Part 1 of Article 47 229-FZ provides an exhaustive list of grounds for ending enforcement proceedings. These include: fulfillment of the requirement; return of the document to the applicant, expiration of the statute of limitations or redirection of the document. But although the enforcement proceedings are considered completed, this does not indicate that the outstanding debt is canceled if it has not been collected. The specified three-year periods are interrupted by partial execution of the document by the debtor. And after the bailiffs return the writ of execution to the creditors due to the impossibility of its execution and the exhaustion of available measures for collection (lack of income or property from the debtor), the creditor has the right to re-submit the writ of execution within 3 years after its receipt. In this case, enforcement proceedings will resume.
Writing off debts from a bailiff and the procedure for carrying out the procedure
Attention
In some cases, debtors simply do not want to part with their money and do their best to prevent debt repayment.
However, there are also objective situations when debt repayment may not be possible for a long time (loss of job, serious illness). To enforce enforcement, the claimant must perform the following actions:
- receive a certified copy of the decision and a writ of execution from the court;
- send the specified documents to the bailiff service;
- make sure that the FSSP official has initiated enforcement proceedings.
When contacting the bailiffs, the validity period of the writs of execution issued by the court is important for the claimant. This circumstance is no less interesting for a debtor who finds himself in a difficult life situation.
According to paragraph 12 of Art.
Bad debts will be written off in 2020
Unfortunately, in Russia the situation has developed that every 4 people have an unpaid debt and enforcement proceedings are pending with a bailiff. This could include unpaid fines, debt on housing and communal services bills, alimony, credits and loans.
The reasons are different for everyone. Some are barely balancing on the verge of the minimum wage, some have retired and their income has changed significantly, others have lost the very opportunity to earn money.
The government has spoken more than once about this problem and options for solving it. However, not all citizens know that some debts can be written off as bad. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Statute of limitations for debt collection by bailiffs
Debt write-off is carried out by the debt collector - for example, a bank. However, in the absence of the debtor or his property, the bailiff issues a special order to terminate the proceedings.
After a decision is made to terminate the case, the debt is recognized as uncollectible. A prerequisite for issuing such a resolution is that the bailiff takes all measures for collection.
The actions taken must be ineffective. According to the position of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation, the hopelessness of a debt and the issuance of a decision to stop proceedings only mean the fact of the impossibility of collecting the debt in a specific time period. The obligation itself is not extinguished. If circumstances change, collection may be made.
Confiscation of property during collection
Can bailiffs seize a car for debts unrelated to the purchase of a car? Yes they can. Citizens are liable with all their property in the event of debt obligations. It does not matter whether the property is collateral under a specific loan agreement, the collection of which is carried out.
We invite you to read: Dismissal due to lack of confidence, judicial practice
However, items that are encumbered cannot be confiscated and, as a result, sold without the consent of the creditor. Also, property that the debtor only uses but does not own is not subject to confiscation.
What is the statute of limitations for enforcement proceedings?
In this scenario, it is possible to write off the debt from the unscrupulous borrower, since such a debt is considered bad. Important! If you yourself are sorting out your case related to loan write-off, then you should remember that:
- All cases are unique and individual.
- Understanding the basics of the law is useful, but does not guarantee results.
- The possibility of a positive outcome depends on many factors.
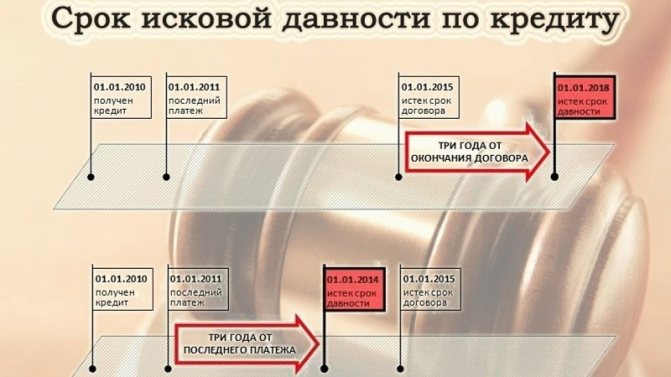
After how many years is the debt written off? The most common option is to write off the debt after the statute of limitations expires. According to Art. 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the general limitation period is 3 years, but the beginning of its countdown can constantly shift due to the fact that the loan agreement ends when the parties fulfill their obligations.
How to write off a loan: after how many years is the debt written off?
This also applies to marking registered mail. If it exists, but the debtor has not been found, then it is considered that the writ of execution has been received.
Important
All claims in this case must be sent to the postal service. It is important to know that notification by telephone or email is not permitted.
Info
The writ of execution has been served. If the writ of execution is nevertheless served, then the creditor turns to the bailiff service. Based on this, production is started. The Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” describes all these points in detail.
Bailiffs are given 2 months to take measures to collect the debt: blocking bank cards, seizing property, etc. This is the statute of limitations for enforcement proceedings (loan).
The issue of the effectiveness of the service, of course, still causes controversy. There are cases when the debtor did not even hide from them.
Limitation period for debt
The period when an organization has the right to recover funds from a defaulter through the court is called the statute of limitations . The bailiff initiates enforcement proceedings on the basis of a written statement from the victim, then, within 6 days, a resolution is prepared, which is sent to the parties to the conflict.
For example, a citizen took money from a bank at interest and does not fulfill the obligations specified in the contract, then the organization takes the violator to court. The judge, having considered the application, has the right to decide on the forced withdrawal of funds from the borrower. The court decision is sent to the bailiffs, and the latter will try to extract money from the debt violator by all legal means.
Important! Having received the notice, the borrower is obliged to pay the lender within the prescribed period. According to Federal Law No. 229, the debtor is given 5 days from the date of receipt of the resolution to resolve the issue with the creditor.
Finding themselves in a difficult financial situation, debtors usually look for ways to cancel debts from bailiffs and play for time, hoping for the expiration of the procedural period. Such actions do not end well, since the creditor, based on the provisions of Article 208 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, has the right to extend the limit to an unlimited time if there are irregularities in the written agreement between him and the violator.
The time limit established by Russian legislation for going to court to collect a debt is three years , but this limit can be extended at the request of third parties or a creditor.
How long can bailiffs collect a debt?
The bank is more willing to write off accounts payable if the amount is small, since forcibly collecting funds through the court requires additional investments, which is absolutely not beneficial for the creditor from the financial side. If the case goes to court and the creditor files a claim for forced collection of the loan debt, then the borrower must be prepared to satisfy the creditor’s claims.
After a positive decision in favor of the plaintiff, the writ of execution is sent to the Federal Bailiff Service (FSSP), where the bailiff issues a decision to initiate enforcement proceedings and begins the procedure for searching for the debtor’s funds. The resolution is sent to the debtor and, in accordance with paragraph.
12 tbsp. 30 of the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” No. 229-FZ of October 2, 2007, the debtor is obliged to pay the debt within 5 days.
A little about the news
In fact, bailiffs write off debts every year, because it is not customary for them to carry over “dead weight” to the new year. Like all government agencies, they have their own indicators and reports, and bad debts must be cleared by the end of this year.
However, this does not mean that everything is forgiven and forgotten. No, the debt will not disappear, it will not evaporate. The legislation (Federal Law No. 229) has a specific list of grounds on which a debt can be closed and no longer arise.
These include:
How will bad debts be covered? Watch the video:
What debts can be written off
There are certain types of enforcement proceedings that bailiffs are guaranteed to close if there are legal grounds:
- Debt for housing and communal services;
- Loan payments;
- Microloans;
- Debts for material damage, receipts or loans of funds from an individual.
As you can understand, the list is very limited.
The following debts are not covered:
- According to accrued alimony;
- For damage caused as a result of a crime;
- Debts related to the payment of wages and benefits.

Law on debt closure. Photo kpcdn.net
Conditions
Of course, desire alone is not enough. The bailiff must have sufficient legal grounds to terminate the proceedings.
What does this include:
- If a person does not have official earnings or was laid off due to layoffs;
- If a citizen does not have any property that can be seized.
When is a loan debt written off?
Many disputes over debt obligations go as far as filing an application in court, and most often the decision is made in favor of the creditor. After a decision is made, the case is transferred to the bailiff service, whose responsibility is to directly collect the debt. In this regard, people are wondering what will happen if they continue to ignore their obligations to the bank? Is there a statute of limitations, and is it possible to write off debts through bailiffs? Debt write-off The short answer is, it’s possible! However, there are many pitfalls in this matter. Yes, there is a certain statute of limitations, but even when this period of enforcement proceedings expires, nothing will change for the debtor. The debt will still remain with him, as well as the obligation to pay it.
How to close debt and get rid of inhibitions
In fact, it is not necessary to wait for a miracle and rely on a bailiff. The debtor can independently contact the FSSP with an application and ask to close the debt. You can base your position only on the reasons stated above.
How to get money back after repaying the loan? See the link.

The most important thing will be to prove your insolvency. Show that the property is absent or so insignificant that there is no point in seizing and describing it.
Is there a statute of limitations for bailiffs following a court decision?
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation already from the first day of debt accrues penalties in the form of fines and penalties, which leads to an increase in the principal amount of the debt;
- try to resolve the situation peacefully and using the methods offered by the creditor (debt restructuring, refinancing, etc.).
Following these rules will show that the debtor does not refuse his obligations and does not bring the matter to court proceedings that threaten to deprive the borrower of property and funds. If the debtor has submitted a written application to the bank to write off the loan debt, then such a decision is made collectively by the heads of the financial organization, if the amount of debt does not exceed 100 thousand rubles.
After how many years the debt from the bailiffs is cancelled.
Debts can be completely written off in the following situations:
- the debtor dies or goes missing, and the person did not leave an inheritance;
- it is impossible to identify the debtor, since the loan was issued using forged documents (in this case, a criminal offense occurs, and the application is submitted to the investigative body);
- there is a court decision according to which the bank is denied reimbursement of the debt (due to the bankruptcy of the defendant, the expiration of the statute of limitations, the recognition of the credit transaction as invalid, violation of procedures and rules of law, etc.).
Whatever the reasons for the delay in loan obligations, according to the loan agreement, the defendant is always the debtor. Refusal to pay a debt does not always come from a willful defaulter.
Debt write-off. Can bailiffs write off debts?
This will result in a new fine equal to double the previous one. Officers can also apply arrest for up to 15 days. Failure to pay alimony The statute of limitations for enforcement proceedings on alimony worries many in our country. Our debt to children is one of the most voluminous. There is no statute of limitations for it. Alimony workers are a headache for bailiffs. They “hang” in the database constantly. They constantly have to make readings. The obligation to pay alimony begins after a claim is filed in court. Therefore, at the same time, during a divorce, you need to immediately write such a petition.
Mothers naively believe that alimony payments start to roll in automatically. In exceptional cases, the court recovers from the ex-spouse for the previous three years, but no more.
You cannot come to court after 10 years and demand alimony for the entire time.
Deadlines
A little about something important, i.e. timing. How much debt can performers have? Is it possible to wait out unfavorable times without damaging your reputation? Let's take a closer look.
As already stated, the bank has enough time to contact the supervisory authorities - 36 months . This is the period during which enforcement proceedings against individuals are valid. Bailiffs have 2 months to carry out the will of the court.
Otherwise, the writ of execution will be returned to the bank, and fines and restrictions will be removed from the borrower. For example, he can move abroad.
Unfortunately, timing is not always clear. If we are talking about a credit institution, then the three-year reporting period begins from the moment of last contact with debtors. Be it a visit to the bank or an official letter.
As for housing and communal services, this period does not arise after the end of the month, but on the date when a citizen or organization is obliged to pay . In addition, the time when the debt can “hang” with the bailiffs varies in different situations. For example, check collections last only 6 months, but environmental collections can last decades.
ATTENTION! An assignment agreement—the transfer of a debt to a third party—does not affect the statute of limitations. In some situations this is a definite plus for the debtor.
In addition, Article 208 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that some cases do not have a statute of limitations . These include:
- requesting deposits from a credit institution;
- claim for recovery of health damage in an accident;
- restoration of property rights to real estate;
- damage to the plaintiff's health caused by the defendant.
In general, the exact period depends on the specific situation, and you can find out it from the executors of the case. Note that alimony debts are paid even when the defendant is officially declared insolvent. But there is another interesting nuance.
If the children were adopted by a new father with whom his ex-wife currently lives, then the citizen has the right to stop paying alimony. The Bank has the right to suspend the limitation period in certain cases established by law:
- Due to a natural or man-made disaster.
- The borrower serves in the army or participates in combat.
- A third party joined the proceedings to smooth out the conflict.
- A change has been made to an act or law.
The debtor has the right to file a counterclaim if he does not agree with the moment when the payment deadline was restored. This should be done no later than 30 days after receiving the official notification.







