The concept of external control
During bankruptcy proceedings, an external manager is often appointed.
External management, as one of the bankruptcy procedures, is carried out for certain categories of debtors. The list includes:
- Legal entities - the procedure is applicable in case of temporary insolvency proven by the court. The problem can be eliminated by carrying out a number of health measures. When working with a bankrupt, a variety of measures are used, the result of which is an improvement in the monetary situation and the continuation of the activities of the potential defendant after the return of debt obligations.
- Enterprises - for companies, an external manager is appointed as a specialist in financial improvement of the system. The maximum duration of the stage does not exceed two years, and initially it was designed for 18 months. To increase the duration, you can apply for a change in time. The procedure is recommended by the Arbitration Court and is carried out for city-forming and other large companies.
- Developers - the process is applicable for construction companies; as a result of actions, they can complete started projects and repay debts to potential creditors. If the assistance does not help restore the condition, then bankruptcy proceedings are established with the sale of existing property, including unfinished objects.

external management External management means a set of actions that make it possible to stop bankruptcy and return organizations to their previous performance. The Arbitration Court can choose this option, and implementation takes place if there is a chance of material restoration of the company.
In addition to the set of financial features that caused this situation, the level of professional literacy of the external manager is important for the revival of the company. According to practice, a bankruptcy procedure under a temporary document can be prescribed under certain conditions:
- if there is a real chance of the defendant returning to solvency - over separate periods of time;
- with a joint decision of the victims and a statement of claim sent to the courts requesting the introduction of a military license into the company;
- if, after submitting a petition to recognize the organization as uncreditworthy, evidence has emerged that it is feasible to carry out restoration, and the appointment of an appropriate specialist is advisable.
Important! What is the difference between this bankruptcy step: the removal of officials from management and the transfer of their functions to the VU. The latter, having assumed the rights, can dismiss directors, deputies, the chief accountant and independently determine future policies for the activities of the enterprise.

Work plan
External administration procedure in bankruptcy
The interim manager is obliged not only to agree on the company’s recovery plan with financial counterparties, but also to report on the progress of its implementation upon request.
One of the stages of solving the bankruptcy problem is external management. It is appointed by the court with the aim of restoring and stabilizing the financial situation of a potential bankrupt, after which he will be able to repay his debts again. The implementation of this stage is carried out in accordance with the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” No. 127 of 2002. What it is?
It is the external manager who becomes a full-fledged management body of the company, replacing the general director, and even receiving the right to dispose of the organization’s assets (with some regulatory restrictions). All actions of the manager are focused on achieving a single goal - to return the legal entity to a stable position in the market.
Taking into account all the characteristics of the enterprise, based on an analysis of accounting documentation, concluded transactions, existing contracts, number of personnel, availability of production assets and other factors, the external manager must provide creditors with step-by-step guidance on how to bring the debtor out of bankruptcy.
What are the differences from the financial recovery of an enterprise?
The rehabilitation stages of the bankruptcy procedure include financial recovery and third-party management. They are introduced in relation to an uncreditworthy enterprise and are used to maintain the company in the role of a market entity. Both options provide benefits for conducting business and are applied after the initial meeting of borrowers or by decision of the court.
The fundamental differences between the two options include the difference in organizing the economic and financial rehabilitation of a problem company:
- during stabilization (recovery) - the company’s management retains the right to leadership, but receives restrictions on its powers;
- when operating a court, all functions are performed by a court-appointed specialist.
Important! Material restoration is similar to an installment plan for the gradual repayment of debts using certain guarantees. External management uses comprehensive measures to change the entire functionality of the company.

Comparison of two concepts
Bankruptcy as a way of financial recovery - Storozhenko and Partners
Bankruptcy as a way of financial recovery
“Are you ready to fight for your business?” S. Storozhenko
Business is like a living organism. And like any living organism, endowed with the instincts of self-preservation and procreation, it strives for safety and “reproduction” (growth).
When a business is in dire straits, a good leader must help it get better. Do everything possible to preserve the company and give a powerful impetus to its full development. Increase the competitiveness and market value of the company.
No matter how strange it may sound, it is bankruptcy that provides troubled businesses with effective tools for financial recovery.
Restoring solvency is possible
If a company is bogged down in debt, but there is at least the slightest prospect of restoring solvency, maintaining a positive image and healthy business relationships with partners, it is necessary to initiate a bankruptcy procedure as soon as possible in order to profitably use its recovery procedures for the financial “reanimation” of the business.
Bankruptcy, as a tool for financial recovery, allows you to:
- free the company from doubtful debts;
- defer and restructure bank loans;
- optimize collateral and guarantees;
- protect yourself from creditors' claims;
- remove seizures from property,
which means - temporarily freed from all obligations; concentrate all your strength and capabilities on solving financial and management problems. With a high degree of probability, it will restore solvency and breathe new life into a business with “unsustainable” debts.
What is the essence of financial recovery?
Financial recovery within the framework of bankruptcy is actually two consecutive bankruptcy recovery procedures, called “financial recovery” and “external management”.
Both have the same goal - to help businesses regain solvency.
The main difference is that in the first case, the management is not removed from managing the company, and in the second, the “reins of government” pass into the hands of the arbitration manager. Sometimes the debtor only needs the first procedure.
The essence of financial recovery is the desire to overcome the debt crisis of the organization, while simultaneously providing guarantees to creditors in accordance with the debt repayment schedule approved by the arbitration court.
The management bodies of a potential bankrupt continue to function, with minor restrictions. Their actions are controlled and regulated by the meeting of creditors and the arbitration manager.
A debtor-friendly manager essentially leaves control of the business in the hands of its owners and management.
We develop an individual financial recovery plan
Financial recovery is carried out according to an individual plan for each company, which is a detailed description of the overall strategy and individual tactics of “financial resuscitation”, as well as indicative indicators of their expected effectiveness.
A financial recovery plan is a fairly effective tool that provides the opportunity to see a complete picture of the debtor’s current and future financial condition, control the process of implementing the developed recovery measures and, if necessary, adjust them.
No later than a month before the end of the financial recovery procedure, the debtor must provide the manager with a corresponding report, confirmed by accounting documentation data.
We implement effective financial recovery measures
Financial recovery, aimed at restoring the solvency of a company, clearing it of “ballast” and aimed at increasing the efficiency of business activities, can be a set of various measures that are selected individually, based on the characteristics of a particular business.
If one organization has enough diversification of production and competent work with accounts payable, then another company requires searching for a radically new path and a new business paradigm.
But there are universal methods of financial recovery within the framework of bankruptcy that have proven effective for almost any type of business. You will find out which ones exactly further.
“Cutting down” expenses
Maximum reduction of unproductive expenses is one of the main conditions for business survival.
During the recovery procedures, an analysis of the debtor's costs is carried out, on the basis of which ways to reduce costs are identified.
Expenses that can be reduced almost painlessly for any business include:
- production costs: costs of fuel, electricity, raw materials, etc. Reduced by introducing the “lean production” regime.
- “Image” costs are the costs of “maintaining status,” which can be easily reduced by eliminating excesses. For example, by switching to more affordable household items, moving production or office to a less expensive area, etc.
- “extra” cash payments, for example, dividends and bonuses.
- “hidden costs”, unaccounted costs.
It is permissible to revise personnel costs. Without resorting to staff reductions, you can, for example, cut costs for employees attending sports clubs, training sessions and other events, and reduce the amount of “travel allowances”. Reducing wages and bonuses is resorted to as a last resort.
When planning measures to reduce costs, it is important not to overdo it; it is best to find a “golden mean”.
Getting rid of unprofitable assets
Non-core assets that are not involved in the main production processes, unused or not used to their full potential (old buildings, empty premises, equipment beyond repair, etc.) not only do not bring profit, but also absorb financial resources, which are already in shortage.
During financial recovery, an inventory is carried out, unprofitable assets are identified, written off, disposed of, rented out or sold, without damage and even for the benefit of the organization.
Increasing income
Increasing income is the main task of financial recovery.
An increase in profitability is achieved not only through savings in the expenditure of funds, but also through measures to improve the efficiency of using the assets at the disposal of the company.
During bankruptcy, the debtor can develop and implement measures specifically suitable for him to increase profits. It can be:
- improving the quality of goods or services;
- increase in production volume;
- reducing the cost of manufactured products through more rational use of material, time and labor resources;
- diversification of production;
- work to attract new clients;
- expansion of the sales market, etc.
Paradoxically, the roots of some sources of income grow directly from the financial crisis. In particular, from the circumstances that caused damage to the organization. It can be:
- fines that can be collected from contract violators;
- one-time income from successful collection of receivables.
You can also increase profits with the help of anti-crisis marketing. For example, by carrying out simple but original PR campaigns and strategies.
We optimize the organizational structure and analyze business processes
The competitiveness and profitability of the organization depend on the “harmoniousness” of the organizational structure and the effectiveness of business processes
In the course of financial recovery, the organizational structure may be significantly restructured, the basis for the interaction of existing divisions may be revised, and new units may be created.
As a result of such optimization, costs are reduced, the quality of work is improved and the business management process is simplified.
Sometimes the debtor has to destroy the organizational structure to the ground in order to build something radically new, in accordance with a new business development strategy.
Results of financial recovery
If, as a result of financial recovery measures, the creditors' claims are fully satisfied, or a settlement agreement has been concluded, the arbitration court terminates the debtor's bankruptcy case.
If the obligations are not repaid and financial recovery turns out to be ineffective for the problem company, the court may declare the debtor bankrupt and order a liquidation procedure.
Important: when choosing between resuscitation or liquidation of a business, even an experienced and knowledgeable manager may not notice hidden reserves for increasing profits or may not have all the skills to effectively increase business profitability.
But in determining the fate of the company, it is very important not to make a mistake, not to miss the moment.
Source: https://lfsp.ru/poleznaya-informatsiya/finansovoe-ozdorovlenie-predpriyatiya/
Duration of the procedure
The standard period of work under external management does not exceed 18 calendar months. It complies with the provisions of Art. 93 No. 127 of the Federal Law and is executed after a court decision. The maximum extension period is six months and is introduced at the request of borrowers. To implement it, there must be compelling arguments:
- making corrections to the original company management plan;
- achieving visible results at the stage of normalizing the operation of the enterprise.
According to Art. 92 under No. 127, clause 2 of the Federal Law, the total time of reorganization and temporary rehabilitation cannot exceed 24 months or two full years. The period of work under a third-party manager can be shortened at his own request or at the decision of the meeting of plaintiffs (Article 93, paragraph 3). Execution takes place immediately.
Important! For city-forming enterprises and farms affected by natural disasters, the time frame lasts 2.5 years.

Acceptable deadlines
Rights and obligations of participants
The courts, taking into account all the circumstances, will most likely accommodate the debtor himself, the manager or creditors and delay the procedure for some time.
An application for declaring a citizen bankrupt can be submitted to the arbitration court by a citizen - a debtor, a creditor, as well as an authorized body.
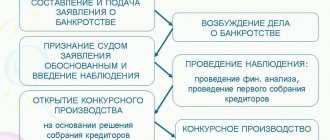
The law provides for 4 procedures, which are highlighted in separate chapters in the regulatory framework governing the bankruptcy procedure, namely in the law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy).
An application for declaring a citizen bankrupt can be submitted to the arbitration court by a citizen - a debtor, a creditor, as well as an authorized body.
The law provides for 4 procedures, which are highlighted in separate chapters in the regulatory framework governing the bankruptcy procedure, namely in the law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy).
The most important difference between external management is the removal of senior-level actors from the management of the enterprise and the transfer of powers to an external manager, who has the right to dismiss the previous administration (Clause 1 of Article 94 No. 127-FZ) and dispose of the property of the legal entity at his discretion.
The financial recovery plan, prepared by the founders (participants) of the debtor, the owner of the property of the debtor - a unitary enterprise, is approved by the meeting of creditors.
The financial recovery plan must contain a justification for the possibility of satisfying the claims of creditors in accordance with the debt repayment schedule.
The conduct of bankruptcy procedures in the Russian Federation is regulated by the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” No. 127-FZ of October 26, 2002, hereinafter referred to as the Bankruptcy Law. Cases of bankruptcy of legal entities and citizens, including individual entrepreneurs, are considered by the arbitration court at the location of the debtor - a legal entity or at the place of residence of the citizen.
Introduction of a moratorium on satisfying demands. A moratorium is a suspension of the debtor’s fulfillment of monetary obligations and payment of mandatory payments.
The decision to declare the debtor bankrupt and open bankruptcy proceedings in the first instance is made in accordance with Art. 17 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, by a collegial composition of the arbitration court. Clause 2 sets the deadline for bankruptcy proceedings. The Act's one-year period for insolvency proceedings and the possibility of extending it for an additional six months is the final limit.
At the same time, the current value of future income that the new owner can receive from the acquired enterprise (business) of the debtor represents the upper limit of the market price of this business on the part of the buyer, and is the price at which the external manager should strive to sell the enterprise (business) of the debtor .
An individual entrepreneur-debtor, within 5 years after the debtor is declared bankrupt, he himself cannot re-file an application for his own bankruptcy; 2) any of the creditors for business obligations (whose claim is related to the debtor’s business activities); 3) authorized bodies.
It is not permitted to publish or otherwise disclose information about the debtor’s bankruptcy until the publication of the arbitration court’s decision declaring the debtor bankrupt. Persons who violate this requirement bear liability established by the Bankruptcy Law (clause 3 of Article 26 of this Law).
Applications of insolvency practitioners and complaints from creditors are considered by the court no later than two weeks from the date of receipt of the application or complaint (Clause I, Article 55 of the Bankruptcy Law).
This bankruptcy procedure is applied to the debtor company in order to restore its solvency and repay the debt in accordance with its repayment schedule. This procedure cannot be introduced for a period of more than 2 years.
Management is introduced by a decision of the arbitration court if a meeting of creditors or the debtor himself filed an application with the court. The rationale for introducing external management is the potential ability of the enterprise to restore its financial position.
External management is a stage of bankruptcy aimed at improving the health of an enterprise recognized as a debtor.
External control cannot last indefinitely. Its maximum period should not exceed six months. However, under certain conditions, the period can be extended to one and a half years.
Stages of external control
The duties of the bankruptcy trustee include drawing up a detailed action plan, which is consistently executed as all stages are passed to obtain the status of insolvency. The VU includes the following sequential steps:
- search with further approval and hiring of a specialist;
- development of a step-by-step strategy and areas of work;
- creating a plan for the financial recovery of a troubled company;
- holding a general meeting of borrowers to voice the goal and discuss measures and adjustments to restore the status of the enterprise;
- start of activities and planned procedures;
- execution of contracts in relation to the plaintiffs.
External managers are specialists who develop step-by-step plans for the revival of companies with subsequent positive results in solving the problem. To suspend the recognition of an enterprise as insolvent, the strategy prescribes the following steps:
- step-by-step actions that have a direct impact on restoring creditworthiness;
- calculating the timing of the implementation of promises made to borrowers;
- drawing up an estimate for implementation;
- the time during which solvency problems will be eliminated;
- presenting facts and arguments proving that the return of the company’s stability is real;
- a description of the responsibilities of the creditors and the committee that must approve the actions of the problem enterprise.
Important! The appointed specialist is required to prepare reports and communicate the activities performed to interested parties at their first request.
After completing all stages, the procedure is considered successful only if the creditworthiness status is restored and debts are returned to the interested companies.
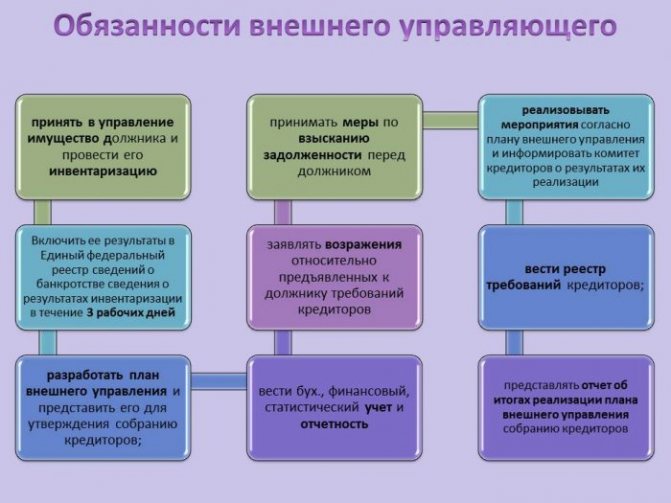
Responsibilities of the VU
How an enterprise is sanitized
The rehabilitation itself can be implemented in three cases:
- Before creditors file for bankruptcy, the company decides to seek outside help through external financing.
- When the company itself applies to the court for bankruptcy, simultaneously offering conditions for its own financial recovery (more often this is typical for government agencies).
- When a decision is made by an arbitration court based on requests received from creditors.
The last two options provide for the conduct of business during bankruptcy proceedings. It is preferable to stick to the first option. Then there are chances to get out of a difficult situation by coordinating actions with your needs. The effectiveness of measures in this case is higher than when the initiators of the resolution are creditors.
Listing the stages during the period of managing a company for the purpose of recovery, we can highlight the following.
Feasibility of reorganization
At this stage, an analysis of the internal financial condition of the company is carried out, after which a decision is made on the advisability of implementing health measures. Determining feasibility occurs through the belief that the measures taken and the use of finances will not aggravate the current state of affairs. Sometimes the best option is to attract investors, which gives quick and satisfactory results.
Sometimes the best option is to attract investors.
Concept rationale
At this stage, acceptable types and forms of remediation are discussed and recorded. As a rule, the choice falls on a defensive or offensive concept. Defensive implies a reduction in the volume of investment on the part of the enterprise in order to balance cash flow. At this stage, divisions and branches may be closed, investments may be withdrawn from assets. An offensive strategy involves diversifying a company's investments.
Determining directions
After the complexity and neglect of the company’s condition has been assessed, ways and methods of resolving the current situation are determined. There are two directions, including:
- Actions aimed at debt refinancing. This implies assistance for the enterprise in order to bring it out of insolvent status. However, the new status does not in any way eliminate the company's need for reorganization actions.
- Direction for restructuring. It is used in very difficult cases when a large-scale reorganization of economic production is carried out.
Definition with rehabilitation form
At this stage, a specific mechanism of action is determined that will be applied throughout the company’s recovery journey. Rehabilitation when choosing debt refinancing may include one or more types of measures, which may include:
- Issue of securities.
- Restructuring short-term debt into long-term debt.
- Deferment of debt obligations.
- Write-off of part of debts by creditors.
- Transfer of debt to another legal entity.
- Obtaining bank guarantees.
- Financial subsidies, including government ones.
Recovery through the use of restructuring implies:
- Processes of merging a bankrupt company with more financially stable enterprises.
- Renting out vacant space.
- Privatization.
- Acquisition (an example of such reorganization can be found especially often among large organizations).
Choosing a sanatorium
When refinancing debts, the sanator can be: the owner(s) of the enterprise, creditors, or the bank that services the company.
In the case of rehabilitation in the form of restructuring, the main sanators can be creditor companies, the workforce of the company being reorganized, third-party economic entities (legal entities) and the owners of the company.
Development and preparation of a business plan
Everything that was thought out at the previous stages should be clearly stated on paper in the form of a business plan. The development of such a document, as a rule, falls on the shoulders of the sanator or an audit company. It needs to carry out all the calculations and steps that prove the potential effectiveness of the measures taken.
A business plan must be written, which details the calculations made and indicates the steps to improve the company.
Next comes the final stage - approval of the business plan. This action is carried out by all interested parties. Upon receipt of approval and signing of the relevant papers, the measures come into effect. Next, monitoring is activated to monitor the implementation of the established plan. Rehabilitation is considered completed immediately after establishing the fact of an established economic structure. In this case, all restoration measures for health improvement come to an end.
Carrying out financial and recreational activities, bypassing the decision of the arbitration court, has its positive aspects: deadlines are set by agreement and according to a real plan, tools for reviving the enterprise are selected taking into account all interests, it is possible to make adjustments to the plan with the prior consent of creditors.
Reorganization of an enterprise is a smart strategic move that allows you to both save a company that is on the verge of bankruptcy and bring it out of a difficult situation. However, the health improvement plan needs to be thought out as precisely as possible, taking into account force majeure, so that in an attempt to do “the best” it does not turn out “as always”.
Features of the procedure
Third-party management is not mandatory and is appointed by a court decision at the initiative of plaintiffs or arbitration. It is aimed both at repaying the debt and at:
- improvement of the defendant’s material base;
- maintaining the company as an operating entity.
Important! At the request of the bankrupt enterprise, this type of recovery is not used.
The features of the procedure include the following provisions:
- introducing a moratorium on the fulfillment of borrowers' claims under debt documents, with the exception of compensation for moral damage, fulfillment of requests of the first and second priority plaintiffs, return of property from illegal possession;
- cancellation of announced measures to ensure the requirements of interested companies;
- the seizure of the debtor's property is carried out within the framework of bankruptcy;
- a restriction is introduced on large transactions with the defendant’s property.
Important! The collateral is sold at public auction and with the consent of the borrowers, the purpose is to secure their requests.

Features of accounting at a university
Activities carried out under external management
Termination of powers of the debtor's management bodies (general meeting of shareholders, general meeting of participants, board of directors, management board, etc.) and the owner of the debtor's property - a unitary enterprise.
The external management procedure actually begins to work after the official transfer of rights from the previous head of the company to the new manager.
Unsatisfied claims of creditors may be presented in the manner prescribed by civil law.
Procedure for introducing external control
The beginning of the process takes place according to the provisions of Art. 75 and 93 of the Federal Law No. 127, based on the decision of the meeting of plaintiffs or a court ruling. Good reasons for its implementation include the possibility of resuscitating the creditworthiness of a bankrupt organization. Judicial rehabilitation allows the debtor to enjoy a certain type of benefits and is aimed at changing priorities and finding a way out of the current economic crisis.
The date of entry of the procedure provokes:
- deprivation of powers of the previous management - the exception is the preservation of technical functions;
- introduction of a moratorium on the payment of various types of remuneration to interested parties.
Important! The invited specialist carries out work in accordance with the law and his immediate responsibilities. All previously agreed measures to ensure settlements with borrowers are cancelled.

The procedure for introducing the VU
Stabilization methods
You can predict possible bankruptcy by analyzing the financial situation of the enterprise over several past reporting periods. If indicators indicate a steady deterioration in the situation, this is a reason to take stabilization methods. Forms of financial recovery are actions to regulate and restore the economic mechanism. They include the following events:
- Based on the analysis of negotiable documents and financial statements, influencing negative factors are determined. They are divided into external and internal. External ones include the impact of the economic crisis, unprofitable relationships with counterparties, etc. Internal ones include the ineffectiveness of the actions of the management team, conflicting relations between structural divisions, etc. The main task of the first stage of recovery is to find the reasons for the destabilization of the economic situation at the enterprise and find ways to eliminate them.
- A forecast of the economic situation is formed and the possibility and ways out of the financial crisis are considered. The main objective of this event for the financial recovery of the enterprise is to assess the potential opportunity to establish an economic mechanism within the company. In this case, only the internal reserves of the enterprise are taken into account, capable of restoring solvency without the participation of external factors.
- Development and formation of a rehabilitation program. This stage is characterized by defining specific goals and methods to improve the financial situation. To do this, an analysis of all the assets of the enterprise is carried out. These are fixed assets, construction in progress, materials, goods, production equipment, finished products. Licenses, patents, intangible assets, and commercial networks are also taken into account.
All of the above types of financial recovery, provided for by the insolvency law, are carried out with the aim of significantly changing the activities of the debtor enterprise. One of the most significant activities is the retraining of production activities, for example, the release of new products. Solvency can also be increased by concluding agreements on the restructuring of the company's debt obligations and diversifying consumers and suppliers.
Similar articles
- What is an audit observation procedure?
- Minutes of the meeting of creditors sample
- Publication on the introduction of the observation procedure
- Refusal of a bankruptcy petition
- Repeated meeting of creditors
Possible consequences
A court decision to introduce an outside employee into the management of a company, appointed to solve the material difficulties that have arisen, leads to the transfer of management into his hands. The consequences for the enterprise include a change of power, the new manager receiving unlimited powers with the right to move workers to positions and dismiss those who do not correspond to their positions.
The list of additional results of introducing a full-fledged leader includes:
- lack of rights and powers among property owners in the company’s activities;
- cancellation of any agreements previously signed with creditors.
During work at a troubled enterprise, a ban is imposed on paying debts from the budget, regular payments and other payments. Exceptions include certain cases established by law.
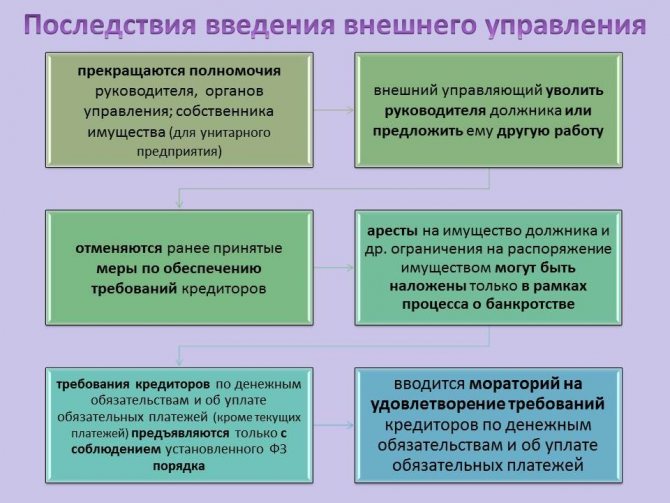
Consequences of VU
The bankruptcy procedure is recommended if there are no other rescue options and it is impossible to sign a settlement agreement. The Law “On Bankruptcy and Insolvency” recommends VU for rehabilitation measures and the return of lost stability. If the business is successfully conducted, the company will be able to pay off its debt obligations, and if the process is unsuccessful, the court establishes additional measures to resolve issues with borrowers.
0
Author of the publication
offline 17 hours
Financial recovery in the bankruptcy procedure of an enterprise
The introduction of financial recovery in the bankruptcy procedure implies the potential opportunity for a legal entity to overcome a crisis situation and continue to carry out activities after implementing a number of measures designed to pay off the company’s debts and restore the pre-crisis state. The successful completion of financial recovery benefits all participants in the process.
The main provisions concerning the procedure for implementing financial recovery, the appointment of a responsible person, his powers and consequences are contained in Chapter 5 of the current edition of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”
When is the financial recovery procedure introduced in bankruptcy?
Financial recovery is one of the possible stages that comes after the observation stage. The transition from observation to rehabilitation is carried out according to the official conclusion of the arbitration court, issued on the basis of a petition, which the following entities have the right to submit:
- legal entity based on the minutes of the meeting of founders;
- separate founder/manager;
- creditors;
- other persons interested in a favorable outcome of the process.
A petition to apply this stage will be allowed for discussion and consideration if the document is submitted in a timely manner - 2 weeks before the scheduled date of the first meeting of creditors.
It is necessary to prepare a couple of copies of the document: one for the temporary manager, the second for the arbitration court.
To substantiate the proposal to introduce a stage, the petition must be supported by documents, a detailed list of which for each of the possible initiators is contained in Articles 77 and 78 of the Bankruptcy Law. Common to all subjects are:
- debt repayment schedule according to the register of creditors;
- guarantee to ensure the fulfillment of obligations (bank, municipal or state; pledge or surety);
- financial recovery plan for the organization.
Copies of the petition and documents established by the Law for preliminary review and study are sent to all participants in the first meeting of creditors.
Carrying out the procedure
The starting point for the financial recovery period begins with the court making a decision on the implementation of the stage, which contains information about the time frame, the established debt payment schedule and the appointment of an administrative (financial) manager. The primary task of the stage is to cover the organization's debt obligations ; in second place is the return of the legal entity's activities to pre-crisis levels.
The claims of 1st and 2nd priority creditors must be fully satisfied in the first six months of financial recovery.
All debts included in the register, certified by members of the first meeting, must be repaid 30 days before the completion of this stage of bankruptcy of the enterprise.
At the same time, the debtor prepares a report reflecting the results of the stage, on the basis of which the arbitration manager makes an opinion on the effectiveness of the procedure and sends it to the meeting participants.
During the period of introduction of the financial recovery stage, managers do not lose their powers, but are required to act within the limits established by the Law . The number of transactions for which the manager must certify the decision with the permission of the administrative manager includes:
- transactions that increase the organization’s debt by 5% or more;
- transactions related to the purchase, sale, gift of property of a legal entity;
- transactions involving the sale or transfer of debt to third parties;
- transactions involving borrowed funds.
As for the company’s activities as a whole, financial recovery entails the following changes :
- presentation of creditors' claims is carried out in accordance with the provisions of the Law;
- measures to cover debts by the organization, introduced before financial recovery, are abolished;
- the seizure of property and the establishment of restrictions regarding the disposal of the organization’s property is carried out within the framework of the current Law by decision of the arbitration court;
- payment of property penalties is temporarily not carried out, with the exception of executive documents that were issued before the recovery stage;
- all actions related to the purchase and sale of shares of the founders are suspended;
- dividend payments and payment of a share of profits to the founders are stopped;
- The assignment of a debt of a legal entity is prohibited if it entails a violation of the order of repayment of debts to creditors;
- Penalties for late payments are accrued only on current payments.
Ways of financial recovery
Financial recovery is aimed at repaying the accounts payable of a legal entity and resuscitating its solvency. The choice of possible ways of financial recovery to overcome a crisis situation depends on the results of observation and the specifics of the organization’s work. The causes of organizational failure are the interaction of external and internal factors.
Reasons for the insolvency of a legal entity
| External factors | Internal factors |
| Changes in legislation | Incompetent management |
| Economic decline, inflation, rising prices for raw materials and equipment | Large administrative apparatus |
| “Chain” bankruptcy (an organization becomes bankrupt due to the insolvency of its partners) | High accounts receivable |
| Political situation in the country | Ineffective investment policy |
| Increase in the number of competitors | Opening of additional branches |
| Declining consumer purchasing power | Equipment wear and loss of productivity |
| Changing consumer preferences | Lack of sales strategy and marketing |
The share of all bankruptcy procedures begins precisely because of the internal problems of the organization, therefore, in addition to the way to pay off existing debts in order to avoid a financial crisis in the future, it is necessary to develop measures to eliminate internal factors. Primary activities include:
- change of management team;
- staff reduction;
- redistribution of responsibilities;
- liquidation of divisions and illiquid production;
- development of a sales and marketing system;
- cost reduction;
- reduction of accounts receivable.
The ways of financial recovery for a specific debtor and the method of repaying current debt are set out in detail in the administrative management plan of the legal entity.
Enterprise recovery plan
A financial recovery plan is a mandatory document at the bankruptcy stage, which determines the mechanism for repaying debt and getting the organization out of the financial hole.
The main provisions of this document in the Law are contained in Article 84.
The responsibility for developing a plan falls on the debtor, who must propose realistic ways to ensure the fulfillment of obligations to creditors according to the established payment schedule.
The financial recovery plan is similar in structure to a regular business plan drawn up when creating a new organization. The structure of the plan is represented by the following main points:
- overview of the enterprise and its characteristics;
- information about the current state of the business;
- the financial analysis;
- marketing and sales;
- measures to overcome the crisis;
- production or sales plan;
- sources of financing.
An independent expert, a financial (administrative) manager, will monitor the debtor’s execution of the debt payment schedule and compliance with the developed plan.
Administrative manager in bankruptcy proceedings of a legal entity
The administrative manager begins to perform his duties from the date the court makes a decision to introduce financial rehabilitation. The selection of a suitable candidate and his appointment is the responsibility of the court, while payment of the administrator's remuneration falls on the debtor.
A financial manager at this stage is necessary to monitor the implementation of the recovery plan, mediate between the participants in the insolvency procedure and formulate a conclusion on the results of the stage. The conclusion, together with the financial statements, is submitted to the court 10 days before the completion of the stage.
The activity of the administrative manager ends simultaneously with the decision to terminate financial recovery, unless he was removed or recused himself.
If the debts have not been repaid in full or the debtor has not prepared a report on the results of the organization’s work, then the manager must submit the issue of determining further actions in relation to the legal entity to the meeting of creditors.
Duration of the financial recovery procedure in bankruptcy
The law establishes a maximum period for the procedure for financial rehabilitation of an organization not exceeding 24 months from the date of the court’s decision. During this period, the organization must pay off all existing debts and restore its own solvency.
The stage can be terminated early if the following grounds exist:
- violation of the deadlines for submitting an agreement on guarantees of fulfillment of obligations to creditors to the arbitration court;
- payment of debts to creditors is carried out in violation of the established debt repayment schedule, the delay in payments is 15 days or more;
- the organization liquidated all existing debts before the end of the period determined by the court.
Rights and obligations of participants in financial recovery
The bankruptcy procedure at the stage of financial recovery includes 3 main participants in the process who have legal rights and obligations.
Rights and obligations of participants in financial recovery
| Debtor organization | Creditors | Financial Manager* | |
| Rights | apply for the application of the recovery stage; carry out activities taking into account the restrictions applied to it; go to court to appeal the decision. | return your own funds in accordance with the established priority; submit petitions for the removal of managers or the administrative manager; familiarize yourself with the debtor’s report and the manager’s conclusion. | request any data from the debtor; coordinate transactions; apply to the court with a petition. |
| Responsibilities | development of a financial recovery plan; compliance with established deadlines and amounts of payments; preparation of a report for the manager. | in accordance with the provisions of the Law. | draw up a register of creditors’ claims; monitor the implementation of the financial recovery plan; draw up a conclusion based on the results of the stage *more details in Article 83 of the Law |
Consequences of the procedure
Based on the results of financial recovery, set out in the conclusion of the administrative manager, the arbitration court may determine one of the further outcomes of the action against the debtor:
- upon timely repayment of debts and penalties to creditors, the bankruptcy process of a legal entity is terminated if there are no justified claims against the debtor;
- when a potential possibility of restoring solvency is identified, a decision is made to introduce external management ;
- in the absence of opportunities to overcome the financial crisis, a decision is made to open bankruptcy proceedings.
Source: https://bankrotstvo-lite.ru/bankrotstvo-yuridicheskih-lits/finansovoe-ozdorovlenie/