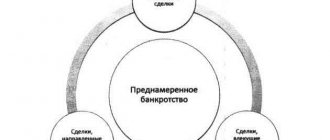
When a company accumulates debt obligations and it can no longer carry out business activities, there are two options - to declare itself bankrupt and leave the market, or to restore solvency.
Bankruptcy is not the most pleasant reorganization procedure for a company in a difficult financial situation. Declaring a debtor insolvent involves legal proceedings and subsequent liquidation of the legal entity.
However, bankruptcy is not always advisable, because the company may have temporary difficulties or the value of its assets may exceed the amount of debt. Adverse consequences can be avoided if timely measures are taken to help pay off debts and return the company to the ability to make a profit. One of these measures is rehabilitation.
What is the essence of restoring solvency?
Rehabilitation is a set of actions aimed at avoiding liquidation of an enterprise, full or partial settlement with creditors, and restoration of solvency.
In the Ukrainian state, this procedure is regulated by the Economic Code, the Law on the Resumption of Solvency of the Debtor, and the Regulations on Rehabilitation of 2013. In October 2020, the Verkhovna Rada adopted the Bankruptcy Code, which will come into force six months after publication, and the law mentioned above will no longer be in effect.
Restoring solvency is possible through:
- disposal of the debtor's property;
- enterprise restructuring;
- attracting investors.
According to lawyers, reorganization is meaningless if the company’s products are not in demand, as well as if management is low in efficiency. In such cases, the only way out is bankruptcy.
Bankruptcies of national importance
The Federation Council is preparing a bill on a new structure for the reorganization of enterprises
A new specialized state company, the idea of which is being developed in the Federation Council, should prevent the bankruptcy of enterprises. Business doubts its necessity: Russia already has all the necessary support tools
Photo: Sergey Fadeichev / TASS
The Federation Council is developing a bill on the creation of a state Business Rehabilitation Center. The author of the initiative is Senator Maxim Kavdzharadze, the Upper House Committee on Rules of Procedure told RBC. RBC has a draft explanatory note to the bill.
“We are talking about creating a fund to protect employees of enterprises, including developers who have gone bankrupt,” the Regulations Committee explained to RBC. “We want to hear the opinion of the Accounts Chamber, the Commissioner for Human Rights, relevant ministries and departments.” The initiative will be discussed on Tuesday, April 16, at a meeting of this committee. If the committee and experts approve it, it will form the basis of the bill, RBC’s interlocutor in the chamber’s office clarified.
Vladimir Kravchenko, a member of the Federation Council Committee on Economic Policy, told RBC that the project is currently only at the idea stage, but in the future it could become a bill. “The idea is interesting from the standpoint of what we see in the regions, especially with regard to developers,” he emphasized. “They have such a problem, and it will only grow.” In this case, the government’s opinion will be key, the senator is convinced.
Why do we need a state-owned sanatorium company?
The need to create a Business Rehabilitation Center is due to the fact that in Russia the number of bankruptcies among legal entities is growing, the draft explanatory note says. In 2014, there were 3,649 bankruptcies in the Central Federal District, and 11,469 at the end of 2020. In 2020, 30 natural monopoly entities, 12 strategic enterprises and one city-forming organization were declared insolvent, the document notes.
Rehabilitation procedures - financial recovery and external management - are not common. In 2020, they were applied to 396 companies, which is 2% of the total number of procedures introduced by the courts (the same share was in 2020). “These statistics indicate a huge number of closing and bankrupt enterprises, unpaid loan obligations, job losses and, as a result, social tension,” the document explains. “In this regard, in order to prevent bankruptcies of legal entities and restore their solvency, it is proposed to create a Business Rehabilitation Center in the form of a joint-stock company, the only participant of which is the Russian Federation.”
With the help of the new structure, a business in a difficult situation will have the opportunity to receive information, analytical and legal assistance, restructure debt obligations, attract a sanator and investor to prevent bankruptcy and restore its solvency. The creation of a sanatorium will reduce the level of social tension, increase tax revenues to the regional budget by preserving business and increasing its profitability, and the possibility of implementing projects in the form of public-private partnerships.
It is expected that the Rehabilitation Center will be a platform where businessmen will be able to interact with banks, investment funds, expert organizations and creditors.
The project has great potential, says Senator Kravchenko. “There may be assistance in restructuring debt obligations through interaction with banks, interaction with regional authorities,” he explained. In his opinion, the bill “may well be passable, based on the tasks that this institution can solve.”
What the documents don't say
It is not yet clear how it is proposed to replenish the center’s fund and who will manage its funds. The draft explanatory note does not specify the financing mechanism of the Business Rehabilitation Center and the principles of its work. It is not clear from the document the amount of funding, the government agency that will oversee the work of the center, and its powers.
A reorganization mechanism already exists for the banking sector: the Central Bank sanitized large banks, including FC Otkritie and B&N Bank, through the Banking Sector Consolidation Fund. Additional capitalization of banks took place through additional issue. The draft explanatory note on the Business Rehabilitation Center does not mention additional capitalization of enterprises, and besides, the government, unlike the Central Bank, does not have the opportunity to launch a printing press.
At the same time, in Russia there is a Fund for the Protection of the Rights of Shareholders, the budget of which is formed from contributions from developers. In particular, together with the government of the Moscow region, he is engaged in the rehabilitation of a large developer - Urban Group, which went bankrupt this summer.
So far, the creation of a Rehabilitation Center looks like a dubious idea, co-chairman of Business Russia Anton Danilov-Danilyan told RBC: “Now bankruptcy is most often carried out as the destruction of an asset: the property complex is not preserved. If this problem begins to be solved, then this idea can be seriously considered. And if this is a conditional recovery for those who will still go bankrupt in a cycle or two, then this is a senseless waste of money.”
“There are already sanatoriums like VTB Capital and Sberbank Capital. I’m not sure that there is a need to create something separate and state-owned,” he added. If line ministries or regional authorities see the risks of bankruptcy of strategically important enterprises, they can already be supported through subsidized rates and reserve funds of budgets at various levels, says Danilov-Danilyan. Another effective tool is various development institutions, but now they cannot stop the growing problems of companies that are developing well, but too quickly, he believes.
The formation of state policy in the field of bankruptcies of legal entities falls within the powers of the Ministry of Economic Development. A ministry representative told RBC that the department “received general information about proposals to create a Business Rehabilitation Center.” “Such proposals are planned to be discussed in the Federation Council at a round table, during which more complete information can be obtained to form a substantiated position on the advisability of creating such a center, taking into account the characteristics and sources of financing its activities,” he added.
The Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Construction and the Accounts Chamber did not receive proposals on the concept of the central bank, representatives of these departments told RBC.
Pre-trial and judicial rehabilitation
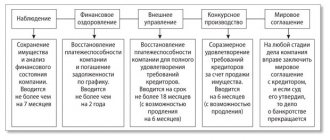
Restoring the company's solvency and starting the reorganization procedure is possible both pre-trial and in court.
In the first case, the “recovery” process begins before the court begins the bankruptcy case. The pre-trial procedure requires the written consent of the founders of the debtor company, as well as creditors whose claims amount to more than 50% of the debts. The reorganization plan is agreed upon with all creditors and approved by the economic court. The latter issues a ruling and imposes a moratorium on satisfying creditors' claims.
Judicial reorganization involves the appointment of an arbitration manager, who is entrusted with all the functions of managing a legal entity that has debts.
Enterprise finance
Topic 12. Financial rehabilitation and prevention of enterprise bankruptcy. Bankruptcy of enterprises
Plan
12.1. The essence and necessity of reorganization of enterprises with a difficult financial situation
12.2. Assessment of internal and external factors of financial insolvency of an enterprise
12.3. Financial sources of rehabilitation
12.4. Assessment of the possibility of bankruptcy and grounds for initiating bankruptcy proceedings
12.5. The procedure for declaring an enterprise bankrupt and the mechanism for distributing the bankruptcy estate.
12.1 The essence and necessity of reorganization of enterprises with a difficult financial situation
The term “sanitation” comes from the Latin “sanare” and is translated as healing or treatment. In the Financial Dictionary, reorganization is interpreted as improving the financial condition of an enterprise through the implementation of a system of measures to prevent its bankruptcy or increasing competitiveness. Usually, reorganization is carried out through a structural restructuring of production, in particular, through a change in the product range, the fragmentation of the enterprise, a change in sales markets, the merger of an enterprise that is on the verge of bankruptcy with more powerful ones, the issue of new shares and bonds to mobilize capital, and other measures.
In Ukraine, due to imperfect legislation, the lack of necessary technical and methodological support for reorganization processes, and a shortage of qualified specialists, a large number of potentially viable enterprises become potential bankrupts.
Purpose of financial rehabilitation
- covering current damage and eliminating the causes of their occurrence, restoring or maintaining the liquidity and solvency of enterprises, reducing all types of debt, improving the structure of working capital and the formation of funds of financial resources for carrying out activities of a production, technical and organizational nature.
The so-called “classical rehabilitation model ”,
which is widely used as the basis for developing a mechanism for the financial recovery of business entities in countries with developed market economies. In accordance with the classical model of rehabilitation, the process of financial recovery of enterprises begins with the identification and analysis of the causes and factors of the financial crisis. Based on data from information carriers (primary accounting documents, financial plans, etc.), external and internal factors of the crisis are determined, as well as the financial condition of the company and the depth of the crisis. .
Within the framework of the reorganization audit, an in-depth study of the financial condition is carried out based on the calculation of a number of coefficients. The main ones are indicators of solvency, liquidity, profitability, etc. After obtaining the necessary data regarding the financial condition of the enterprise and the causes of the financial crisis, a conclusion is made about the feasibility or inexpediency of reorganizing a given business entity.
A separate analytical block in the classical model of reorganization is the formation of strategic goals and tactics.
Of course, pre-trial rehabilitation has more advantages than judicial rehabilitation:
- such a procedure does not involve significant loss of reputation;
- minimal court intervention;
- the appointment of an arbitration manager is optional;
- lower costs compared to court proceedings.
At the same time, pre-trial reorganization is advisable if the debt is small and the founders do not plan to close the enterprise.
Legal is ready to help you with the liquidation of the company, if necessary, or with the restoration of solvency and a speedy return to profitability.
Completion of reorganization, consequences of its implementation
According to Article 86 of Federal Law No. 127, in case of early repayment of debts, the debtor must prepare a report and submit it for consideration to the arbitration court. In the absence of objections and complaints (or their rejection by the court), the arbitration is obliged to terminate the bankruptcy case.
Article 87 of Federal Law No. 127 also allows for early termination of reorganization at the request of the manager. To do this, within 15 days from the moment of recording the debtor’s violations of the payment schedule, he must gather the creditors and raise before them the issue of going to court to stop the reorganization. In this case, the debtor is obliged to report to creditors on the fulfillment of the debt repayment schedule. Creditors, in turn, have the right, if the debtor’s arguments are unconvincing, to apply to the court with a demand to introduce external management or declare the debtor bankrupt.
If the reorganization is not terminated ahead of schedule, the debtor, in accordance with Article 88 of Federal Law No. 127, is obliged to send a report to the manager on the fulfillment of his obligations. If the report is not submitted or the debts are not repaid, the manager raises the issue with the creditors about going to court to introduce external administration or declaring the debtor bankrupt.
Results of the reorganization
Based on the results of the recovery, the arbitration, in accordance with paragraph 6 of Article 88 of Federal Law No. 127, must make one of the decisions:
- Terminate bankruptcy proceedings if the debtor has repaid debts to creditors.
- Introduce external management if debts are not repaid, but the possibility of repayment still exists.
- Declare the debtor bankrupt if it is obvious that he will no longer be able to pay off his debts.
***
To summarize, we note that financial recovery in bankruptcy is the debtor’s chance to save his enterprise. At the same time, to repay the debt, it can additionally attract both personal funds of its participants and third parties.
When and in what types is sanitation carried out?
The reorganization procedure is required in some situations, among which the main ones are the following:
- The company is independently looking for options for obtaining external assistance to overcome the crisis situation. At the same time, the creditors do not initiate bankruptcy of the company.
- The organization, on its own initiative, applies to the arbitration court. The application indicates its own bankruptcy and makes a proposal for reorganization.
- As a result of receiving applications from creditors of the debtor organization, a court decision on reorganization is made.
Depending on the criteria for obtaining financial support from outside and the severity of the crisis situation, the reorganization of the organization includes:
- Reorganization of an enterprise's debt, not accompanied by a change in its legal status. The method is applicable to liquidate insolvency in situations of crisis, assessed as temporary.
- Reorganization of a company, during which the legal status of the debtor being reorganized changes. The method is used in case of a hopeless crisis situation in the organization.
For your information! The measures taken to rectify the situation without changing the status of the organization are the allocation of budget funds (for government agencies) or a targeted loan from a bank (after receiving an audit report), preferential taxation, issuance of securities (if there is a guarantee from the sanatorium) or transfer of debt to another company who expressed a desire to participate in the rehabilitation of a problem debtor.
The reorganization of the reorganized enterprise can be carried out in the form of:
- Mergers. The debtor company merges with a financially stable company, losing its legal (independent) status. When organizations in the same industry merge, a horizontal merger occurs; when companies from related industries merge, a vertical merger occurs; and if enterprises do not have industry or other overlaps, the process is called a conglomerate merger.
- Division applied to organizations engaged in production activities of a diversified nature.
- Takeovers. The sanator, by absorbing a problem company, receives as a result a complex of property and the bulk of the assets of the debtor, which is retained as a legal entity upon receipt of the status of a subsidiary.
- Transformation (by decision of the founders) into a joint-stock company. When choosing this procedural form, it is necessary to ensure the minimum amount of funds provided for by current legislation to create the authorized capital.
- Privatization, which is also in demand during the procedure for reorganizing state-owned enterprises.
- Renting. The form is applicable to state-owned enterprises that are leased (along with the organization’s debts) to members of the workforce.
Department of Rehabilitation and Bankruptcy
There is a government body whose main task is to determine economic insolvency - the Department of Rehabilitation and Bankruptcy.
The department's responsibilities include:
- conducting certification of temporary managers;
- issuing licenses for the activities of anti-crisis managers;
- accepting, analyzing and responding to complaints from citizens and legal entities who address the issue of improper fulfillment of obligations to recognize bankruptcy;
- control over temporary managers;
- implementation of government programs to prevent internal crisis and bankruptcy;
- implementation of measures to restore solvency to companies within the framework of current legislation;
- organization of monitoring and analysis, accounting of the financial conditions of state-owned enterprises or those that are state-owned to some extent.
The activities of the Department are a mandatory authority that directly affects the country’s market economy.