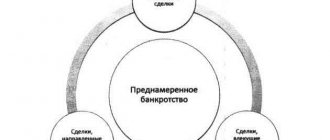
- What is not recommended to do before declaring yourself bankrupt?
- Challenging transactions
- Consequences of violating the rules of bankruptcy of individuals
In accordance with the new provisions of the Bankruptcy Law, which came into force in October 2020, an individual can file for bankruptcy. This requires simultaneous compliance with the following conditions:
- inability to repay existing debts within the established schedule for objective reasons;
- the insufficiency of the property owned by the citizen to fulfill obligations to creditors was confirmed.
In many situations, the ability to declare yourself bankrupt is practically the only possible way to resolve the problem of accumulated debts and protect yourself from possible unlawful actions of debt collectors. However, it must be borne in mind that this procedure must be carried out taking into account certain requirements. It is especially important to consider what is not allowed before bankruptcy - this will help avoid negative consequences, as well as refusal to declare an individual debtor bankrupt.
Bankruptcy procedure and debts
The concept of financial insolvency is inseparable from the lending system. Today, even large and wealthy companies regularly resort to the mechanism of financial borrowing. The volume of loan obligations determines how successfully a business is run. Moreover, the absence of raised funds in the company’s budget may indirectly indicate that the development potential of the enterprise is very limited or that it does not inspire confidence among credit institutions. Meanwhile, the company’s debts, or rather the impossibility of repaying them on time, is the main reason for bankruptcy.
Even if we imagine a company that does not attract credit funds at all, this does not guarantee its absolute resistance to bankruptcy. Such an organization has obligations to pay wages, transfer taxes, other budget fees, as well as monetary obligations to counterparties. A decrease in the profitability of an enterprise over time inevitably leads to delays in making mandatory payments, which may result in bankruptcy proceedings.
Is bankruptcy profitable?
The procedure for declaring financial insolvency has a number of advantages. Who benefits from bankruptcy law? Both parties can be interested. Debtors have the opportunity to get rid of obligations that they cannot pay off. At the same time, you should not hope for quick debt write-off. A preliminary search for an optimal solution remains to be done, be it the restructuring of overdue amounts or the sale of part of the property to pay off the debt.
For creditors, including banks, supplier counterparties and other interested parties, recognition of insolvency sometimes seems to be the only way to collect debt. If the defaulter is an organization, you can demand part of the debt from the management.
A mandatory point for declaring bankruptcy is the presence of large debts
How to avoid bankruptcy proceedings?
Many entrepreneurs would spare no expense to answer this question. However, there is simply no universal recipe. Even very efficient use of an enterprise’s material, financial and labor resources does not always help: cyclical factors in the economy play a role. A certain branch of production may be under attack due to changes in market conditions; fluctuations in the exchange rate of the national currency and changes in legislation that tighten requirements for enterprises play a negative role. All these factors, individually or in combination, can bring even a very successful enterprise to the brink of bankruptcy. Admitting the insolvency of an organization is an unpleasant procedure, but it has its undoubted advantages. The most important of them is relief from the debt burden: after bankruptcy procedures established by law, all obligations of the enterprise are considered extinguished. This also applies to:
- debts to counterparties;
- obligations to pay wages;
- tax and other requirements.
Moreover, as a result of bankruptcy procedures, the organization is completely liquidated, and it becomes absolutely impossible to challenge transactions with its participation, make monetary claims or recover losses from it. To summarize, we can say that the bankruptcy procedure is a chance for all parties involved in the process to part with minimal losses and leave the conflict in the past.
What is the procedure for declaring a company bankrupt?
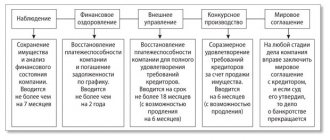
The functions of recognizing the insolvency of organizations are performed by the arbitration court. To carry out the procedure, it is necessary to receive an application to declare the debtor bankrupt. It can come from either an authorized representative of the debtor organization or from the creditor for monetary obligations. In the latter case, the law obliges the applicant to first go through the standard debt collection . It can be carried out in an arbitration or arbitration court, as well as in a court of general jurisdiction. Having received a court decision to collect the debt and submitted it for execution, the creditor must wait 30 days, and only after that initiate bankruptcy proceedings. The arbitration court's reaction to the application also differs depending on who files it: the debtor or the creditor. In the second case, a procedure will be carried out to verify how justified the monetary claims against the debtor are. For these purposes, a court hearing is held to consider the validity of the stated claim. Based on the results of this meeting, a determination is made on the transition to the first phase of the bankruptcy procedure: observation. The main goal of this stage is to record the financial condition of the enterprise, draw up a list of debt obligations and determine their total volume, and hold a meeting of creditors. For these purposes, the court approves a temporary manager. Among other things, he is responsible for taking care of the property of the enterprise. The company's management at this stage is not suspended from activities, but accepts some restrictions.
Bankruptcy of legal entities
The financial insolvency of organizations can be considered as bankruptcy. In this case, the mandatory conditions are as follows:
- The amount of debt is over 300,000 rubles.
- Payments for invoices are not made for 3 months.
Unlike bankruptcy of citizens, in relation to the work of enterprises, a bankruptcy trustee is appointed, whose purpose is to assess current liquidity, the general condition of the organization, and identify profitable areas of activity.
Based on the results of the analysis, reorganization (financial recovery of the entity) or bankruptcy procedure can be carried out. In the latter case, after possible payment of the debt, the organization is liquidated.
The fate of the enterprise is in the hands of creditors
Participants in the first meeting of creditors, which must be held in the observation procedure, are aware that the return of funds through bankruptcy will inevitably lead to costs. It should be noted that only persons included in the register of creditors’ claims can manage bankruptcy procedures. Inclusion of the debtor's creditors' claims in the register is a separate legal process and legal service. Repayment of borrowed funds with due interest is possible only if the enterprise continues to operate and restores solvency. Therefore, creditors must decide: does the enterprise in this situation have prospects for financial development (recovery)? If the proposed development plan and debt repayment schedule are satisfactory to the interested parties, then the arbitration court, based on the decision of the creditors, can make a ruling on the introduction of financial rehabilitation. In this case, the management of the enterprise retains its posts, but acts under the control of the administrative manager. If management does not inspire confidence among creditors, then external management may be introduced by decision of the arbitration court. In this case, management is deprived of all powers and cedes them to an external manager, who reports on his activities to the meeting of creditors.
Ways out of bankruptcy.
Page 1 of 2Next ⇒
Basic concepts of financial management.
The concept of cash flow consists in representing an enterprise as a set of inflows and outflows of cash flows, from any financial operation a cash flow can be realized, i.e. set of distributions over time of payments and receipts. Elements of cash flow:
-Day deed,
- income and expenses,
-profit and payments.
The concept of priorities of economic interests of owners. It was first put forward by G. Simon; he refuted the classical and neoclassical idea of a company as an organization aimed at maximizing profits. He formulated the concept of the cat, who swore that it was necessary to satisfy the interests of the owner. It gradually transformed into Finnish management.
Modern portfolio theory - its founder, Harry Markovets, created it in 1952. It is based on the principles of statistical analysis and optimization of the relationship between the level of risk and return on securities when forming an investment portfolio. The total level of risk can be reduced by combining risky assets of the portfolio. The level of risk for each type should not be measured in isolation, but based on the overall impact on the portfolio of investments.
The concept of the cost of capital - the essence is that the costs of an enterprise differ significantly in the context of individual sources of financing. Each source has its own cost in the form of relative costs that the company is forced to bear for using it, when choosing an alternative source of financing assets, a quantitative assessment of the cost of the attracted capital plays a decisive role. Minimizing the weighted average cost of capital ensures maximum welfare of the owners
The concept of capital structure - Asserts: 1) The presence of a certain share of borrowed capital is useful for the enterprise, and its excessive use is harmful. 2) For each enterprise there is its own optimal share of borrowed capital.
The theory of dividend policy was founded in 1956. It is based on the mechanism of influence of this theory on the market value of a company and the price of its shares, making it possible to determine the size of those dividends in connection with the influence of various factors. There are 3 theories of policy: 1) the theory of dividend consistency. 2) the “bird in hand” theory or the theory of the existence of dividend policy. 3) the theory of tax differentiation.
The concept of the value of money in time - 1930. I. Fisher's essence is that the monetary unit both available today and the monetary unit expected to be received ch.z. for some time, initially today’s ruble is worth more, i.e. its value is greater than that of the ruble, which we will receive in a few years. This is determined by the action of 3 factors: 1) inflation 2) the risk of not receiving the expected amount and turnover.
The theory of the relationship between the level of risk and profitability. -1921 F. Knight, essence: obtaining any income involves risk, and the connection between them is directly proportional, that is, the higher the profitability, the lower the level of risk associated with compensation for the non-receipt of this profitability.
Theory of agency relations - 1976 V. Mikling: agency relations are understood as relationships in which the owner of the company transfers his functions for asset management to the financial manager. Agents have their own interests, often inconsistent with the interests of the owner, a conflict of interests arises. The owner is obliged to take into account interests, using incentive mechanisms. Reward/indication system. There are primary conflicts of interest: between owners and managers, owners and creditors. Managers can be encouraged to act for the benefit of shareholders through incentives and restrictions.
The concept of asymmetric information - 1984 by S. Myers and N. Majlaff: there is always insider information, that is, inaccessible to the general public. As a result, investors suffer certain financial losses.
The theory of market efficiency - 1970 by Yu. Fama: it reflects the dependence of the price efficiency of the stock market on the level of information provision of its participants. Price formation assumes that the expected price, yield of securities prices is a random variable, reflecting: the appropriate level of information of market participants. Depending on the conditions of information support, participants are distinguished: weak, medium, strong price efficiency of the stock market. The most informed participants have priorities.
Perpetual annuity.
An annuity is called perpetual if cash receipts continue for a long time. A typical example of a perpetual annuity is consoles - bonds issued by the governments of some countries, for which regular coupon payments are made, but which do not have a fixed term. In Western practice, perpetual annuities include annuities designed for 50 years or more. A perpetual annuity is also called a perpetual annuity.
The direct task does not make sense (determining the future value of an annuity); the inverse task has the form: PV= this formula is used to assess the feasibility of purchasing a perpetual annuity.
Example: it is proposed to invest a portfolio of securities prices of 5 million rubles. and receive an income of 420 thousand rubles. It is known that the bank offers 14% per annum on time deposits, determine under what conditions the purchase of securities will be more profitable. PV = = 3 million rubles So if the annuity is offered at a price of no more than 3 million rubles is a profitable investment.
Plan-fact analysis in an enterprise financial management system.
Carrying out plan-fact analysis has two main goals:
· planned;
· control and stimulation.
The planned goal is implemented on the basis of certain conclusions made on the basis of plan-fact analysis for the past period when drawing up budgets. As a rule, the principle of “continuing activity” is used, which is applied to budgeting.
The enterprise's budget for the upcoming budget period should be developed based on an analysis of the reasons for deviations of the actual values of indicators from their planned values, as well as the identification and use of internal reserves for increasing efficiency and improving the financial condition of the company.
When drawing up a new budget, two factors are taken into account: objective and subjective.
The objective factor is associated with changes in market conditions and affects the value of the “input” parameters of the budget (market prices for goods, works, services produced by the enterprise, as well as for raw materials, materials, energy, labor and other resources; rules for taxation of enterprise activities; interest rates for loan, etc.).
The subjective factor is associated with the possibility of using the internal reserves of the enterprise, identified at the stage of analyzing the budget execution for the previous period (the amount of receivables and payables, the level of variable and fixed costs, the size of inventories of raw materials and finished products, the timeliness of receipt and expenditure of funds, etc.).
The control and incentive goal of plan-fact analysis is realized with the help of information about deviations of the “fact” from the plan when assessing the results of the work of a structural unit of the enterprise and service.
Budget targets for product sales volumes, production volumes by product range, volumes of purchases of raw materials and supplies, cost levels, deadlines for collection of receivables or repayment periods for accounts payable can be considered as a basis for assessing the work of departments, their managers and individual specialists.
Based on the results of this assessment, it is possible to apply measures of material and moral incentives for personnel. Using various schemes for “linking” the results of plan-factual analysis to incentives (rewards and punishments).
In one case, incentives are possible for exceeding sales targets, generating income, collecting accounts receivable, etc. and penalties for failure to complete these tasks.
In another case, rewards and punishments may be related to the amount of resource savings and cost reductions.
4.Budgeting and types of budgets in financial planning of a company
The transition of domestic enterprises to new economic conditions was accompanied by changes in approaches to management. Foreign enterprises have long been using technologies such as strategic management, marketing, budgeting, process approach, etc. The effectiveness of these technologies has been proven. However, their active use in Russia is associated with a number of difficulties:
– low qualifications of managers;
– reluctance of management;
– lack of financial opportunities to master these management technologies, etc. One of the popular management technologies is budgeting. Despite its wide popularity, its theoretical issues are interpreted by scientists from different points of view. The following point of view is generally accepted: budgeting is the production and financial planning of an enterprise by drawing up the general budget of the enterprise, as well as the budgets of individual divisions in order to determine their financial costs and results.
Budgeting should be distinguished from financial planning. Firstly, budgeting is simultaneously planning, accounting, analysis, motivation and control, and financial planning affects only the planning stage. Secondly, in the budgeting process, planning is carried out in all areas of the enterprise’s activities: sales, production, purchasing, finance, etc. In the process of financial planning, only issues of the enterprise’s financial system are addressed.
The result of budgeting at an enterprise is the development of a system of budgets that can be compiled both in physical and monetary terms. Enterprise budgets can be understood as economic forecasts, a basis for control, a means of coordination, a basis for setting tasks, and a means of delegating authority.
The budgeting system develops many types and forms of budgets. Separate budgets characterize intermediate operations (purchases of raw materials, production budget, etc.) and can only contain information about expenses or income (sales budgets). Integrated budgets (budget income statement, cash budget) show both expenses and income of the enterprise.
There are no uniform requirements for the budgeting system. The state does not regulate this system at the enterprise in any way. Each enterprise itself determines the parameters of the budgeting system:
– composition of budgets;
– planning horizons;
– composition of planned indicators, etc. The introduction of a budgeting system means for an enterprise, as a rule, serious structural changes in economic and financial work. As a result, management processes become more understandable and transparent, ineffective structural units are identified, the motivation of enterprise employees is enhanced, and strategic issues are linked to tactical ones.
Difficulties in implementing budgeting at domestic enterprises are usually associated with the fact that it requires:
– radical restructuring of all business processes of the enterprise;
– implementation of expensive budgeting automation tools;
– advanced training of financial and all management employees;
– additional costs for consultants’ services;
– development of a regulatory framework;
– increasing the execution discipline of internal legal documents, etc.
ways out of bankruptcy.
In accordance with the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, if an enterprise has signs of bankruptcy, the manager is obliged to inform the founders or the owner of the property about this, who must take timely measures to prevent bankruptcy. Measures aimed at restoring the debtor's solvency may be taken by creditors or other persons based on an agreement with the debtor. To prevent bankruptcy, the founders or owner of the organization or other persons may provide financial assistance to the debtor in an amount sufficient to repay monetary obligations and obligatory payments and restore the debtor’s solvency.
The essential signs of insolvency are:
a) the inability of a person to satisfy the claims of creditors. Creditors' claims may relate to payment for goods (work, services), mandatory payments to the budget and extra-budgetary funds;
b) the inability of a person to satisfy the claims of creditors due to the excess of the debtor’s obligations over his property.
c) the inability of a person to satisfy the claims of creditors due to the unsatisfactory structure of his balance sheet. An unsatisfactory balance sheet structure is understood as such a state of the debtor’s property and obligations when, at the expense of the property, timely fulfillment of obligations to creditors cannot be ensured due to the insufficient degree of liquidity of the debtor’s property, i.e., the inability to quickly sell it and use the proceeds to cover debts In this case, the total value of the property may be equal to or exceed the total amount of the debtor's obligations (preamble to the Insolvency Law). More specific criteria for establishing an unsatisfactory balance sheet structure are contained in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 20, 1994 No. 498 “On some measures to implement legislation on the insolvency (bankruptcy) of enterprises.”
The concept of insolvency is characterized, in addition to essential ones, by external features. An external sign of a person’s insolvency is the suspension of his current payments, provided that the person does not ensure or is obviously unable to ensure the fulfillment of creditors’ claims within three months from the date they become due (Part 2 of Article 1 of the Insolvency Law). A person's deliberate inability to ensure the fulfillment of creditors' demands, of course, can only be known to him, therefore, only on his (and not the creditors') initiative is it possible to initiate insolvency proceedings. It should be especially emphasized that the presence of an external sign of insolvency does not mean insolvency itself. Suspension of current payments for a period of at least three months only means that the person is insolvent and there are grounds for initiating insolvency proceedings. In accordance with Part 3 of Art. 1 of the Insolvency Law, a person is considered insolvent after recognition of the fact of insolvency by an arbitration court or after an official announcement of it by the debtor during its voluntary liquidation in the “Bulletin of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation”. Other government bodies and persons, including the owner of the enterprise, do not have the right to make decisions on insolvency.
In the process of bankruptcy, it goes through several stages: the hidden stage of bankruptcy, the stage of financial instability, the stage of insolvency, the stage of official recognition of bankruptcy. At each of these stages, measures are taken to prevent bankruptcy. At the first 2 stages, these measures are taken by the owners and the head of the organization, i.e. the process of crisis management is considered as an internal task of the company. At stages 3 and 4, levers of external influence are used, including judicial procedures.
Work to bring an enterprise out of insolvency begins with an analysis of the financial condition and forecast of the organization’s work in the short term (up to a year ). The forecast is based on the premises of changes in the external environment and the implementation of a system of anti-crisis measures : 1) the possibility of restructuring obligations; 2) Prospects for increasing the volume of production and sales of traditional products; 3) Possibility of liquidation, sale, lease of unused assets; 4) Changes in dividend policy, etc.
This is the so-called “smooth” path of reform, which does not require re-profiling of the enterprise and can lead to an improvement in the financial situation. The second way is associated with the need for re-profiling and is used for those enterprises whose insolvency is caused by a decrease in demand for products. The forecast in this case includes an assessment of the possibilities of using the organization’s assets to produce fundamentally different products, the demand for which is predicted to be high. Based on the results of the forecast of the financial state, a business plan for financial recovery is drawn up, which includes the following measures:
1)Analysis of tangible assets in order to determine the reasons for their use. For each element, a decision must be made: keep, repair, modernize, rent out, sell, dispose of.
2)Analysis of types of products
3)Analysis of intangible assets
4)Analysis of financial assets (it turns out that it is more profitable to keep or sell)
5)Analysis of the commodity distribution network (prospects for cooperation with various intermediary structures are identified)
6)The possible consequences of the reorganization of the enterprise, changes in the production structure and management structure are being studied.
The Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 provides for the possibility of reorganizing companies in the form of merger, division, spin-off, transformation. A merger of companies recognizes the emergence of a new company by transferring to it all the rights and obligations of two or more companies with the termination of the latter . The merger of a company is the termination of one or more companies with the transfer of all their rights and obligations to another company. The division of a company is the termination of a company with the transfer of all its rights and obligations to the newly created company. off of a company is the creation of one or more companies with the transfer to them of part of the rights and obligations of the reorganized company without terminating the latter.
The company has the right to transform into a limited liability company or into a production cooperative in compliance with the requirements established by Federal Laws. The company, by unanimous decision of all shareholders, has the right to transform into a non-profit partnership.
7)Working with debtors and creditors, i.e. developing and including in the business plan such consideration of their interests, which will force them to support the bankrupt enterprise


9)Implementation of highly effective investment projects
A financial recovery business plan is drawn up by the administration and agreed with creditors, the tax inspectorate and other interested parties. If a company is unable to restore its solvency on its own, then, at the request of creditors, a case is initiated against it in an arbitration court. When considering a bankruptcy case of a legal entity, the following bankruptcy procedures : observation, financial recovery, external management, bankruptcy proceedings, settlement agreement. If, based on the results of the first three procedures, the company was unable to improve its financial condition, then, by decision of the arbitration court, the organization is declared bankrupt, which entails the opening of bankruptcy proceedings. Bankruptcy proceedings are introduced for a period of one year and represent the forced alienation of property and liquidation of the company. The bankruptcy trustee evaluates the assets and liabilities of the debtor, and then sells them at open auction, unless a different procedure for the sale of property is established by law. The initial sale price of the debtor's property put up for auction is determined by an independent appraiser. Next, we will satisfy the requirements of interested parties and creditors in the manner prescribed by law. After full repayment of obligations, the register of creditors is closed, and the company is recognized as debt-free. At any stage of the bankruptcy case, a settlement agreement can be concluded between the debtor and creditors and the bankruptcy case can be terminated. Liquidation of pre-I can be carried out on a voluntary basis. In addition, before filing an application with the court, it is possible to resolve problems non-judicially through an extension or a compromise agreement. Prolongation is the postponement of payment deadlines for obligations. Compromise agreement – partial repayment of creditors' claims.
Risk assessment methods.
There are 2 known methods for determining risks:
1 Sensitivity analysis of the situation . Determining the difference between optimistic and pessimistic forecasts of asset returns. An asset with a maximum variation in profitability is the riskiest: R= —
2Analysis of the probability distribution of profitability . Determination of the standard deviation from the average return and the coefficient of variation, which characterizes the level of risk of a given asset. The higher the coefficient of variation, the greater the risk
The calculation sequence is as follows
1) Predictive estimates of profitability are made
2) The most probable profitability is calculated =∑ *
3) Define standard deviations = × (root of the entire formula)
4) Calculate the coefficient of variation V=
The purpose and objectives of FM.
The main goal of Finnish management is to ensure the maximization of the well-being of the owners of the enterprise in the current and future periods. The goal is expressed in maximizing the market value of the enterprise, which ensures the final results for its owners.
Objectives: 1) Formation of a sufficient amount of financial resources for the development of enterprises. 2) Effective distribution and use of generated resources in the main areas of activity of the enterprise. 3) Optimization of cash flow. planning the level of profit.6) Ensuring the constant balance of the enterprise, it must always be solvent and financially stable, which is achieved through: the formation of an optimal structure of assets and liabilities, the desire for self-financing.
1Next ⇒
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
Bankruptcy proceedings
If no measures help creditors to return their funds, then bankruptcy proceedings begin - bankruptcy proceedings. A bankruptcy trustee appointed by the court takes care of identifying and selling the debtor’s property and assets. The former management is completely removed from their positions.
bankruptcy procedure for an enterprise in an arbitration court
The order of repayment of loan funds is determined in the manner established by law. After all the property of the enterprise has been sold, the bankruptcy trustee makes payments from the proceeds to creditors in the established order of priority according to the register of creditors' claims, after which he reports on his activities to the arbitration court. Based on this report, a decision may be made to complete the proceedings and liquidate the legal entity.
What is bankruptcy
This term is usually used to describe the financial insolvency of persons, the inability to pay off creditors’ claims on time and in full. Liquidation of current debt at the legislative level allows you to get rid of previously assumed obligations legally.
The bankruptcy procedure helps to improve the financial situation of the parties to the conflict. Additional funds are being sought for creditors to repay the debt. Individuals who have no options to pay their bills have a chance to relieve their obligations at lower financial costs.