of property (asset) and the degree of reduction in the period of its sale.
Sometimes, based on the liquidation value, the collateral value is calculated, which is used in lending (secured by real estate).
Utilization value is a type of value of an object, determined by the (market) cost of materials and structural elements that make up the building (structure) in a real estate property without taking into account the cost of additional repairs and preparation of elements for sale. This cost is sometimes necessary when assessing compensation for the costs of demolition of a building.
What is the liquidation value of fixed assets
At the present stage of economic development, Russian legislation does not designate the liquidation value of fixed assets as a single concept due to the problem of concrete designation of this concept.
A correct comprehensive concept of salvage value is required in order to correctly calculate financial accounting depreciation. The most common methods used for depreciation are:
1. Cumulative - determined by comparing the cost of depreciation to the cumulative coefficient. The number of years remaining until the expiration of the term of use of the free funds object is divided by the total amount of years of its use:
Kk = N-rest. : n-sum.,
Kk – coefficient;
n-rest. – the remaining period until the expiration date of the product;
n-sum. – number of years of use of the product;
the final amount for the year is calculated as follows: A = (p.s. - hp) * Kk;
p.s. - the initial price of the invested funds;
hp—disposal price for the previous year of product operation;
Kk – coefficient.

2. Production - the amount of depreciation for the month is calculated through the actual production of the product for the month, produced at the depreciation rate:
A = o.p.x*p;
A- depreciation cost (for the previous month, quarter, year);
o.p.f. – the entire volume of the produced product (per month, quarter, year);
p. – depreciation rate from production.
or p. = (p.c –l.c.)/o.p.o,
o.p.o – product volume for the entire period of operation.
3. Straight-line - the amount of depreciation for the past year is calculated by dividing the cost of depreciation by the period of use of the OS product. And the monthly amount is determined by dividing the annual amount by 12.
A = (p.c. – l.c.)/C
p.s. – original price for the product;
l.c. – estimated cost for liquidation;
C—operation period;
A is the amount of depreciation for a specific period.
The purpose of the liquidation value of fixed assets is to calculate the initial cost of the finished product, as well as production costs such as sales, general economic, and general production. They directly include depreciation of fixed assets based on liquidation funds.
Basically, businesses determine salvage value by relying on the expected market value of the product. In the financial accounting of the tax office, this concept is not included and is not used at all.
Divisions of liquidation value of fixed assets:
- Orderly liquidation value - distribution of shares over the appropriate period (for greater proceeds from asset sales), especially if the product is new on the market.
- Forced liquidation value is the distribution of free shares in a critically short time (often at a single auction).
- Liquidation value, which indicates the termination of the real existence of shares of the enterprise. That is, the manufacturer’s shares are simply written off or subject to destruction. And in the vacant space, a new economic or social enterprise is created.
How is the liquidation value of an apartment estimated?
The size of the cost when selling housing is determined by the commercial price of housing, taking into account possible expenses in preparing for the sale of the apartment.
To determine the price of a property, two methods are used:
- straight;
- indirect.
The direct method occurs by comparing a property that is offered for sale with similar housing. This method is used by specialists from real estate firms, since they have statistics on the actual amounts of purchased housing and the ability to accurately set a liquidation price.
The indirect method occurs by analyzing the market value of residential property. The average value of the housing market is revealed, without the amount of money spent on its liquidation.
Important: If the seller does not have actual data on the current turnover of real estate on the market, it is better to use the indirect method to determine the liquidation price of the property.
In this calculation of liquidation value, it is necessary to take into account the effect of the adjustment amendment, which reflects the influence of many reasons on the completion of a real estate transaction. The amount of adjustment that is used in the formula to find the liquidation price is not certain, so the indirect method is not accurate. Currently, the adjustment factor is 20% of the market value of housing.
Formula for calculating liquidation value
How is liquidation value calculated? The formula for calculating this indicator includes the following components:
- current market price of the property;
- adjustment factor;
- an indicator reflecting the fact that the asset needs to be sold within a timely manner.
The sequence of calculations when applying the formula in question is as follows. First, the value of the adjustment coefficient is determined, taking into account the urgency of sales, the current level of demand for the object being sold, and its characteristics. The element of the formula under consideration has an average value of about 0.3. That is, we can say that the liquidation value is an indicator that is approximately 30% lower than market prices for the object being sold.
Once the size of the adjustment factor is determined, it is necessary to subtract it from 1. Afterwards, multiply the resulting figure by the market value of the object being sold. The most difficult thing, therefore, when calculating the liquidation price of an asset is to calculate the adjustment factor. Market value is an indicator that can be determined without any problems. In order to calculate the coefficient, it may be necessary to refer to statistical data reflecting the specifics of transactions for the sale of objects at liquidation value in the past, which were carried out by firms in the same segment in which the enterprise that is promptly selling its assets operates. But it is possible that the coefficient will be significantly lower than the statistical average, especially if certain factors contribute to this. Let's consider their specifics in more detail.
Market and liquidation value of an apartment: what is the difference?
The value of a property usually refers to its market value. However, there are other types of value of real estate, which are sometimes necessary to complete a particular transaction with it. Thus, in a number of transactions the liquidation value of housing is used. How does it differ from the market one? In what situations does it need to be determined?
The value of a property usually refers to its market value. However, there are other types of value of real estate, which are sometimes necessary to complete a particular transaction with it.
Stages of assessing liquidation value
The assessment of liquidation value, regardless of which method is used for this, is carried out in two stages:
- First, the market value of the property is determined;
- Calculate the amount of the adjustment adjustment for the forced sale, for which.
Factors such as:
- How will the transaction be completed?
- When?
- What is the amount of expenses associated with the sale of housing;
- What are the risks of investing?
Documents required for examination of a real estate property
- Copies of any plans or existing maps that have a description, as well as some designation of the location where the property being assessed is located;
- A package of documents from the BTI;
- Data on various buildings in the area where real estate needs to be assessed;
- Certificate of the right to dispose of land.
How is liquidation value calculated?
Having examined the definition of liquidation value and the main approaches to its classification, we will study how the indicator in question is calculated. The solution to the corresponding problem is carried out in several main stages.
First of all, the company's management develops a schedule in accordance with which the liquidation of the company's assets is expected. The next stage is calculating the value of assets, as well as possible costs associated with their liquidation. Next, the corresponding indicator is adjusted taking into account the urgency of the sale of the object and other circumstances of the procedure in question. This may take into account, for example, the magnitude of the company’s obligations, the fulfillment of which requires the sale of the company’s assets at liquidation value.

As for the direct calculation of the indicator under consideration, it is carried out taking into account the data on the company’s balance sheet. Their determination involves conducting an inventory of the company's property. In some cases, when calculating the indicator in question, the gross proceeds from the sale of assets are also calculated. Operating profit figures during the liquidation period may also be taken into account.
When calculating the optimal value of the value of the company's assets being sold, priority costs associated with calculating salaries for personnel, transferring payments to the budget, and monetary transactions to creditors who are not involved in the bankruptcy procedure are taken into account (if the liquidation sale of the company is associated with it).
Questions and answers
Question:
Enterprise (A) is being liquidated, a liquidation commission has been created...
The enterprise has land plots with a book value of 4,000,000 rubles. The cadastral value is 1,200,000 rubles. Enterprise (A) sells the plots to enterprise (B). The goal is to reduce the tax base. At what price can the plots be sold (so that the tax authorities do not have questions)
-balance sheet
- cadastral
-any
Is it possible (legal) to reduce the book value to the cadastral value?
What documents (from the Tax Code) support all this?
If enterprise B is the founder of enterprise A, is it possible to transfer the plots of enterprise A to B without forming a tax base? What's the best way to do it?
Expert:
Alexander.
There is enough property to carry out liquidation without subsequent bankruptcy. Will all creditors be repaid?
Expert:
If enterprise B is the founder of enterprise A, is it possible to transfer the plots of enterprise A to B without forming a tax base? Alexander
if the authorized capital is large, then you can
1. When determining the tax base, the following income is not taken into account: ... 4)
in the form of property, property rights that are received within the limits of the contribution (contribution) by a participant in a business company or partnership (his successor or heir), when reducing the authorized capital in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation Federation, upon withdrawal (disposal) from a business company or partnership or upon distribution of the property of a liquidated business company or partnership between its participants; If enterprise B is the founder of enterprise A Alexander
since these are interdependent persons within the framework of the Tax Code (Article 105.1)
Article 105.1. Interdependent persons 1. If the peculiarities of relations between persons may influence the conditions and (or) results of transactions made by these persons, and (or) the economic results of the activities of these persons or the activities of the persons they represent, the persons specified in this paragraph are recognized as interdependent for tax purposes (hereinafter referred to as interdependent persons). To recognize the mutual dependence of persons, the influence that may be exerted due to the participation of one person in the capital of other persons is taken into account, in accordance with an agreement concluded between them, or if there is another opportunity for one person to determine the decisions made by other persons. In this case, such influence is taken into account regardless of whether it can be exercised by one person directly and independently or jointly with his interdependent persons recognized as such in accordance with this article.
then it is better to evaluate the property (if not) and sell it. In its control, the Federal Tax Service will be guided by the priority method - the method of comparable market prices.
Article 105.7.
General provisions on the methods used in determining income (profit, revenue) for tax purposes in transactions to which the parties are interdependent persons 1. When conducting tax control in connection with transactions between interdependent persons (including when comparing commercial and (or) financial conditions of the analyzed transaction and its results with the commercial and (or) financial conditions of comparable transactions and their results), the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees uses the following methods in the manner established by this chapter: 1) method of comparable market prices; 2) subsequent sale price method; 3) cost method; 4) comparable profitability method; 5) profit distribution method. 2. It is permitted to use a combination of two or more methods provided for in paragraph 1 of this article. 3. The method of comparable market prices is a priority for determining for tax purposes the compliance of prices used in transactions with market prices, unless otherwise provided by paragraph 2 of Article 105.10 of this Code.
The use of other methods specified in subparagraphs 2 - 5 of paragraph 1 of this article is permitted if the use of the comparable market prices method is impossible or if its application does not allow one to reasonably draw a conclusion about the conformity or non-compliance of the prices used in transactions with market prices for tax purposes . The method of comparable market prices is used to determine the conformity of the price applied in a controlled transaction with the market price in the manner established by Article 105.9 of this Code, if there is at least one comparable transaction on the relevant market of goods (works, services), the subject of which is identical (if absence - homogeneous) goods (work, services), as well as in the presence of sufficient information about such a transaction. At the same time, in order to apply the method of comparable market prices in order to determine the conformity of the price applied by the taxpayer in a controlled transaction, it is possible to use as a comparable transaction a transaction made by the specified taxpayer with persons who are not interdependent with the specified taxpayer, provided that such a transaction is comparable with analyzed transaction. Dear lawyers!
Several years ago, under a share participation agreement, I purchased an apartment in a building that was still under construction.
An important factor in purchasing a specific apartment (floor, entrance) was the expected view from the window.
According to the development plan presented at that time, the construction of houses higher than 5 floors nearby was not planned.
Recently it became clear that a high-rise building of the next house will be built, which will block the view of the surrounding area.
In this situation, can I demand from the developer the loss of the market value of the apartment?
Expert:
If your apartment was transferred to you in accordance with the terms of the contract (quality, layout, decoration), then you cannot demand any compensation. I think the view from your window is not specified in the contract as an essential condition, so the developer is not violating anything.
Moreover, neither the law on the protection of consumer rights nor Federal Law 214 on the DDA has the concept of market value (its loss). There may be a low-quality object, or a delay in its delivery, or another violation of the contract. But not the construction site next to you, which does not violate your agreement.
According to Article 451, the contract may be changed or terminated
1. A significant change in the circumstances from which the parties proceeded when concluding the contract is the basis for its modification or termination, unless otherwise provided for by the contract or follows from its essence.
A change in circumstances is considered significant when they have changed so much that, if the parties could have reasonably foreseen it, the contract would not have been concluded by them at all or would have been concluded on significantly different terms.
but here you have to prove that if it weren’t for the view from the window, you wouldn’t have bought the apartment, this is also a problem in itself. Yes, and it is difficult to prove in court that this was your essential condition, despite the fact that it is not stated in the contract.
Expert:
Dmitry, good afternoon! According to Art. 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a significant change in the circumstances from which the parties proceeded when concluding an agreement is the basis for its modification or termination, unless otherwise provided for by the agreement or follows from its essence.
at the same time, under a significant change in circumstances, when they have changed so much that, if the parties could have reasonably foreseen this, the contract would not have been concluded by them at all or would have been concluded on significantly different terms.
As I understand it, the agreed circumstances are in no way reflected in the agreement (that in the future no taller buildings will be erected that will block the view from the window), therefore it is already difficult to prove that you proceeded from this circumstance when concluding the agreement. But even if this point is allowed, then to change the contract, i.e. In this case, reducing the price in court requires the presence of a set of conditions defined by Part 2 of Art. 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, that is:
1) at the time of concluding the contract, the parties assumed that
such a change in circumstances would not occur; 2) the change in circumstances was caused by reasons that the interested party could not overcome after their occurrence with the degree of care and prudence that was required of it by the nature of the contract and the conditions of turnover; 3) execution of the contract without changing its terms would so violate the relationship of property interests of the parties corresponding to the contract and would entail such damage for the interested party that it would largely lose what it had the right to count on when concluding the contract; 4) it does not follow from customs or the essence of the contract that the risk of changes in circumstances is borne by the interested party.
Taking this into account, there are no prospects for such a claim, and there is also no reason to demand compensation from the developer if the transferred apartment complies with the terms of the contract
Expert:
There is, although not numerous, but positive judicial practice in such cases, for example
In the fall of 2020, the developer was held liable due to the fact that the house he built practically deprived the residents of the entrance of the house in Yekaterinburg of sun.
https://oblsud—svd.sudrf.ru/m...
Or, for example, the conclusion of the Supreme Court:
https://vsrf.ru/stor_pdf.php?id...
From the analysis of the above legal norms, it follows that when concluding an agreement for participation in shared construction, the developer is obliged to provide the participant in shared construction with reliable information not only about the consumer properties and characteristics of a specific shared construction object (in this case, an apartment) to be transferred within the time frame established by the agreement, but and other information regarding the apartment building under construction, which would provide the participant in shared construction with the opportunity to freely and correctly select the appropriate premises in the building under construction. In this case, this information should include a description of the location of the property under construction, taking into account the environment, as well as information about the composition and location of common property in an apartment building, for example, electrical, sanitary and other equipment.
Below I will describe the court’s position
Expert:
Dmitriy,
Let's look at the law:
According to Part 1 of Art. 7 FZ-214 The developer is obliged to transfer to the participant in shared construction a shared construction object, the quality of which complies with the terms of the contract, the requirements of technical regulations, design documentation and urban planning regulations , as well as other mandatory requirements.
In the event that a shared construction project is built (created) by a developer with deviations from the terms of the contract and (or) the mandatory requirements specified in Part 1 of this article, leading to a deterioration in the quality of such a project, or with other shortcomings that make it unsuitable for the use specified in the contract , a participant in shared construction, unless otherwise established by the agreement, at his own discretion has the right to demand from the developer: 1) gratuitous elimination of defects within a reasonable time;
2) a proportionate reduction in the contract price; 3) reimbursement of their expenses for eliminating deficiencies.
In this case, you need to look at the project documentation, but it will be difficult to obtain these documents; they can either be demanded through the court, or in pre-trial proceedings, or through administrative bodies that supervise shared construction.
However, the question is what was in the project. If construction outside the window is carried out by a completely different person who has received all permits from the Administration, then the Developer cannot be responsible for their actions, so it will be impossible to receive compensation.
Do you remember what was in the project?